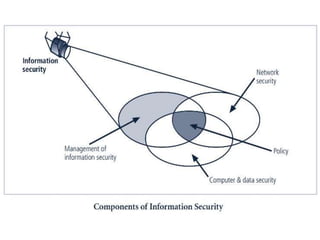
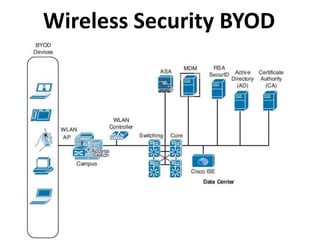
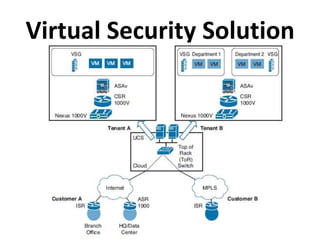
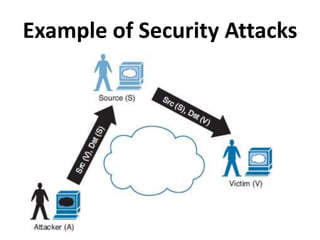
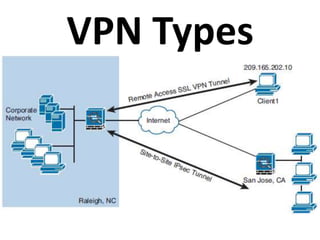
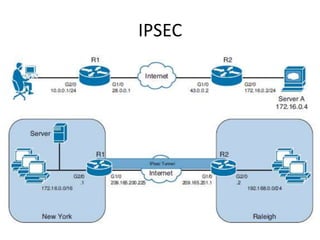
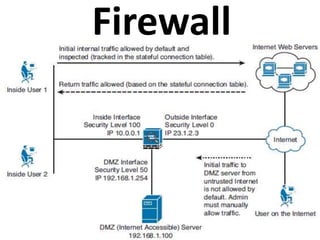
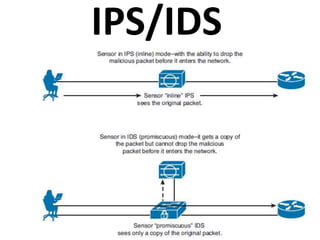
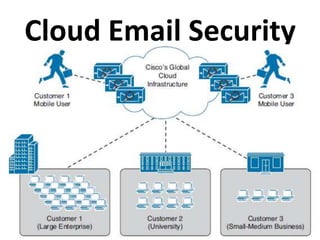
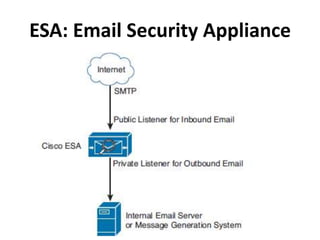
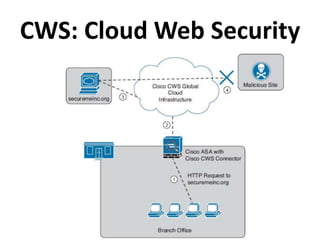
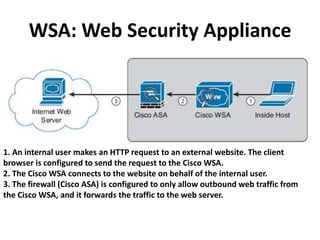
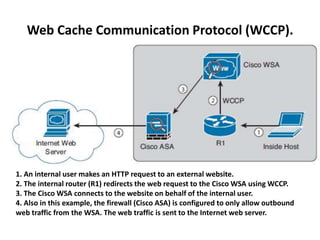
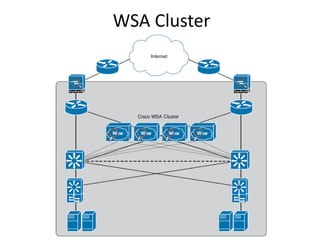
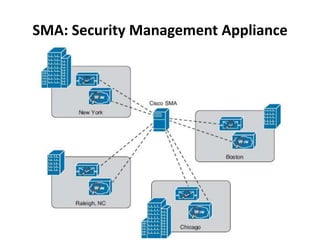
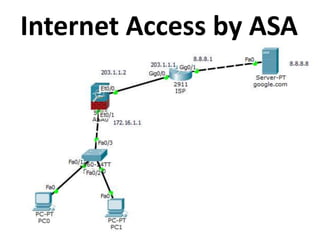
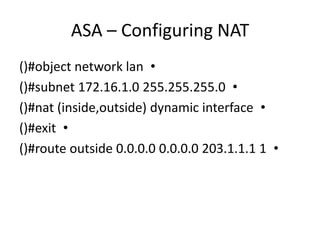
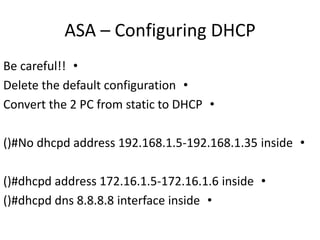
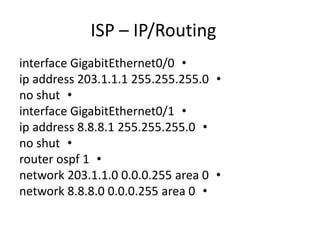
This document outlines a security seminar agenda that includes topics such as security definitions, solutions, VPNs, security devices, AAA (authentication, authorization, and accounting), and firewall configuration. It provides examples of configuring a Cisco ASA firewall, including setting up VLANs, NAT, ACLs, and DHCP. It also describes configuring a Cisco router as an ISP with OSPF routing and connecting an internal server.