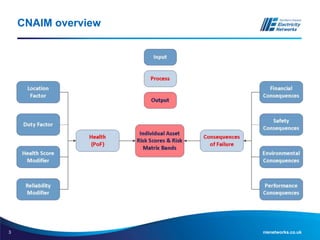
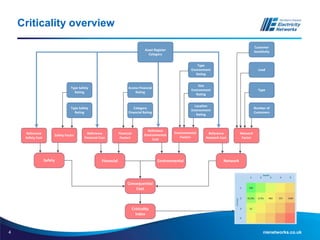
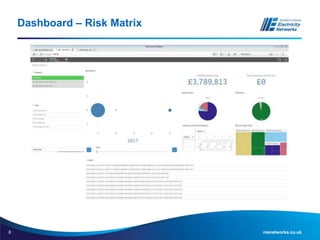
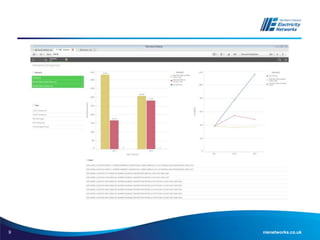
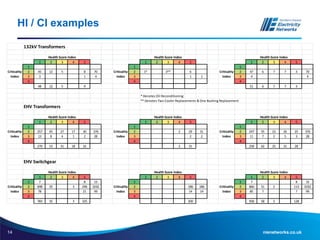
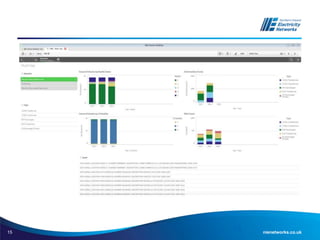
The document discusses the application of the Common Network Asset Indices Methodology (CNAIM) by NIE Networks to support regulatory submissions and investment planning. It highlights the benefits of a standardized approach for assessing asset health and criticality, enabling monetization of risk and aiding in optimization of asset management. Future directions include tailoring CNAIM principles with specific costs to improve investment proposals and explore cross-asset optimization for cost savings.