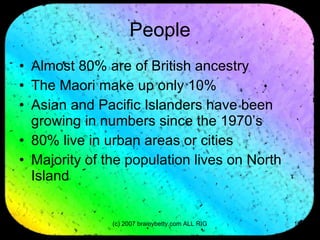
New Zealand has three main islands with varied terrain and climate. The North Island contains volcanic peaks while the South Island is dominated by the Southern Alps mountain range. Wildlife includes endemic species like the flightless kiwi bird. The first settlers were Polynesian people called the Maori who arrived over 1,200 years ago and were farmers and fishers. Later, British settlers colonized New Zealand in the 1800s, though conflict with the Maori continued. New Zealand gained full independence in 1907 and is now a parliamentary democracy and member of the Commonwealth while retaining the British monarch as head of state.