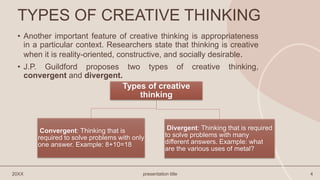
The document explores the nature of creative thinking, highlighting its ability to generate original ideas and solutions. It distinguishes between convergent thinking, which produces a single answer, and divergent thinking, which encourages multiple responses, emphasizing the importance of fluency, flexibility, originality, and elaboration in the creative process. It concludes by underscoring the complementary roles of both thinking types in problem-solving and innovation.