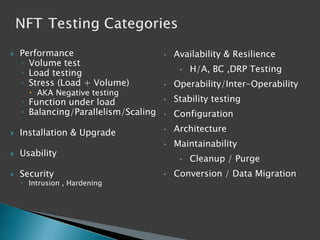
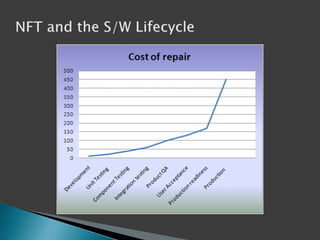
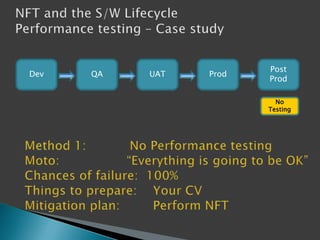
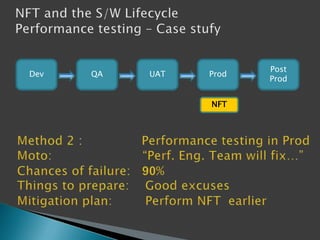
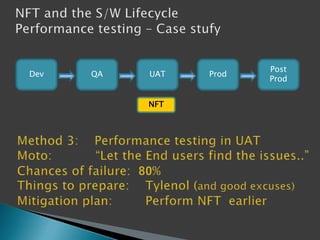
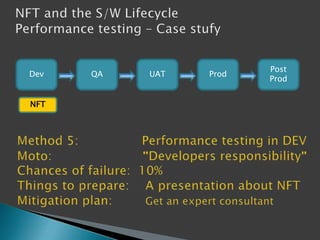
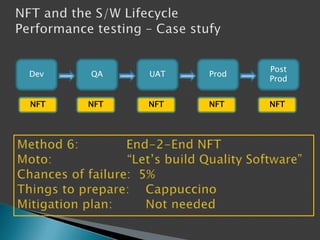
This document discusses the importance of non-functional testing (NFT) in software development. It defines NFT as testing aspects of a product that are not direct functional requirements, such as performance, reliability, security, and usability. The document recommends implementing NFT throughout the entire development lifecycle from development to post-production in order to reduce risks, costs, and improve quality. It provides examples of different types of NFT and emphasizes the resources required to properly perform serious NFT.