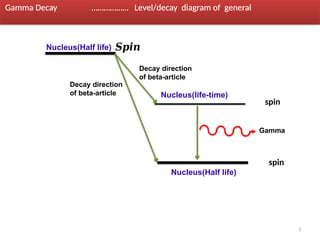
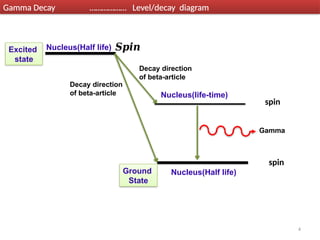
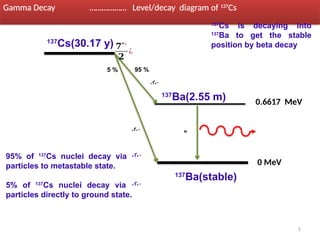
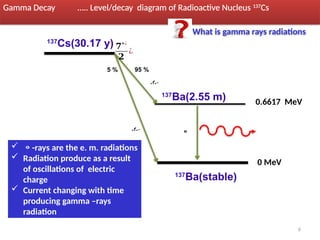
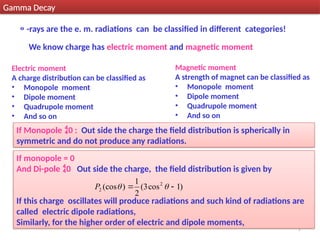
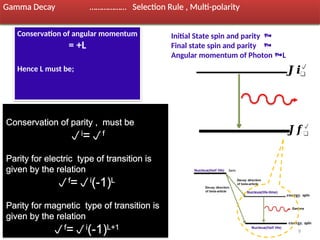
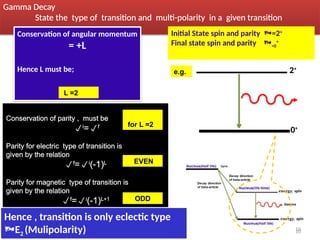
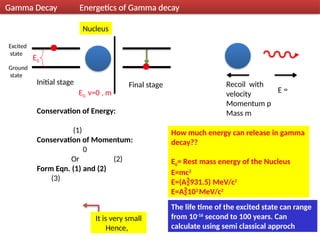
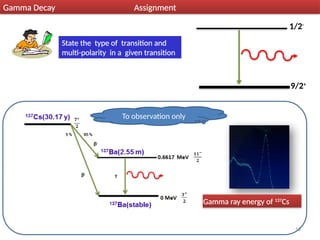
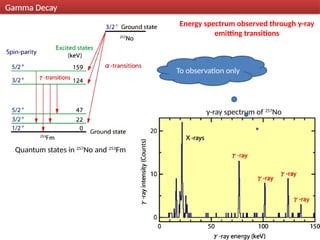
Gamma decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an unstable nucleus emits gamma rays to reach a more stable state, often following other decay processes like alpha or beta decay. The document discusses various aspects of gamma decay, including the classification of gamma rays, selection rules for transitions, and the energetics involved in gamma decay processes. Additionally, it provides examples and diagrams related to specific isotopes and their decay pathways.