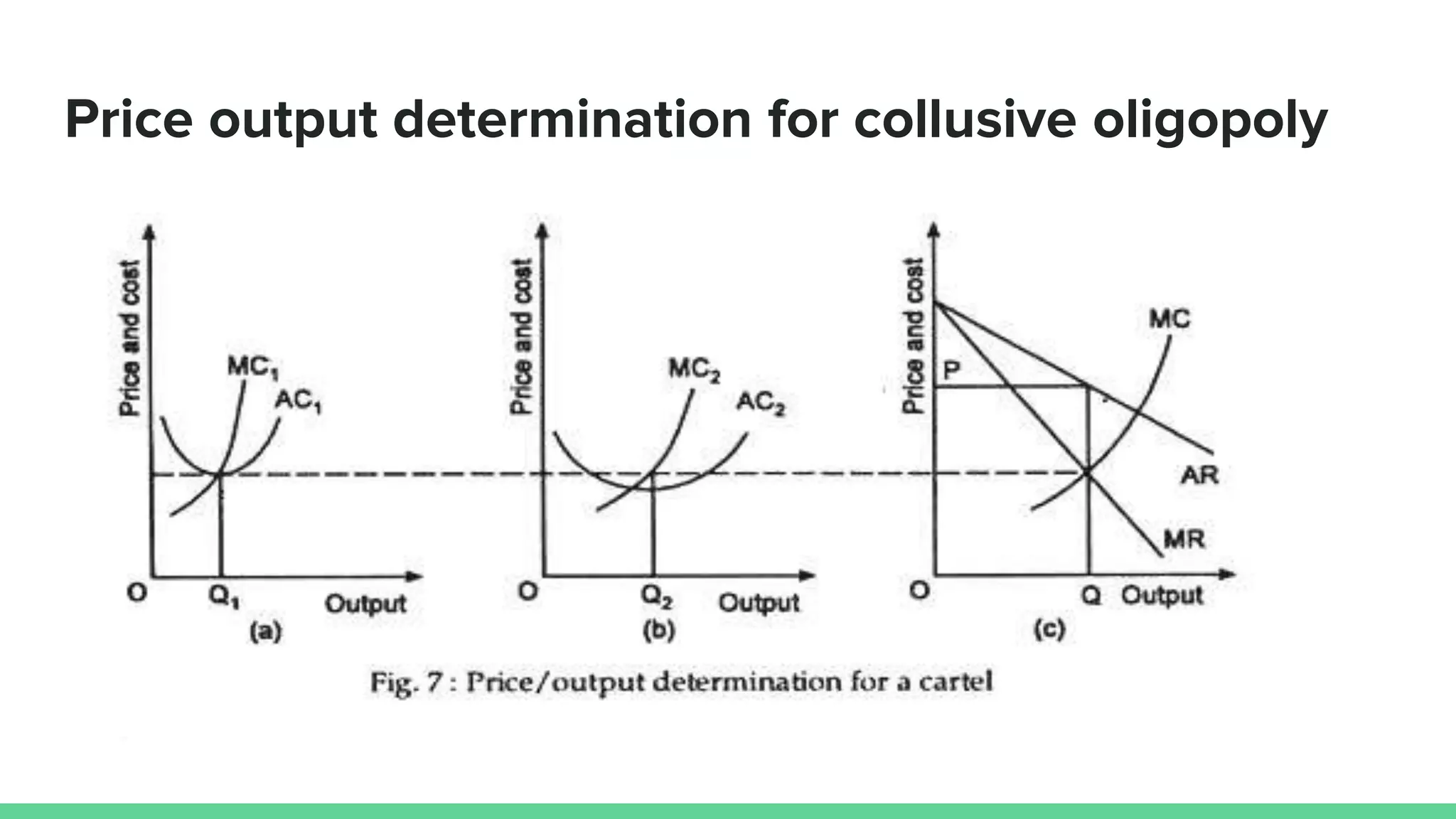
The document discusses non-price competition in oligopolistic markets, highlighting strategies firms use to gain market share without lowering prices, such as aggressive marketing and product bundling. It also examines the concept of collusive oligopoly and cartels, explaining how firms form agreements to influence prices and output, the factors affecting their formation, and examples like OPEC. The case of Reliance Jio illustrates the impact of aggressive non-price competition on market dynamics in the telecommunications industry.