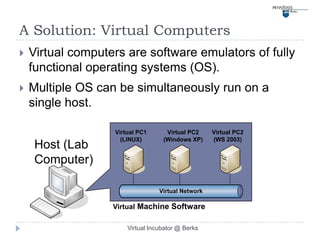
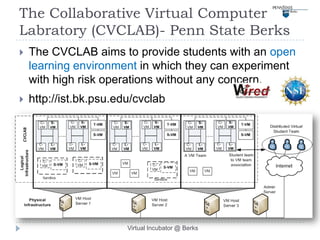
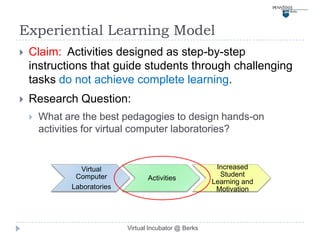
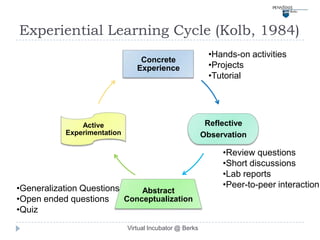
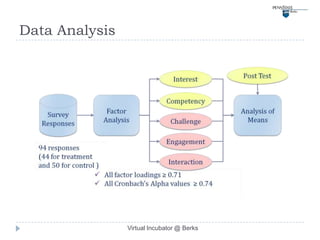
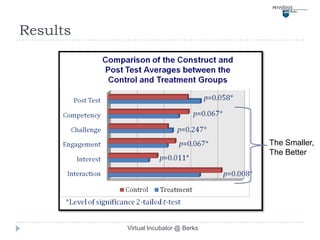
This document describes a virtual incubator called the Virtual Incubator @ Berks (VIB) that was created to promote IT innovations among students. The VIB provides virtual IT resources for student entrepreneurship (E-) teams to prototype their ideas over extended periods without limitations of physical computer labs. It aims to instill an entrepreneurial spirit in IT students and engage them in solving local business problems. The document outlines the objectives, targeted technologies, an example project, challenges, and a plan to evaluate using Kolb's experiential learning model to design hands-on activities for the virtual computer lab.