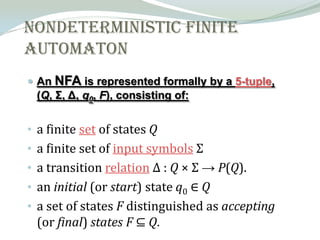
The document discusses regular expressions and how to convert them to nondeterministic finite automata (NFAs). It defines the basic operations used in regular expressions like concatenation, alternation, and Kleene star. It then defines what an NFA is formally in terms of its 5-tuple representation consisting of states, input symbols, transitions, initial state, and accepting states. It mentions the Thompson-Yamada construction algorithm for converting regular expressions to NFAs and outlines the functions like infix to postfix conversion and precedence checking that would be used to implement such an algorithm.



![Code Prototype
char in [SIZE]
//a character array to store the evaluated postfix expression
int out [SIZE][3]
//an output 2-d array which stores the transition information
int stack [n]
//an integer array used for evaluating postfix expression](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nfa-130922140924-phpapp01/85/REGULAR-EXPRESSION-TO-N-F-A-5-320.jpg)
![Primary Functions
Used
void convert (char infix[], char postfix[])
// converting Infix expr. to Postfix expr.
int precedence (int symbol)
// checking the precedence of operator (* . +)
void nfa ()
// evaluating postfix expr. And storing resultant N.F.A. in out[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nfa-130922140924-phpapp01/85/REGULAR-EXPRESSION-TO-N-F-A-6-320.jpg)
