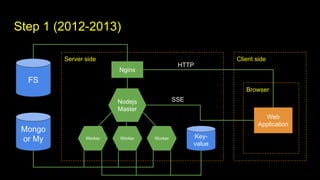
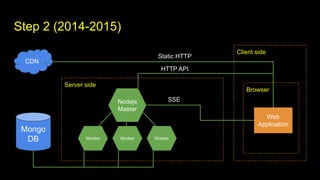
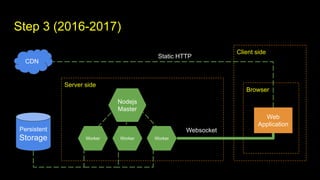
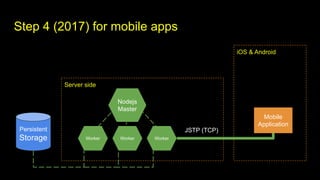
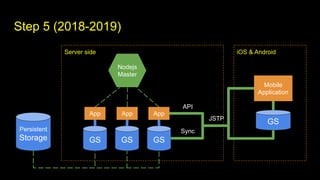
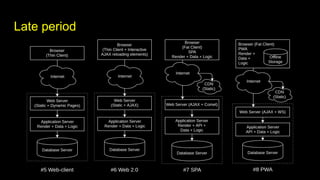
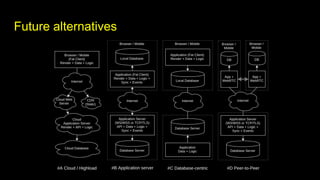
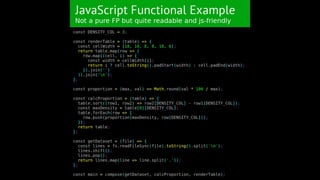
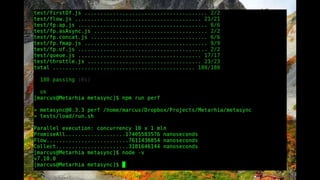
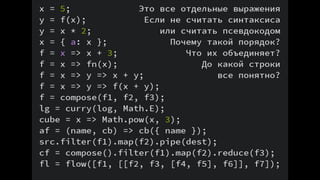
This document outlines different steps in scaling Node.js applications from 2012 to 2019. It begins with using Node.js in cluster mode with Nginx as a reverse proxy. It progresses to using CDNs for static files, in-memory databases, and eventually custom protocols for real-time data synchronization across servers and clients. Key aspects discussed include data synchronization, offline capabilities, interactivity, scalability, and high connectivity. Alternative approaches and bad practices are also addressed.