This document discusses using data from Webcourses to better understand student learning and make informed decisions. It outlines the following:
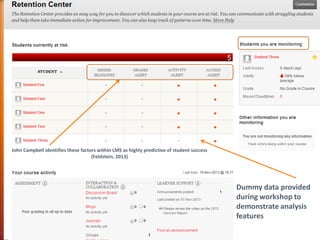
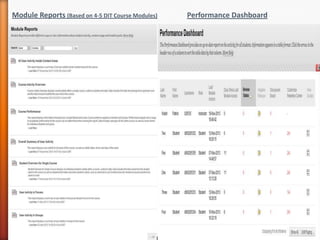
1) Exploring how student engagement with course modules compares to module grades using the Module Reports, Performance Dashboard, and Retention Center features.
2) Conducting a mixed-methods study involving quantitative analysis of module report data from 4-5 courses followed by qualitative interviews with staff participants.
3) Highlighting literature identifying links between LMS data like participation and academic performance, as well as privacy and ethical issues around learning analytics.