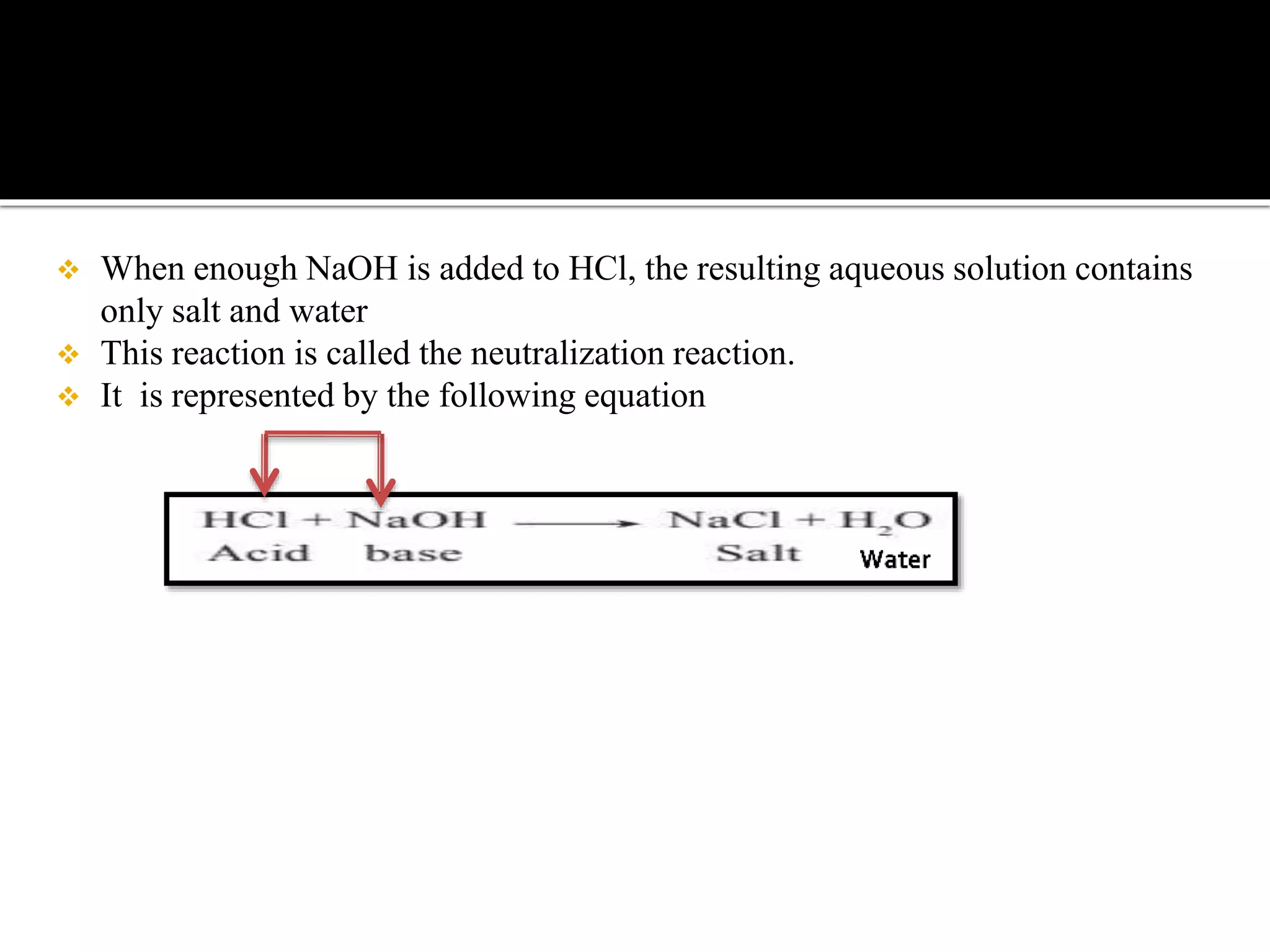
The document describes an experiment demonstrating the neutralization reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH), resulting in a solution with a pH of 7, indicating neutrality. It explains how excess hydroxide ions combine with excess hydrogen ions to form water, and outlines the formation of different types of salts based on the strength of the acids and bases involved. Additionally, it briefly mentions various reactions involving acids and bases, including their interactions with metals and carbonates.