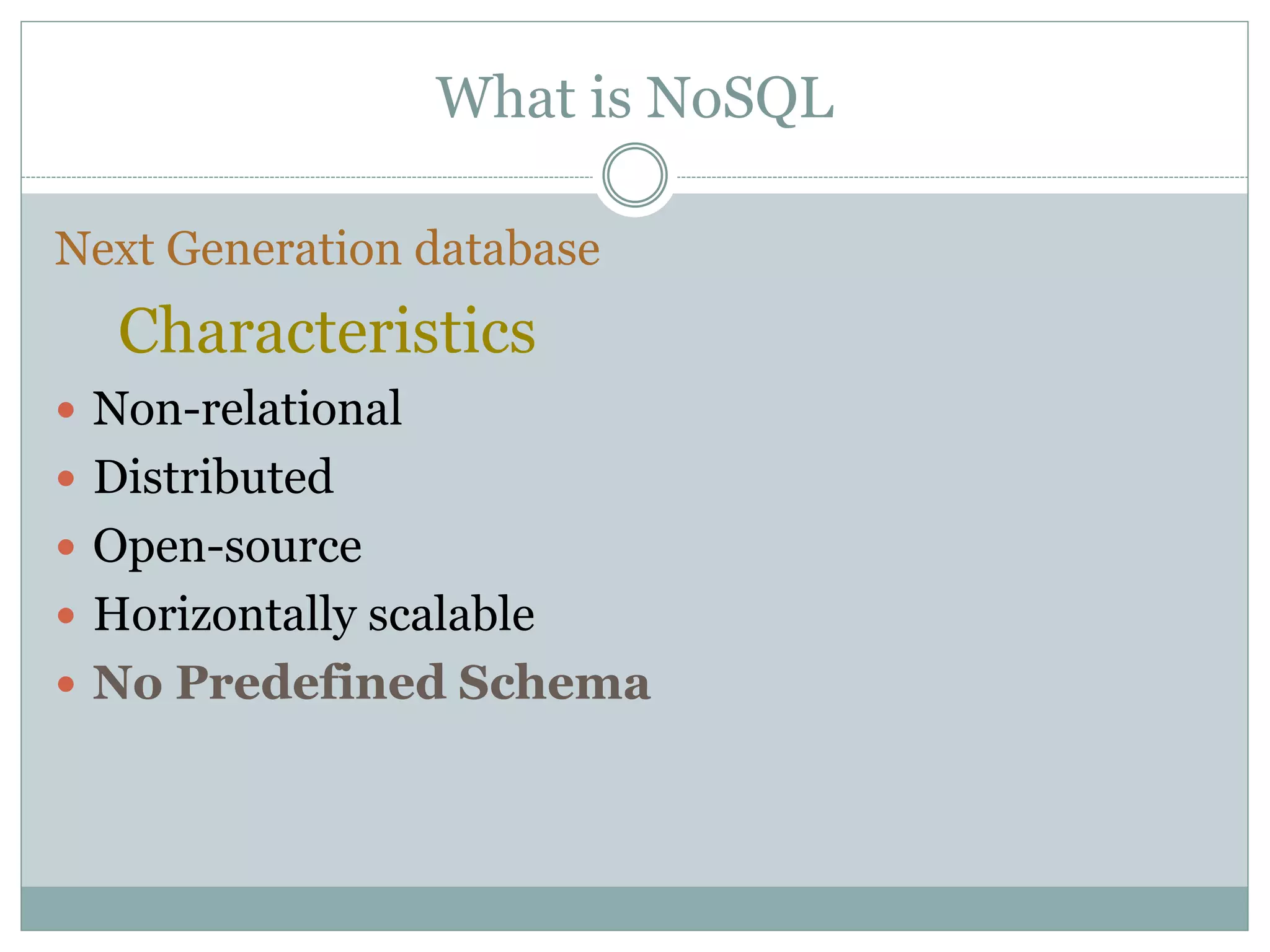
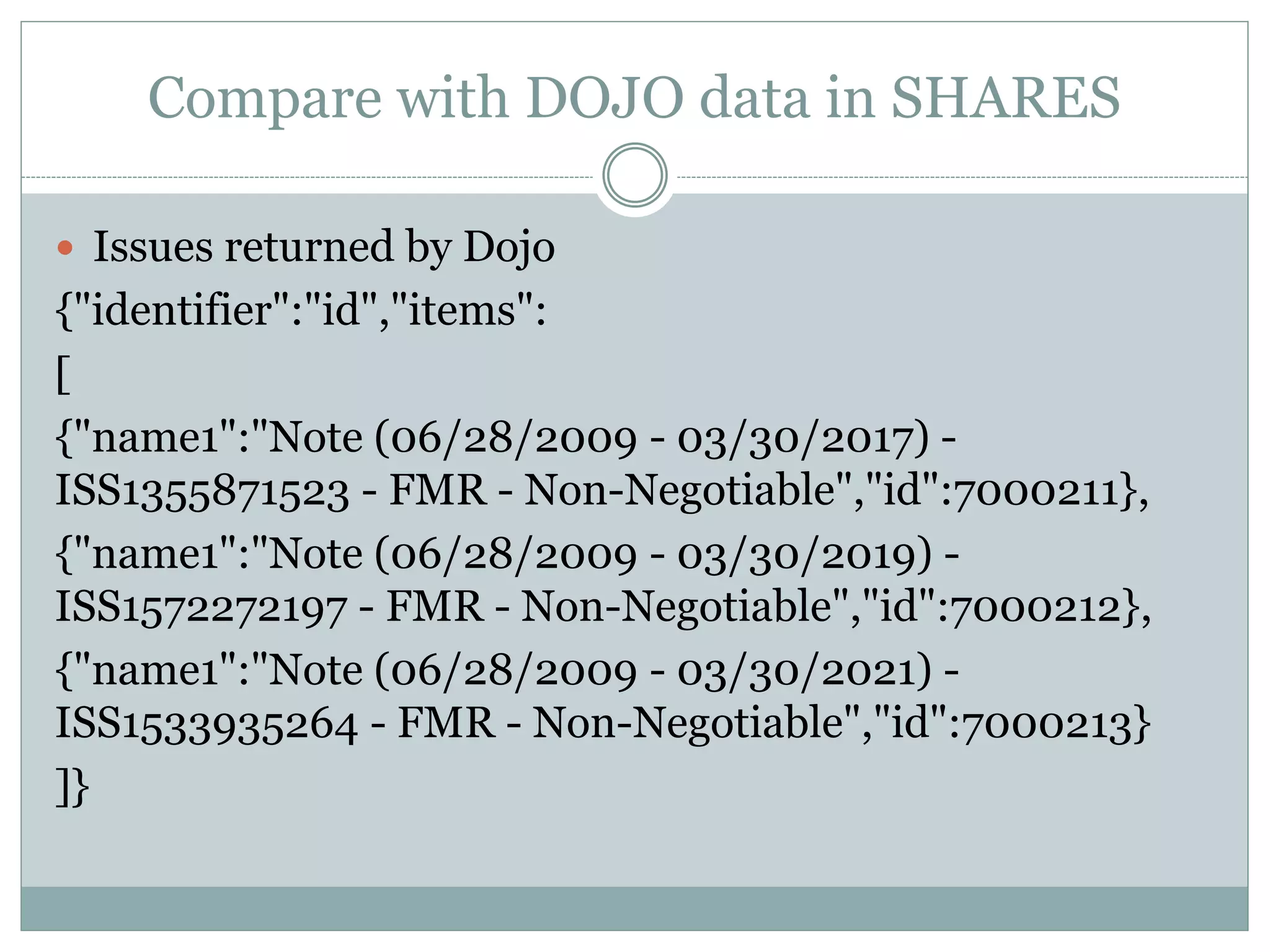
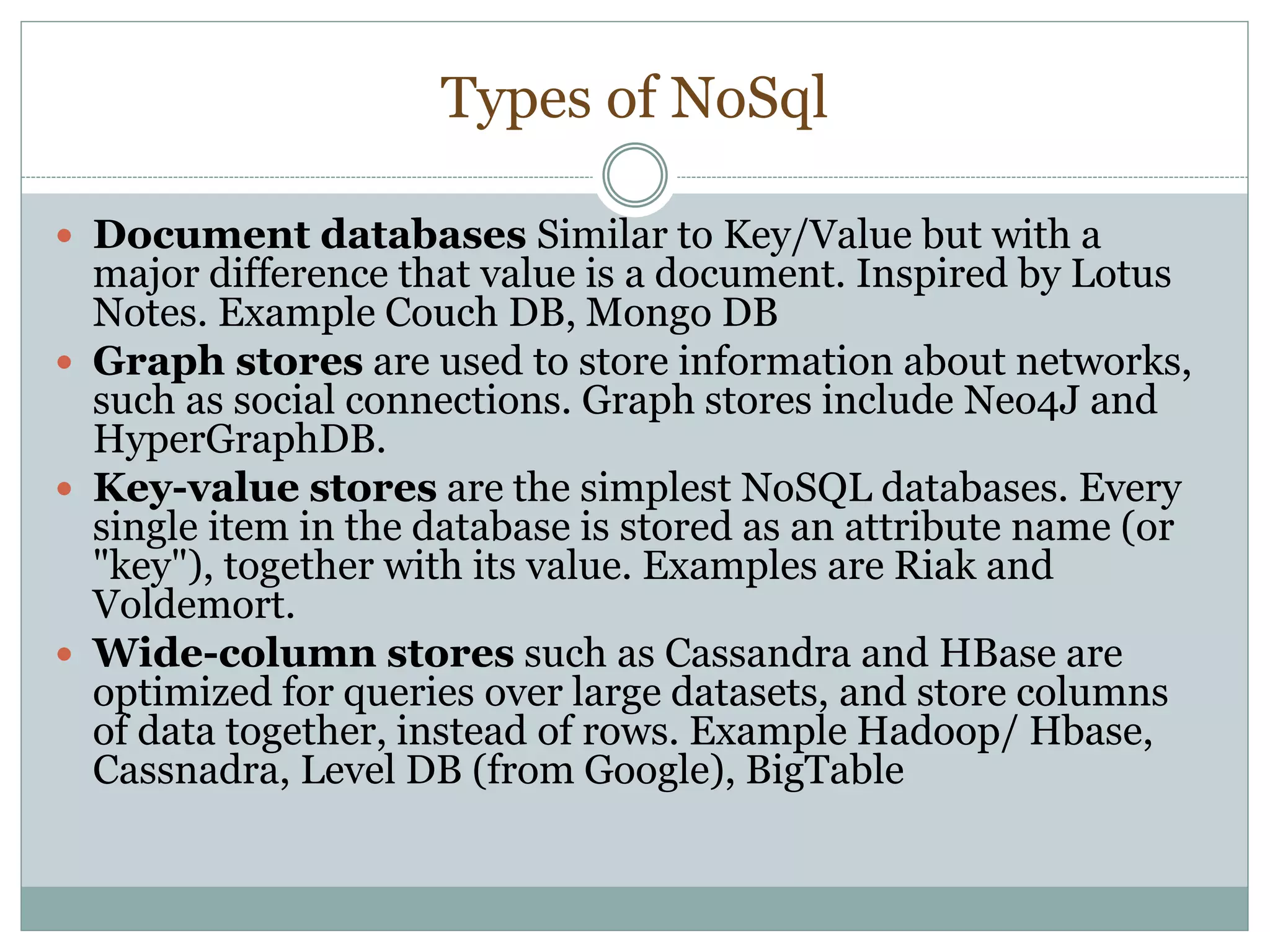
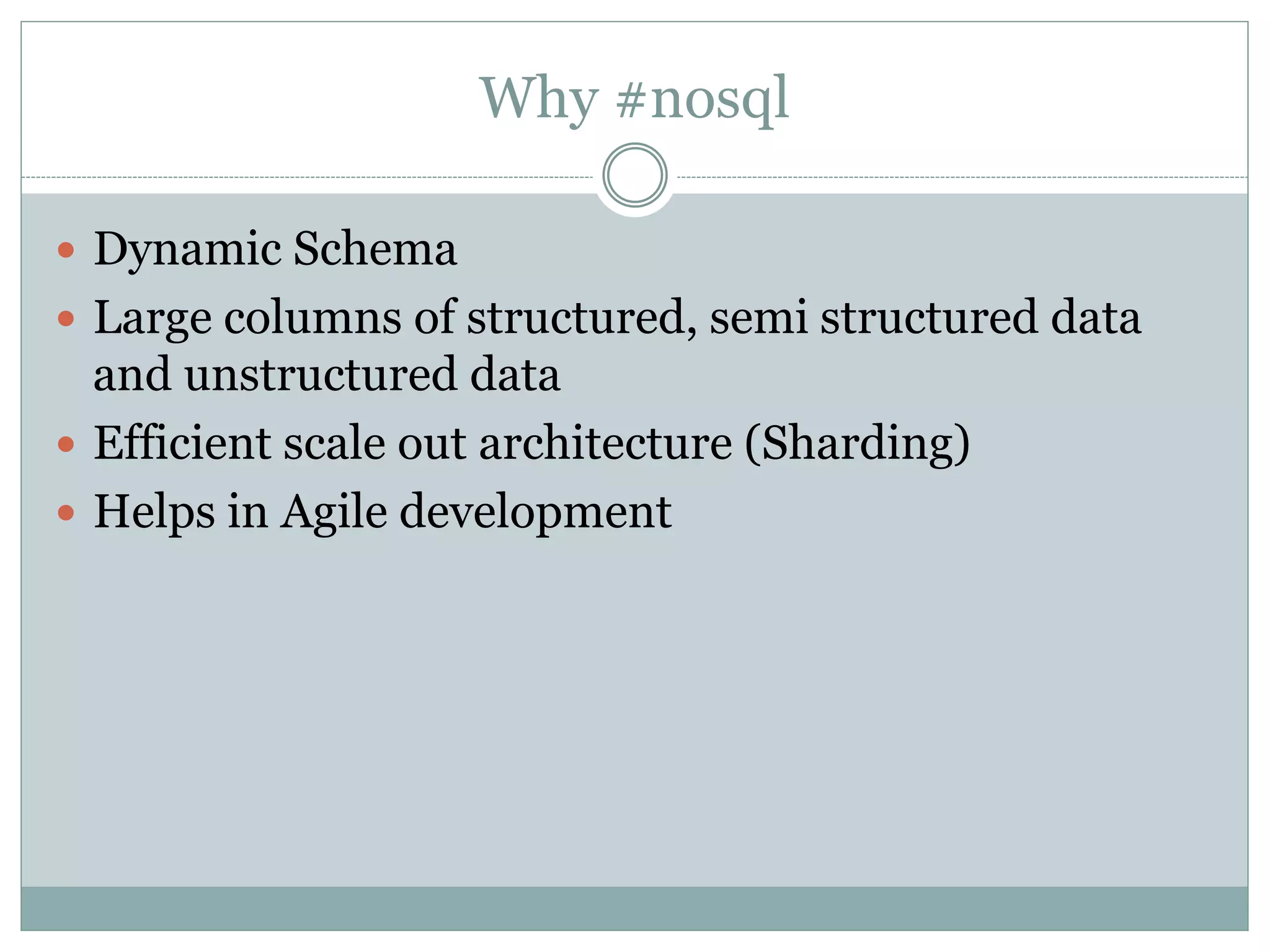
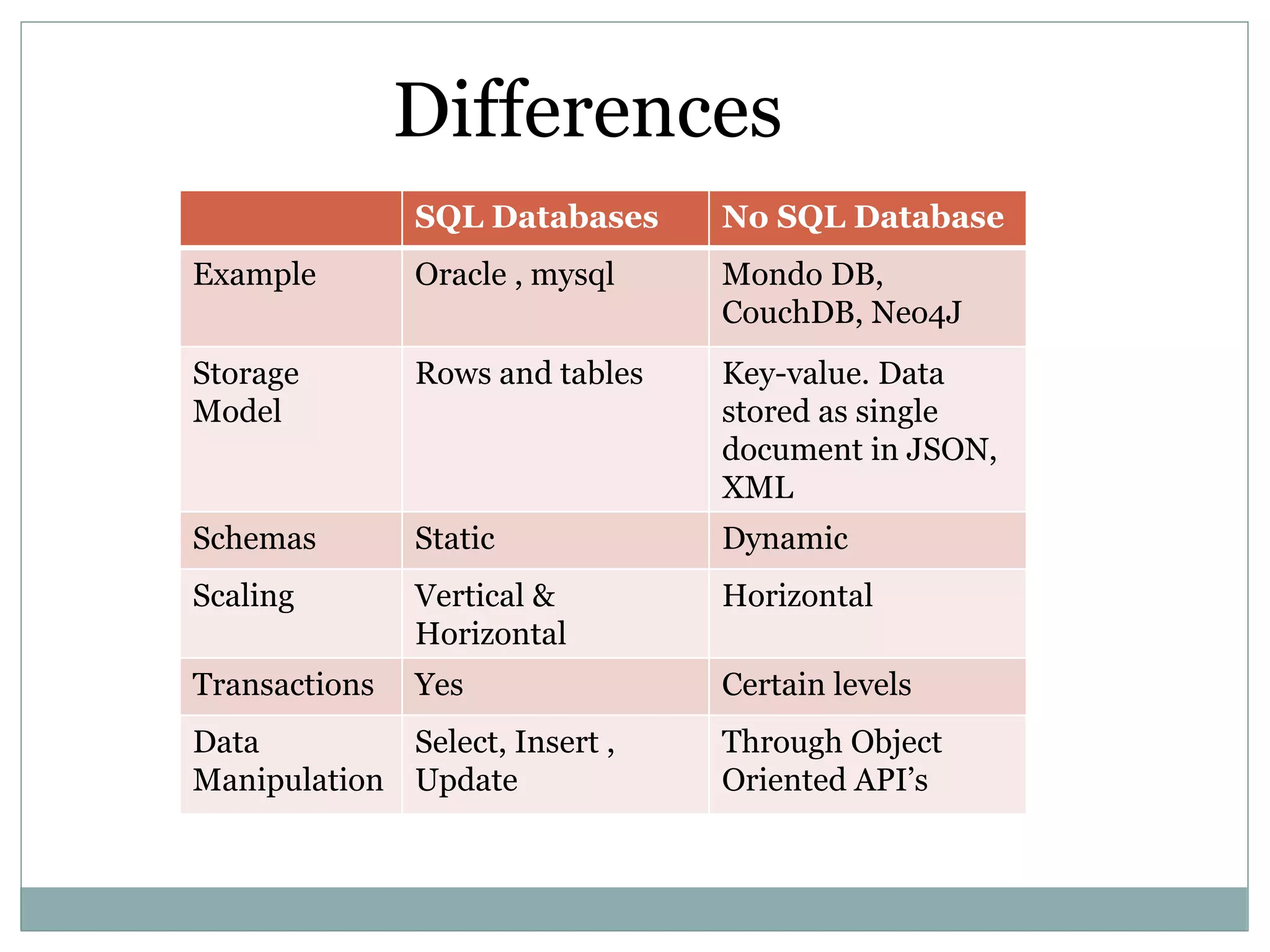
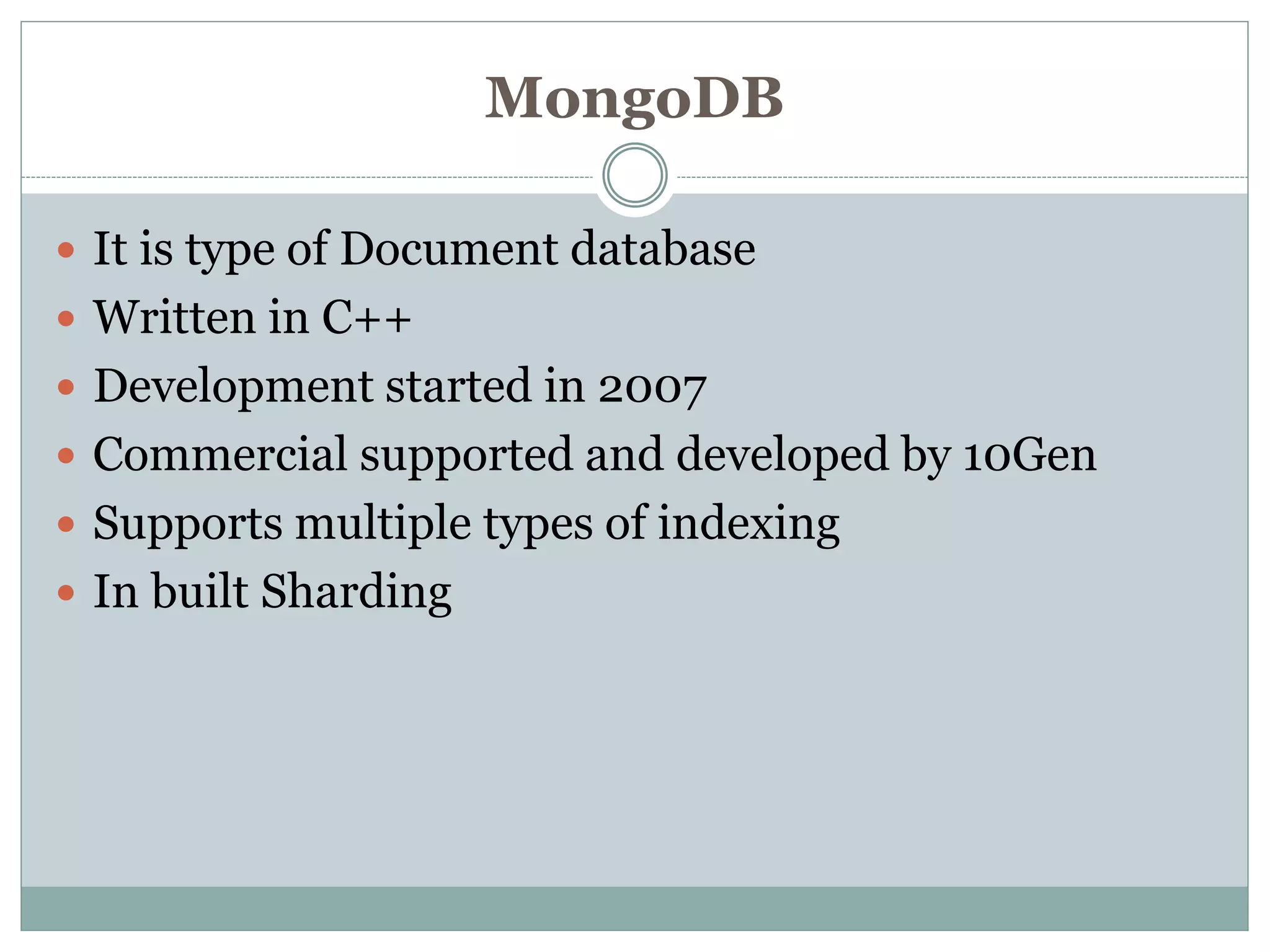
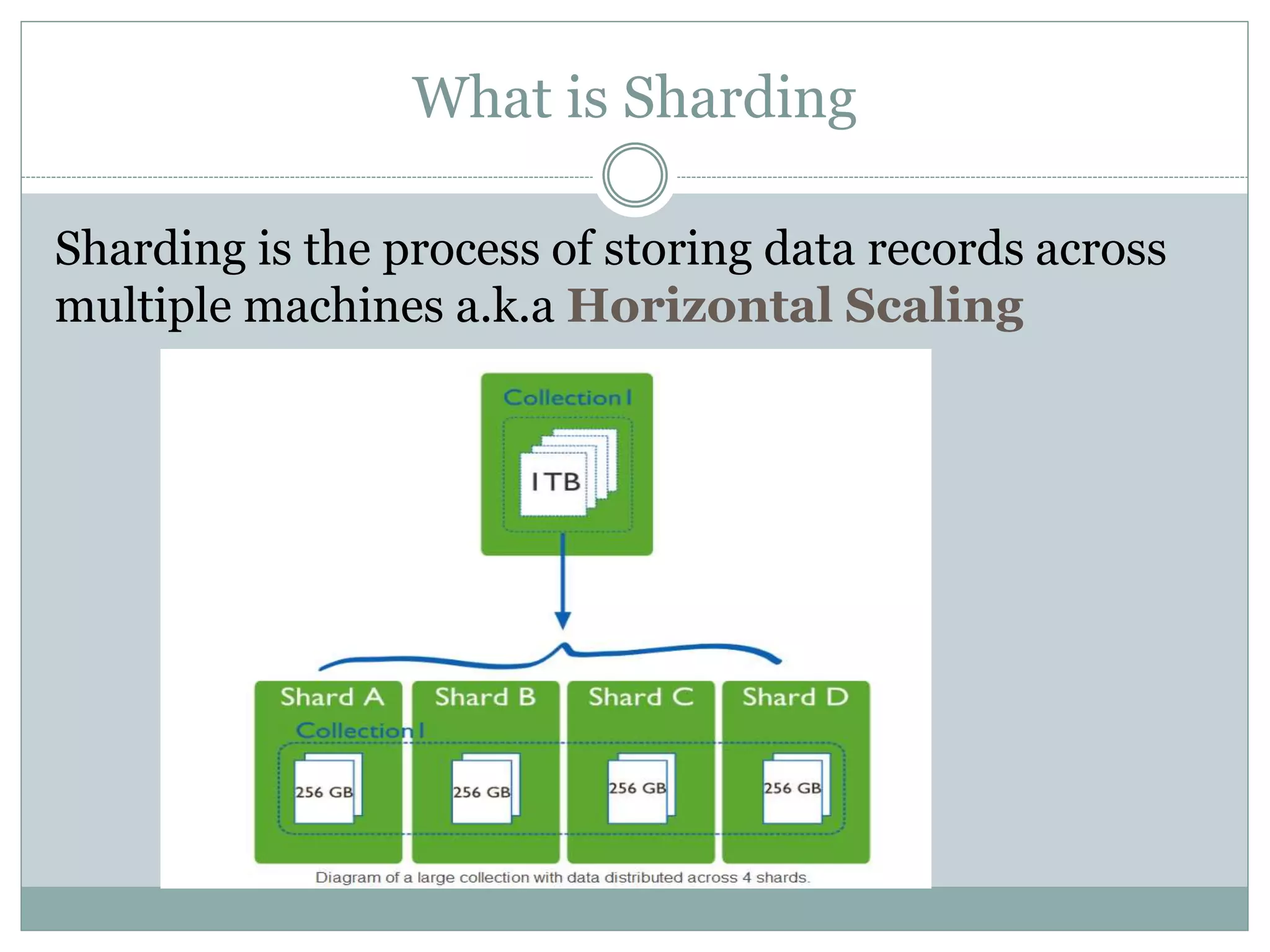
This document provides an introduction to NoSQL databases. It describes NoSQL as non-relational, distributed, open-source databases that are horizontally scalable with no predefined schema. It lists the main types of NoSQL databases as document stores, graph stores, key-value stores, and wide-column stores. The document gives MongoDB as an example of a document database and explains that sharding allows horizontal scaling by storing data records across multiple machines.