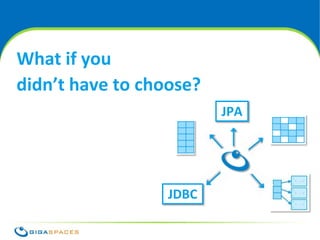
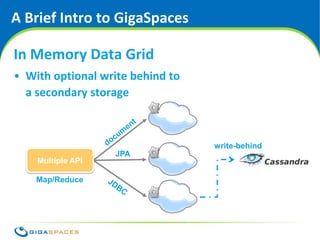
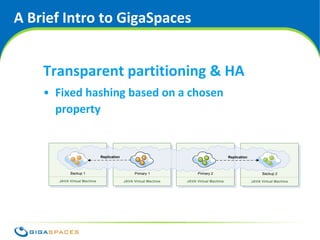
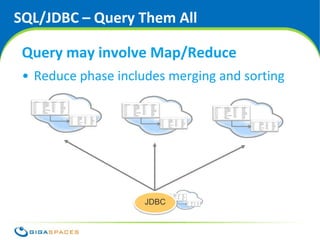
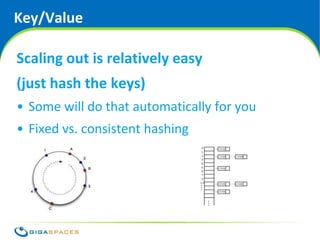
The document discusses SQL and NoSQL databases. It provides an overview of SQL, describing it as transactional and consistent but difficult to scale. It then summarizes several common NoSQL data models: key-value, column-oriented, and document-oriented. It introduces the GigaSpaces in-memory data grid product, which supports multiple APIs including Java objects, JPA, and MapReduce on a distributed, highly available data platform. The document advocates using the right API for the job rather than being constrained to a single data model.

![> SELECT * FROM qcon.speakers WHERE
name=„Mickey Alon‟
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| Name | Company | Role | Twitter |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| Mickey Alon | GigaSpaces | Director | @mickey_alon |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
> db.speakers.find({name:”Mickey Alon”})
{
“name”:”Mickey Alon”,
“company”: {
name:”GigaSpaces”,
products:[“XAP”, “IMDG”]
domain: “In memory data grids”
}
“role”:”director”,
“twitter”:”@mickey_alon”
}
® Copyright 2010 Gigaspaces Ltd. All Rights Reserved](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yessql-mickeyalon-gigaspaces-nov-11-111031180734-phpapp02/85/NoSql-YesSQL-mickey-alon-2-320.jpg)





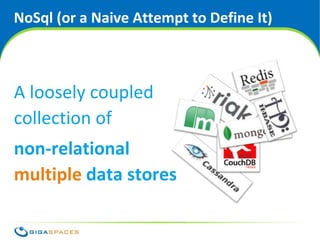



![The Current Leading Data Models
Key / Value Column Document
{
“name”:”uri”,
“ssn”:”213445”,
“hobbies”:[”…”,“…”],
“…”: {
“…”:”…”
“…”:”…”
}
}
{
{ ... }
}
{
{ ... }
}
® Copyright 2010 Gigaspaces Ltd. All Rights Reserved](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yessql-mickeyalon-gigaspaces-nov-11-111031180734-phpapp02/85/NoSql-YesSQL-mickey-alon-15-320.jpg)



![Document
Think JSON
(or BSON, or XML) {
“name”:”Lady Gaga”,
“ssn”:”213445”,
“hobbies”:[”Dressing up”,“Singing”],
“albums”:
[{“name”:”The fame”
“release_year”:”2008”},
_id:1
{“name”:”Born this way”
_id:2 “release_year”:”2011”}]
}
_id:3
{
{ ... }
}
{
{ ... }
}
® Copyright 2010 Gigaspaces Ltd. All Rights Reserved](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yessql-mickeyalon-gigaspaces-nov-11-111031180734-phpapp02/85/NoSql-YesSQL-mickey-alon-22-320.jpg)