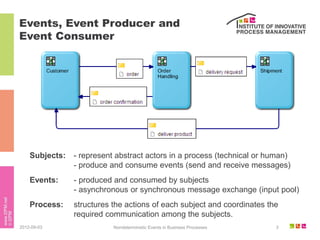
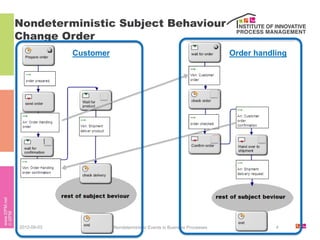
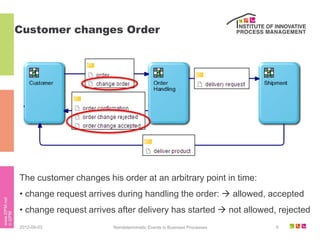
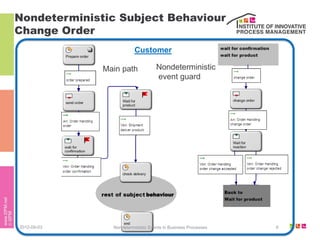
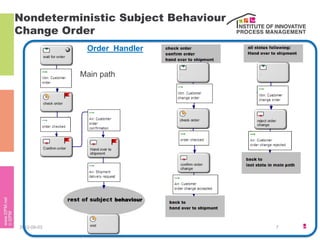
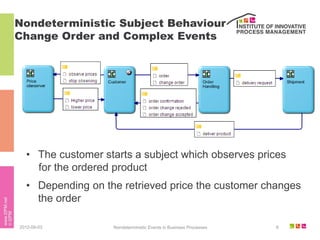
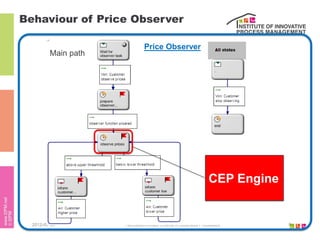
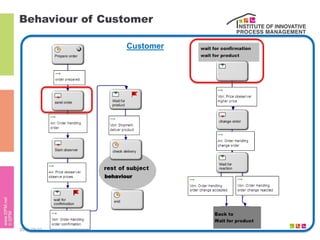
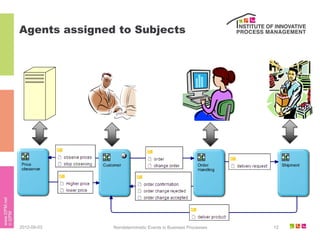
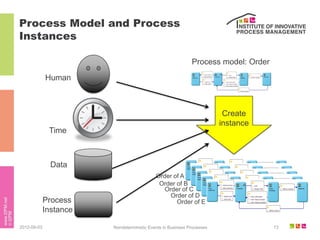
The document discusses the description of business processes through various types of events using the subject-oriented business process management (S-BPM) approach. It highlights the roles of subjects as event producers and consumers, the impact of nondeterministic events on process behavior, and the integration of complex event processing (CEP) engines. Additionally, it emphasizes the distinction between subjects and agents in the execution of business processes.