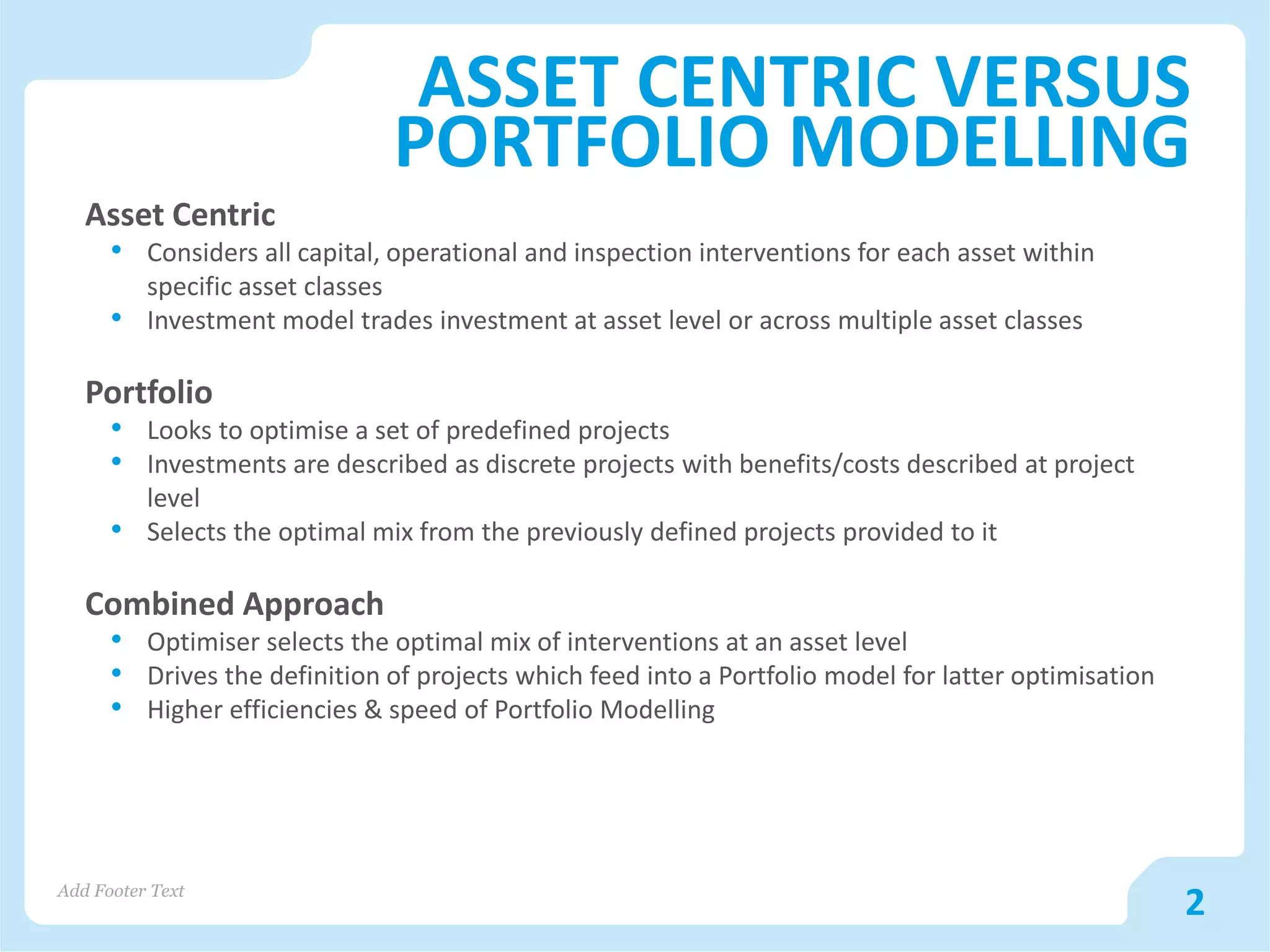
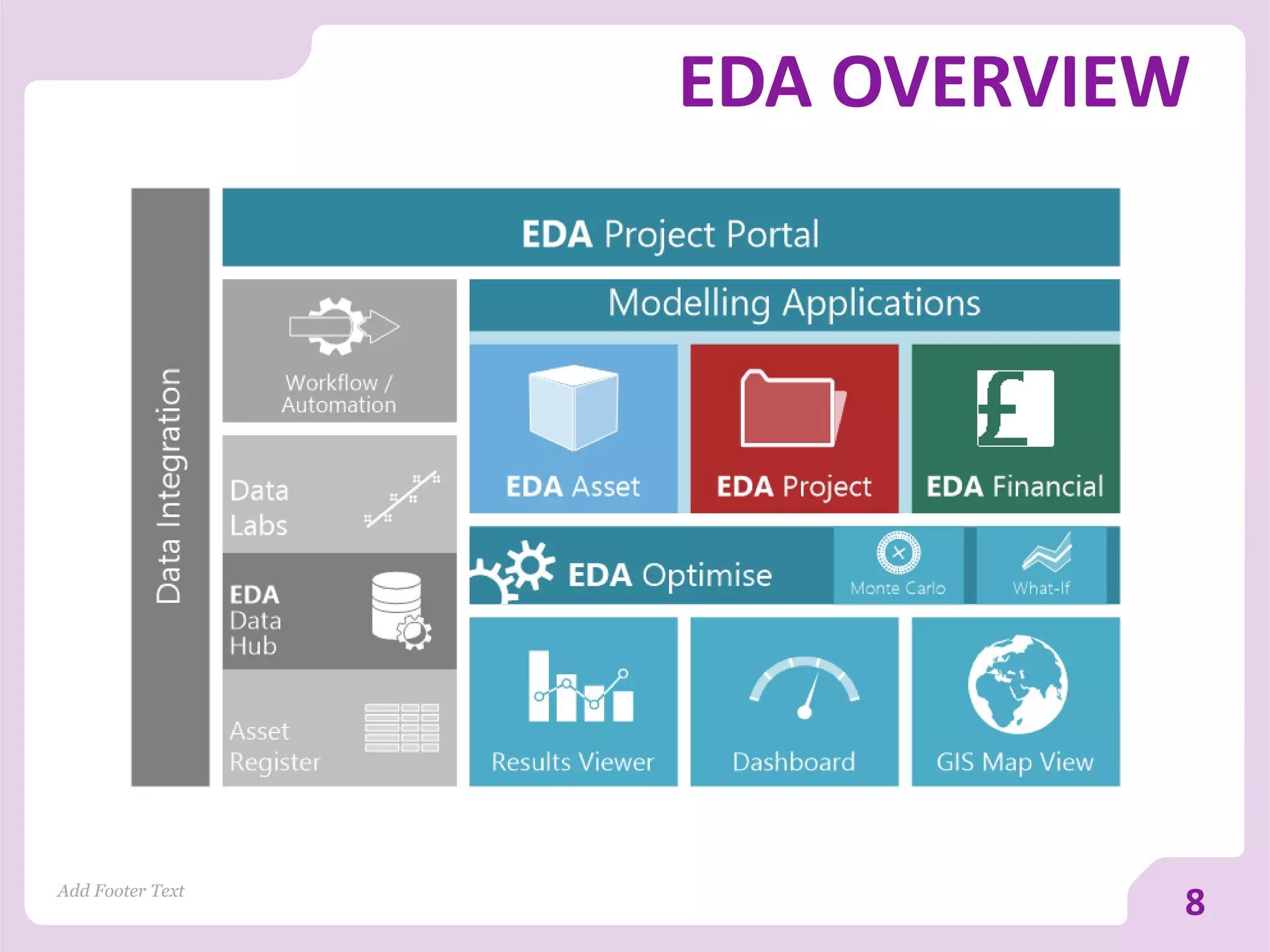
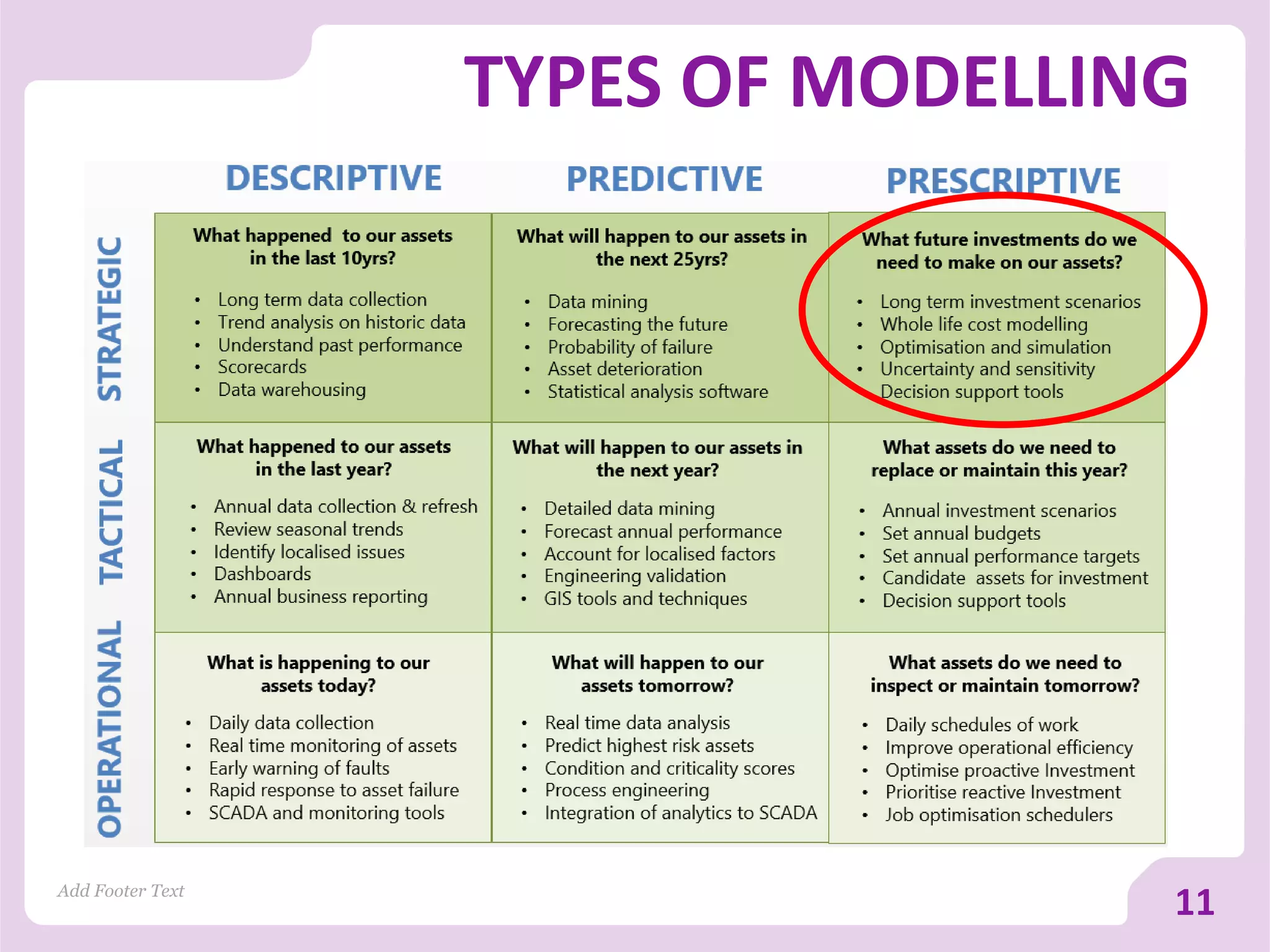
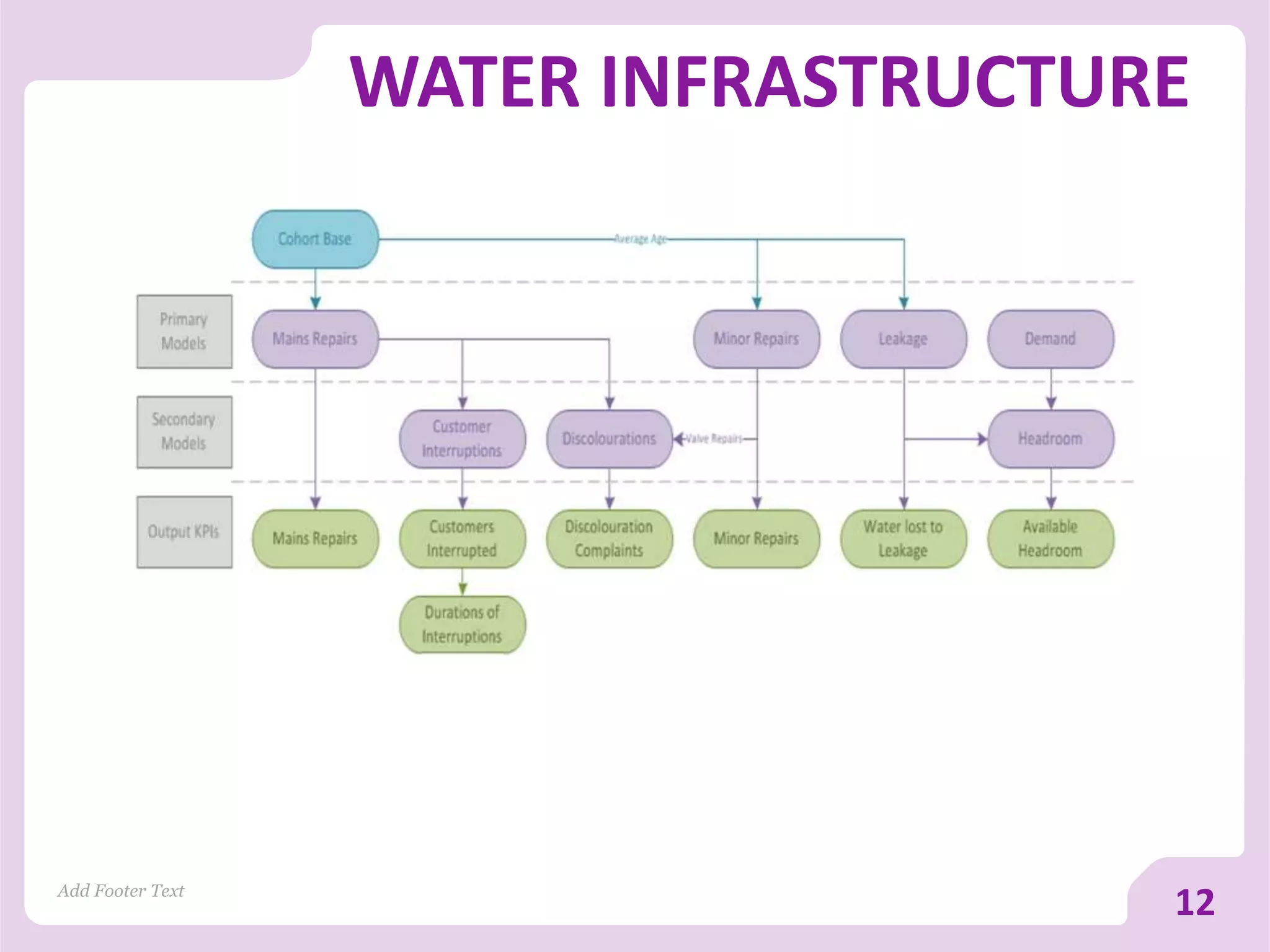
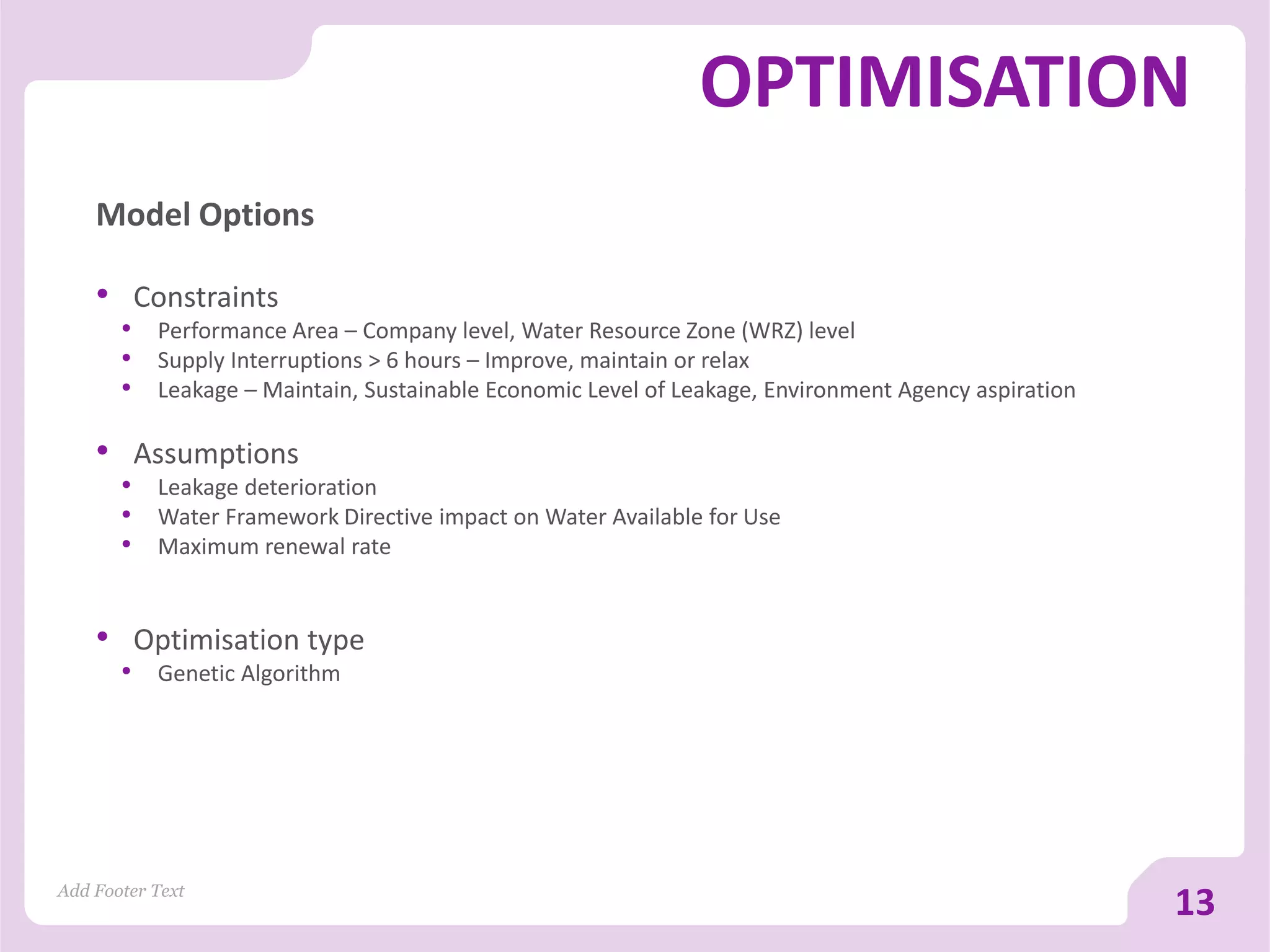
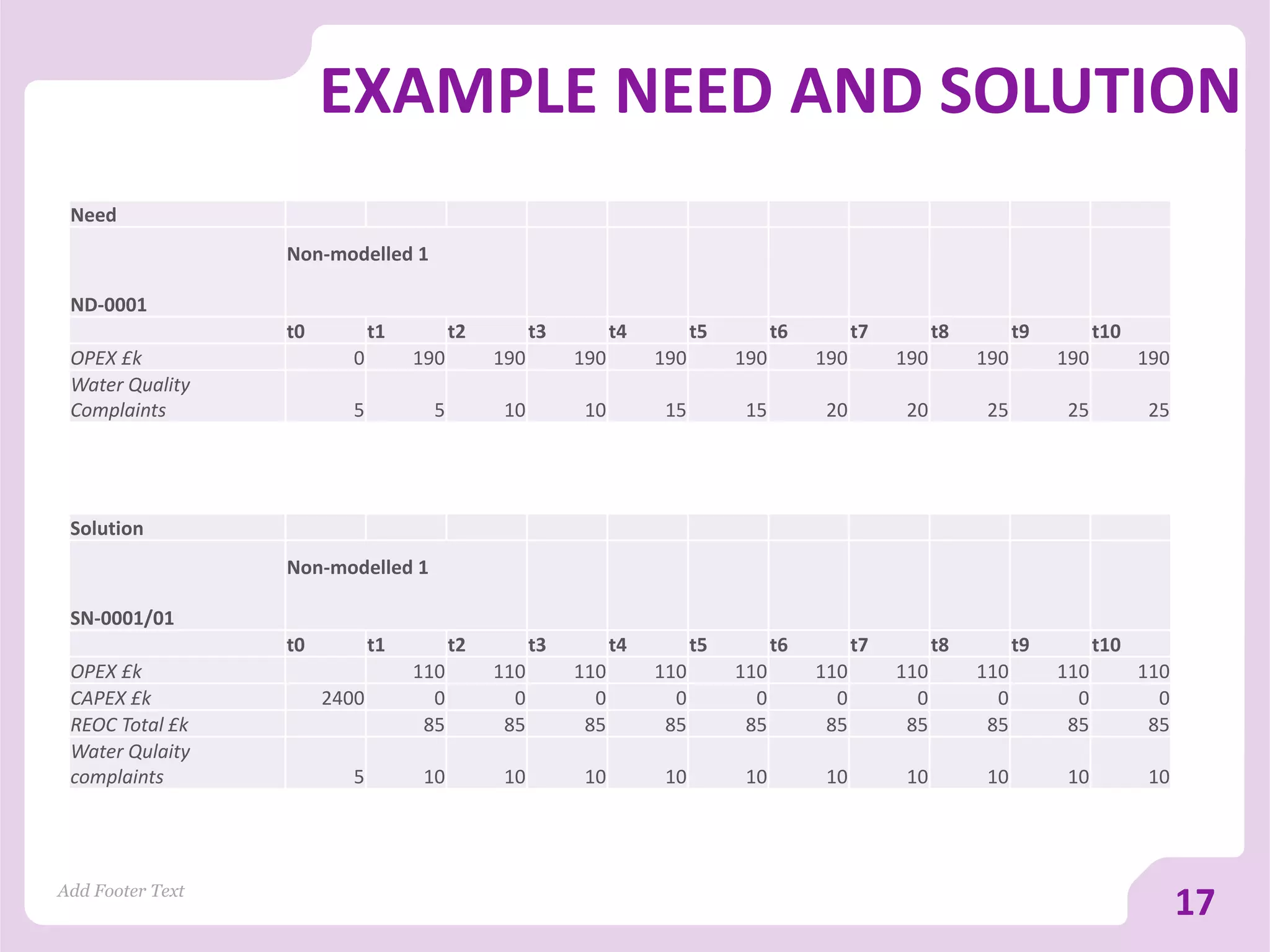
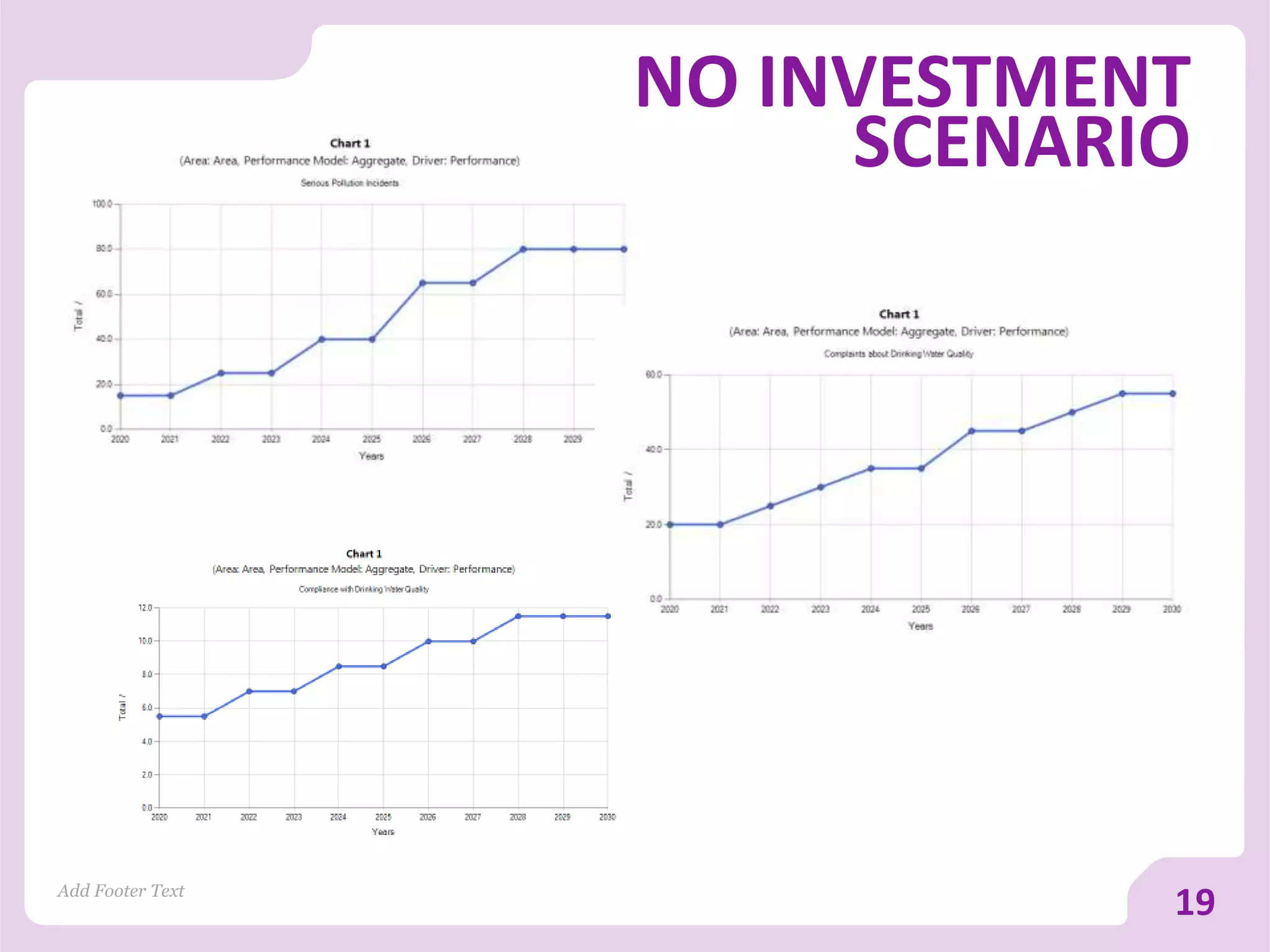
The document discusses asset versus portfolio-centric investment modeling and the role of optimization in asset investment planning, emphasizing complex mathematical algorithms that minimize whole life costs. It highlights the benefits and constraints of both asset-centric and portfolio modeling approaches, using Severn Trent Water as a case study. The document outlines decision support tools that aid in processing complex datasets and improving investment decision-making in water infrastructure.