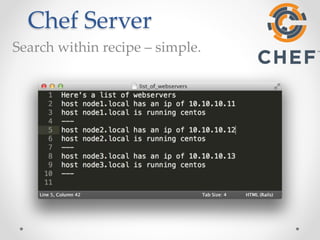
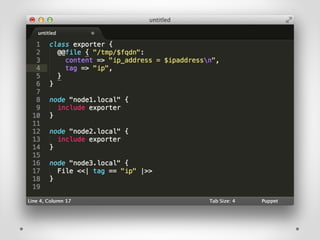
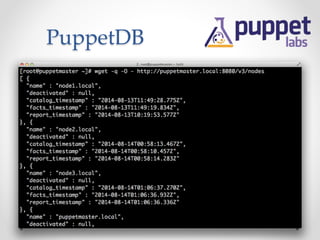
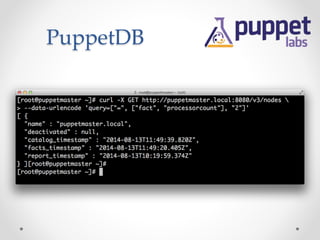
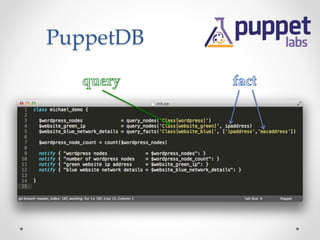
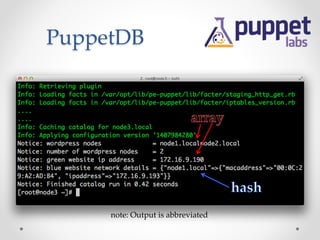
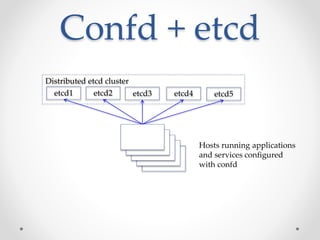
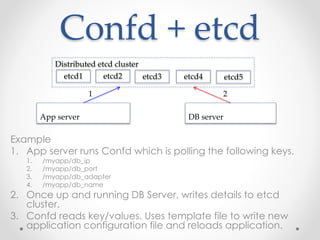
The document provides an overview of methods to share information between systems using Chef and Puppet, focusing on Chef's search capabilities, Puppet's exported resources, and PuppetDB's data collection features. It discusses the integration of configuration management tools like confd and etcd for managing application configurations and service discovery. The primary goal is to enable node collaboration and improve infrastructure responsiveness beyond typical agent run intervals.