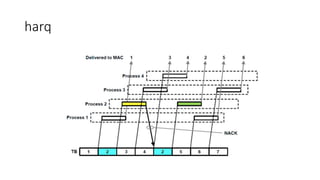
The document discusses Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ) in 5G New Radio (NR). It explains that HARQ is implemented at the MAC layer and provides very fast retransmissions within 1 ms. The RLC layer also has a slower retransmission mechanism to handle errors not corrected by HARQ. HARQ buffers transmitted data and combines retransmissions with buffered data for error correction. It uses an asynchronous SAW protocol with multiple parallel processes to repair transmissions without hindering ongoing transmissions.