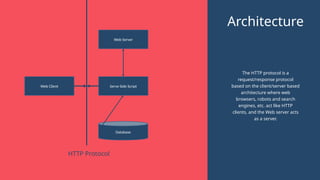
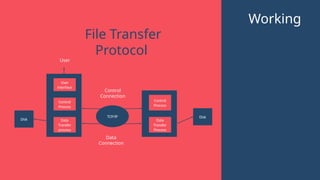
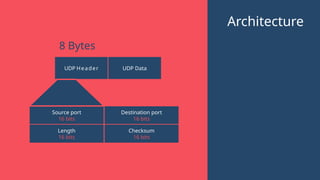
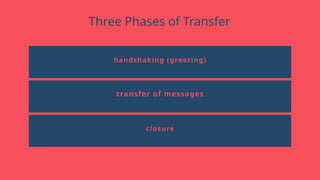
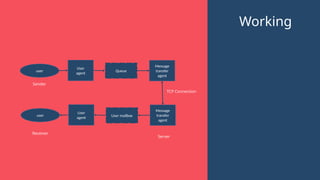
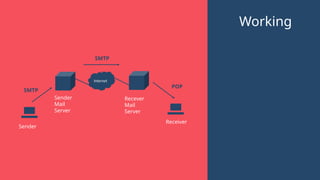
"This presentation covers the fundamentals of networking protocols, their role in data communication, and how they enable seamless connectivity. It explores key protocols like TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP, and DNS, highlighting their importance in modern networking."