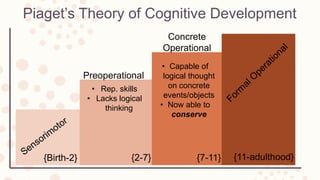
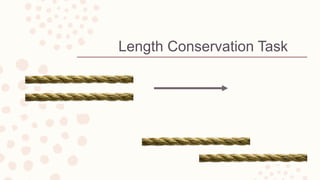
Piaget's theory of cognitive development outlines four stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. The preoperational stage occurs from ages 2-7 and is characterized by the development of representation skills but a lack of logical thinking. Children in the concrete operational stage from ages 7-11 are capable of logical thought involving concrete objects and events and can conserve. The primary difference between the preoperational and concrete operational stages is that logical thinking develops in the latter.