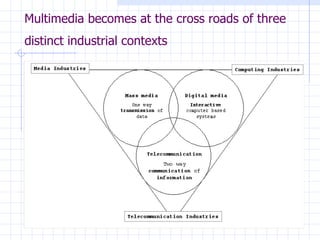
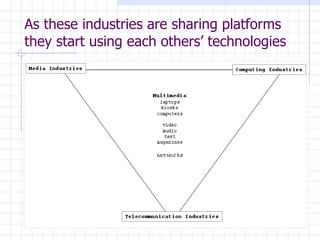
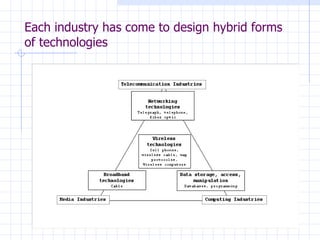
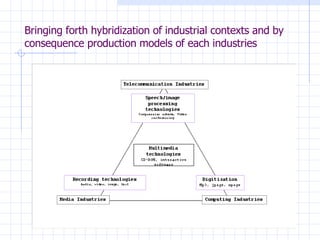
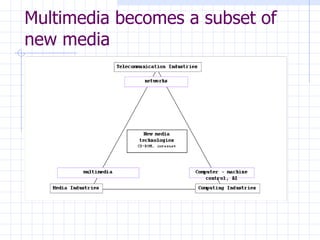
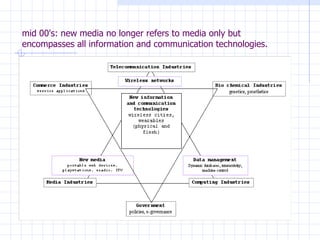
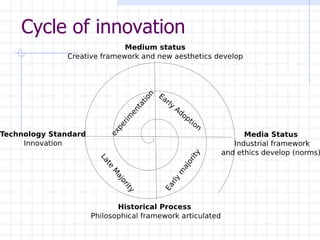
The document traces the evolution of the definition of the term "multimedia" from the late 20th century to the present. It began referring to the combined use of different media types but became centered around computer-based interactive digital environments by the mid-1990s. By the late 1990s, the convergence of different industries led to a shift where multimedia referred to a communication tool. This marked the influence of the telecommunications industry. By the early 2000s, "new media" replaced multimedia as the core of innovation as it referred to the integration of computers, networking and multimedia. New media is now considered a framework rather than a technology.





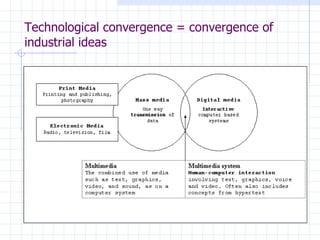
![The need to use Communication systems comes to change the notion of Convergence By the end of the 90’s, the term starts referring to another idea, that of a communication tool multimedia :”transmission that combine media of communication (text and graphics and sound etc.) [syn: multimedia system]”. Source: WordNet ® 1.6, © 1997 Princeton University This shift in definition marks the influence of a third industry, telecommunications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1newmediacontext-1208959629621205-9/85/mpm17-New-media-Contexts-7-320.jpg)