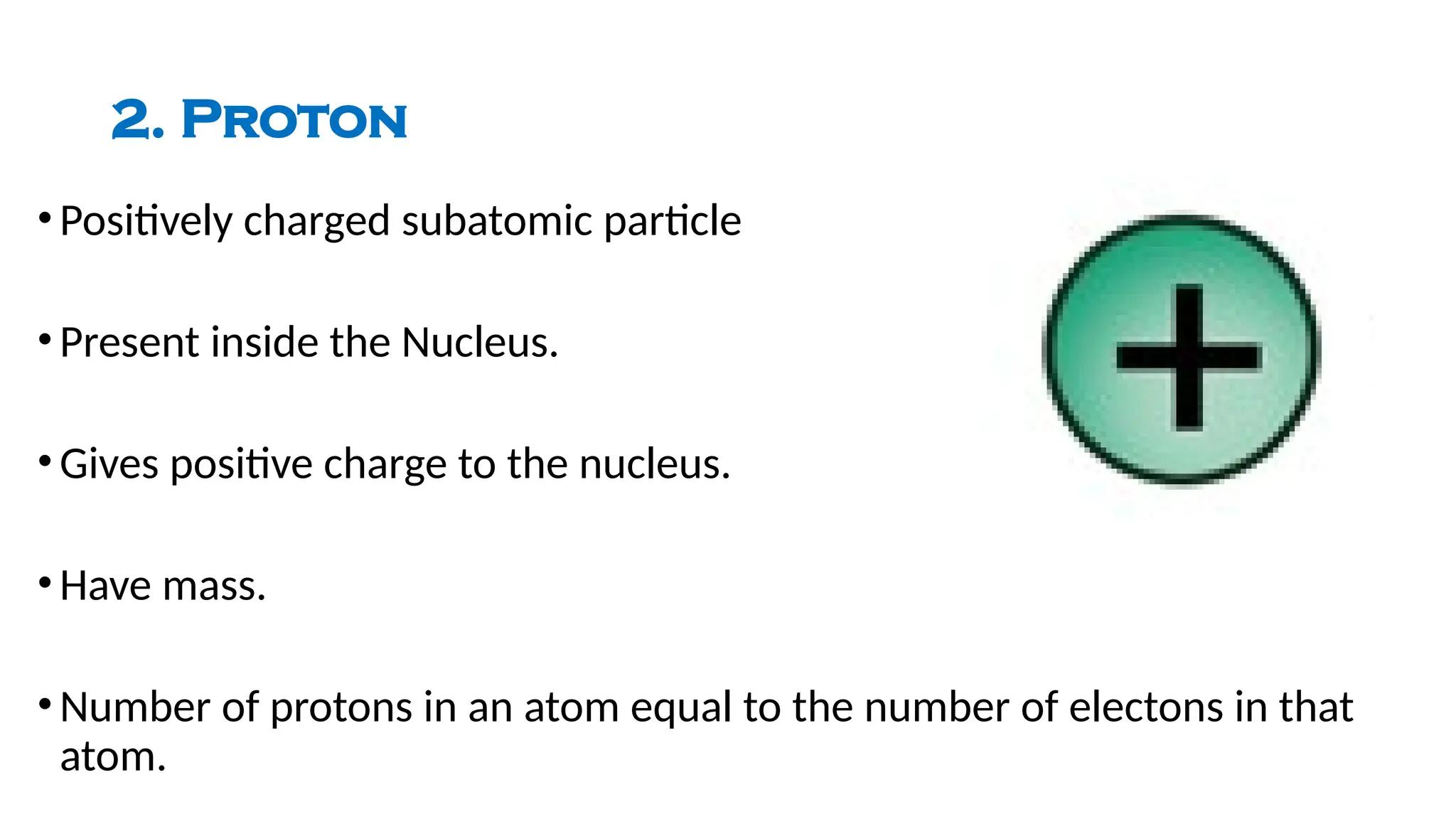
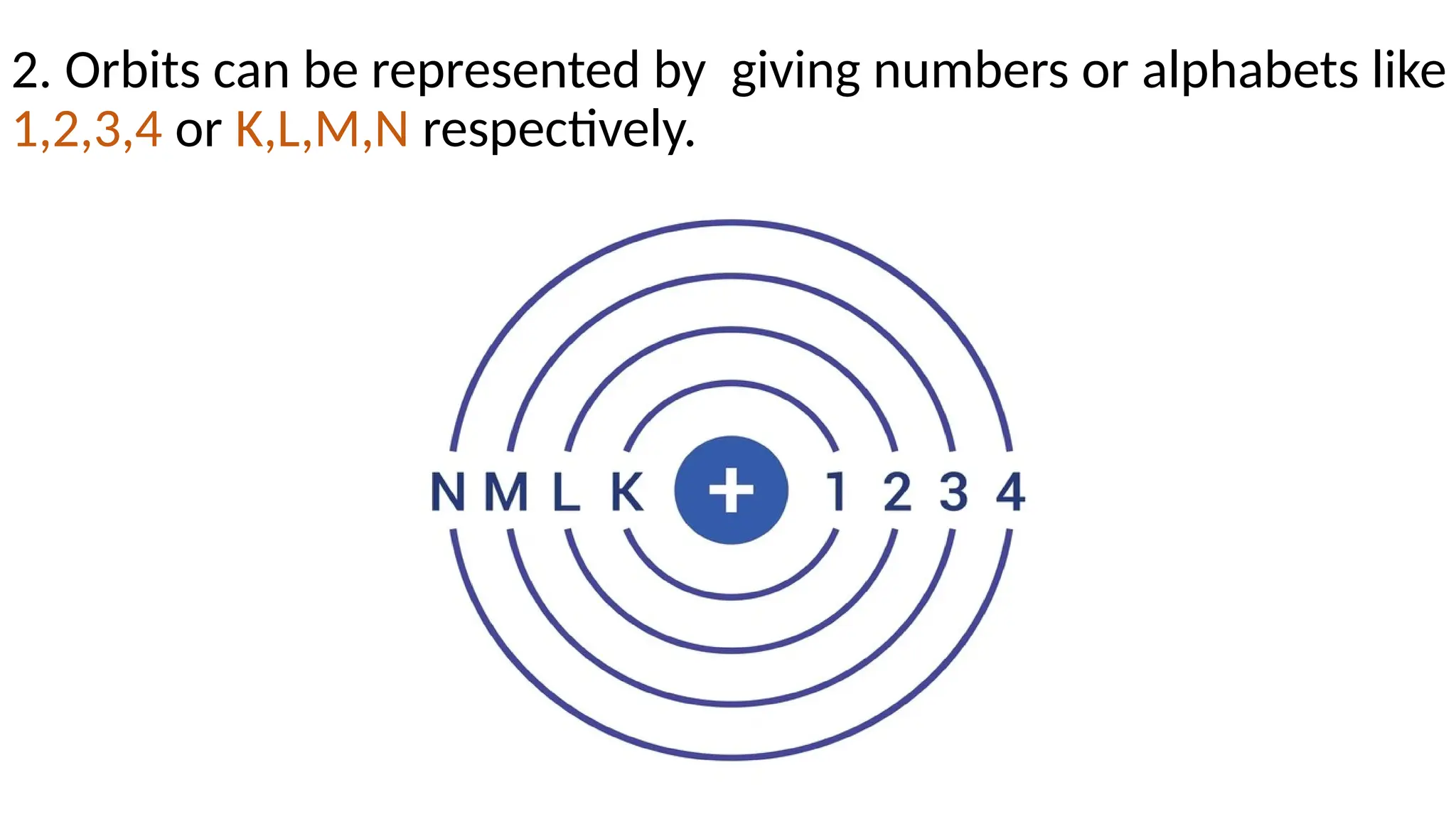
The document describes the structure of the atom, focusing on subatomic particles: electrons, protons, and neutrons. It details Niels Bohr's 1913 atomic model, which introduces the concept of fixed orbits for electrons around the nucleus, with each orbit having a specific energy level. The energy dynamics between orbits include emission and absorption of energy as electrons shift between levels.