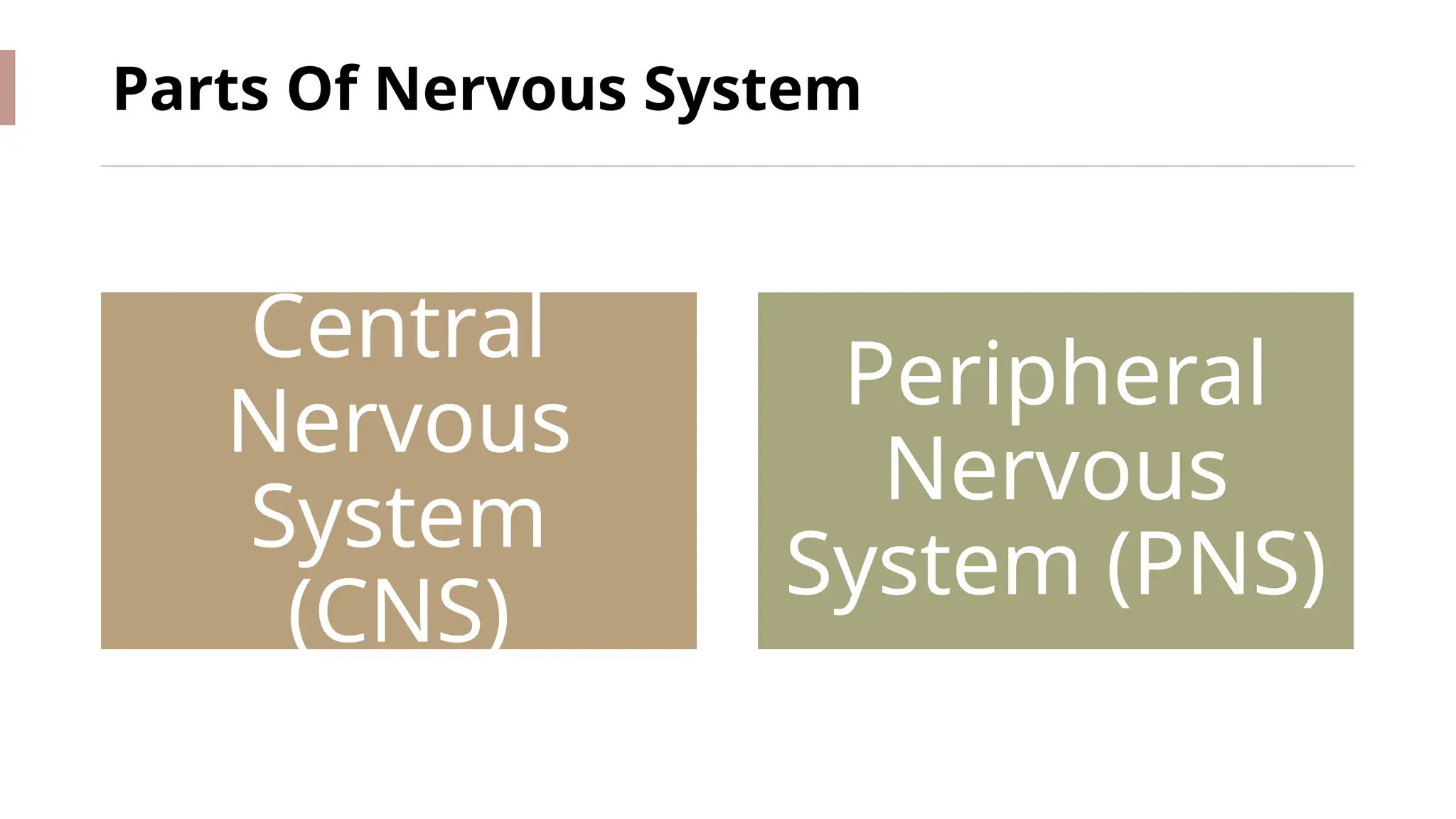
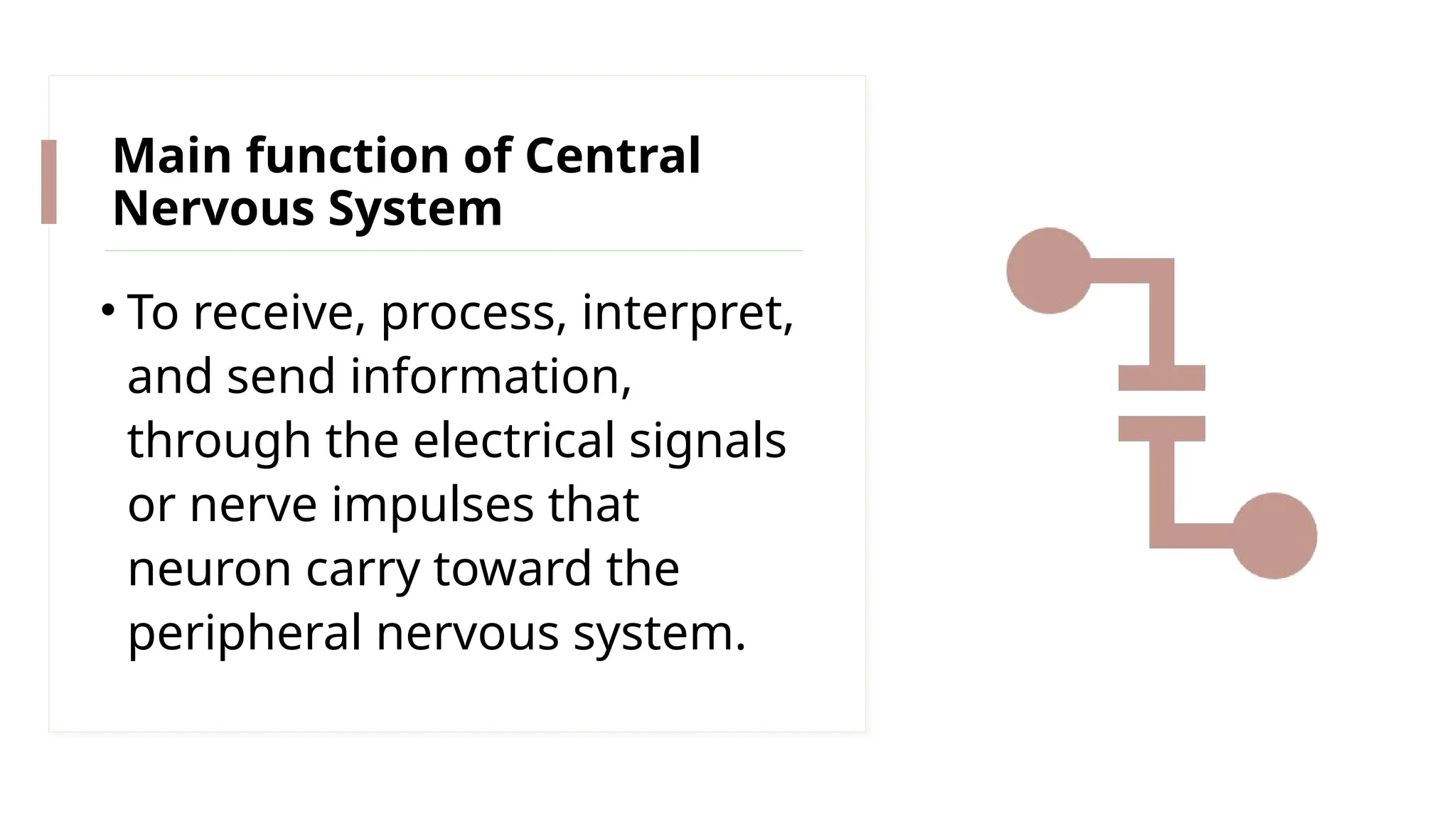
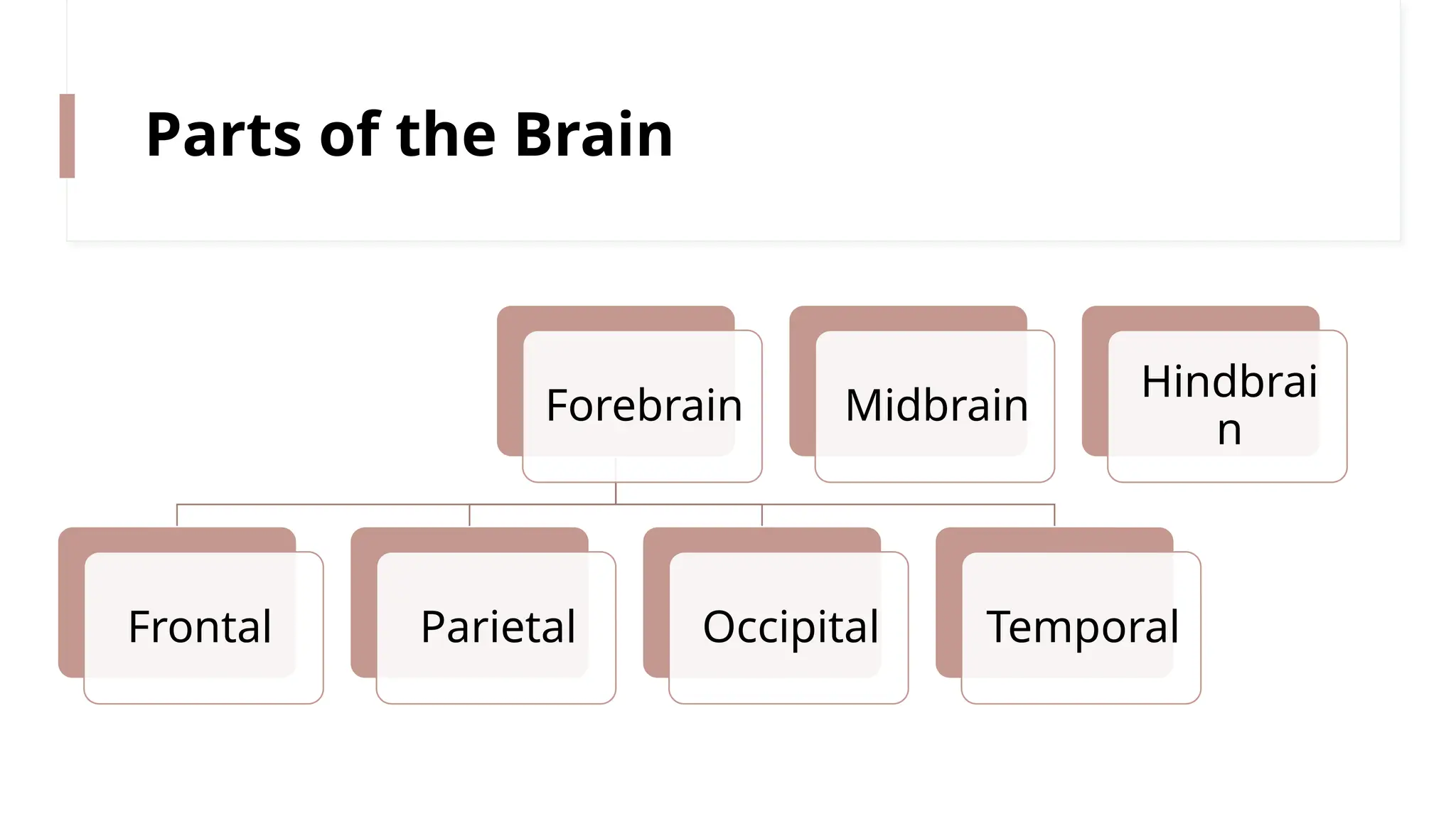
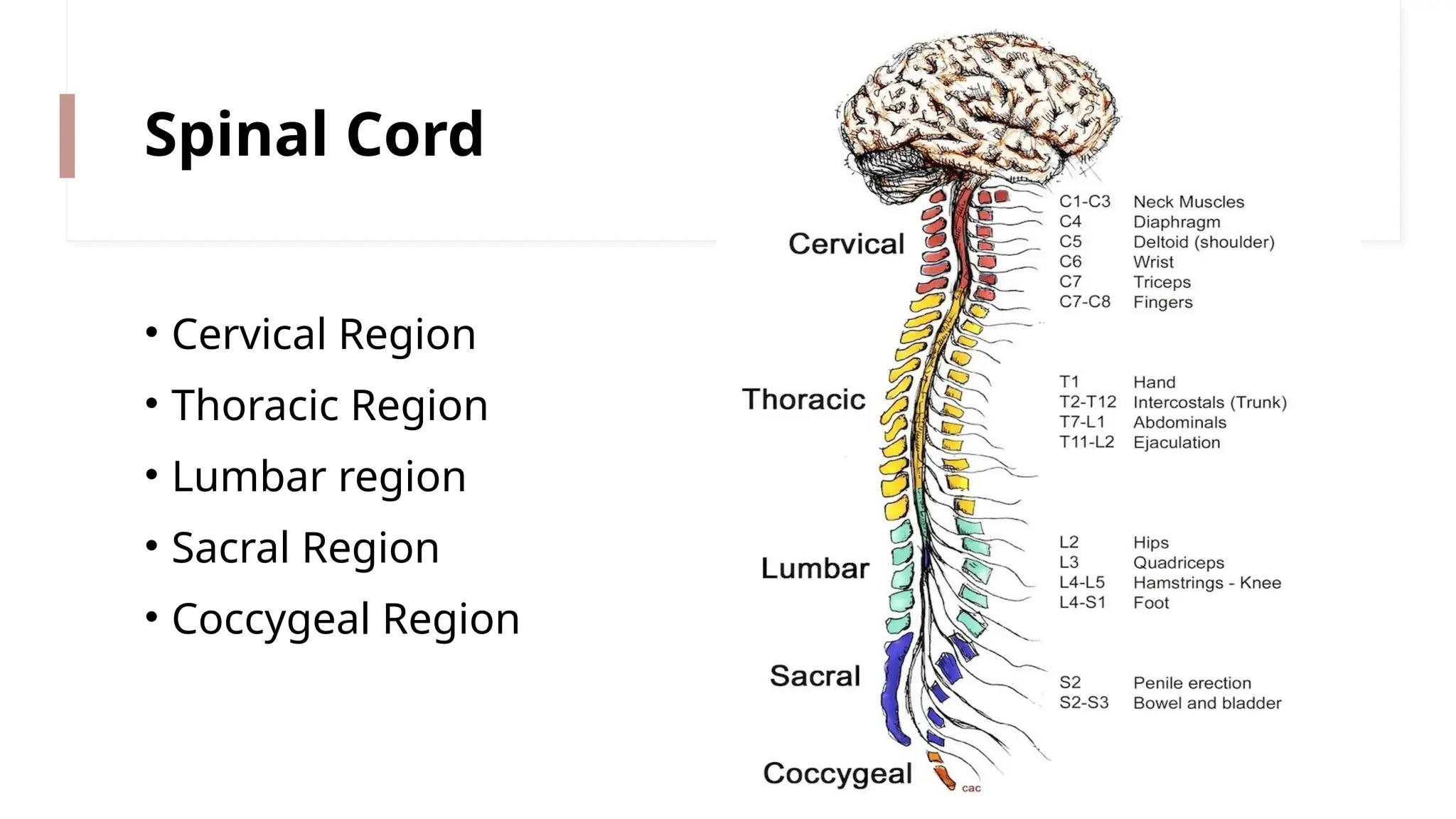
The nervous system is a complex network connecting the brain, spinal cord, and organs, enabling stimulus-response reactions and maintaining homeostasis. It consists of two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS), which processes and interprets information, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which connects the CNS to the rest of the body through 43 pairs of nerves. Neurons are the fundamental units that transmit signals, and the brain controls bodily functions, integrating sensory information and coordinating responses.