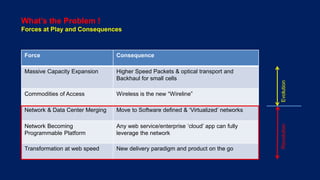
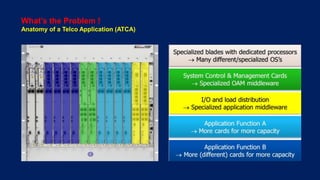
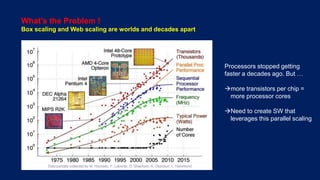
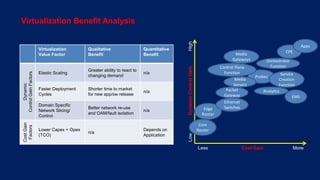
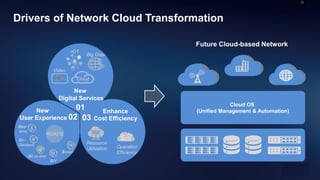
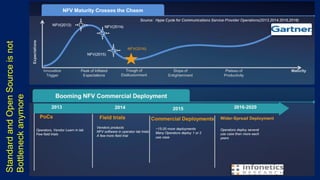
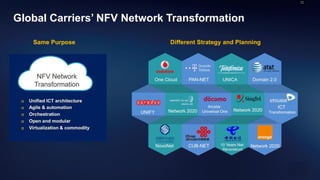
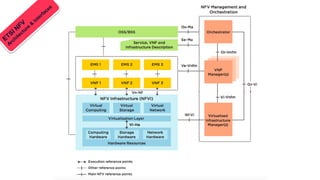
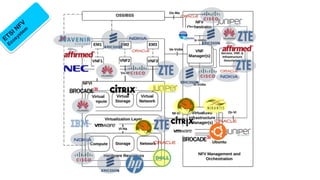
Telco networks are undergoing a transformation driven by factors like increased capacity demands, network and data center convergence, and the need for programmable networks. This is leading telcos to adopt network functions virtualization (NFV), which uses virtualization techniques to virtualize entire classes of network functions into software that can run on commercial off-the-shelf servers rather than proprietary hardware. NFV aims to provide benefits like elastic scaling, faster deployment cycles, network slicing, and lower total cost of ownership. The European Telecommunications Standards Institute established an industry specification group in 2012 with over 50 members to develop NFV standards. NFV allows operators to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and provide opportunities for energy savings, openness and innovation.