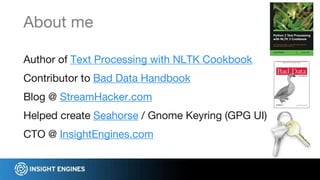
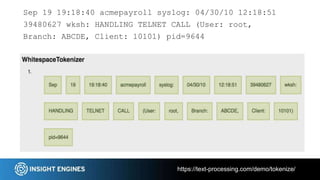
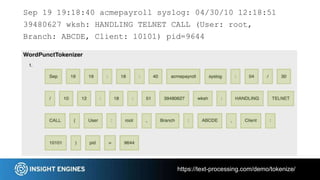
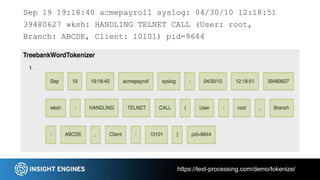
This document discusses using NLP techniques like tokenization, feature extraction, classification, clustering, and anomaly detection to analyze log files. It provides examples of how each technique can be applied including tokenizing log records, extracting features like n-grams and token shapes, classifying records by type or priority level, clustering records to find anomalies, and detecting outliers. The document also recommends tools like NLTK, Scikit-Learn, Logpai and references the author's own work at Insight Engines on log search and analysis products.