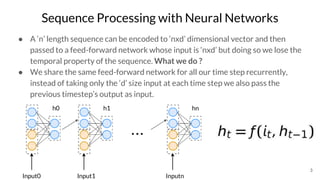
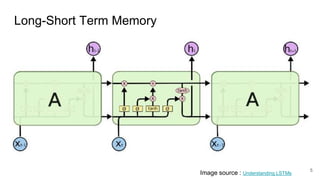
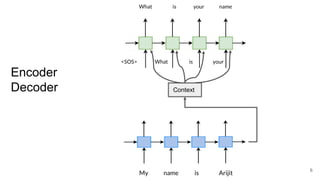
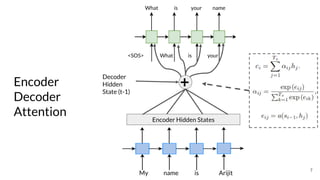
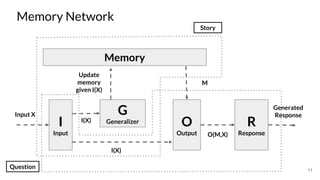
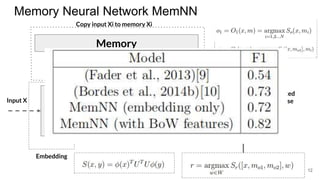
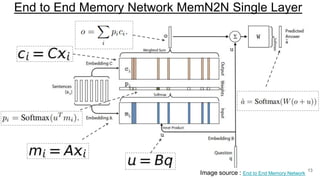
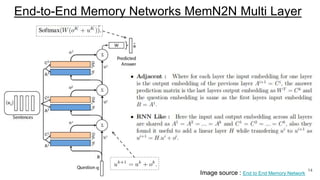
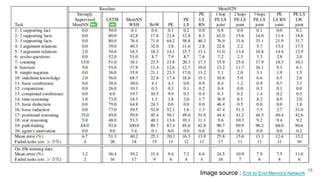
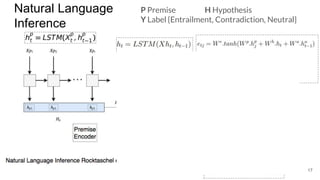
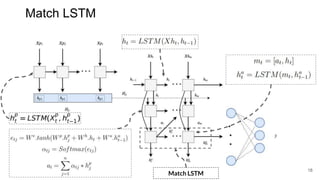
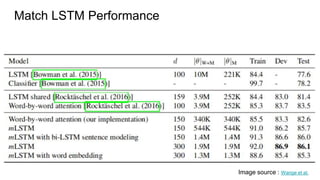
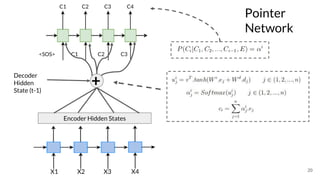
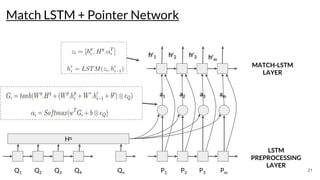
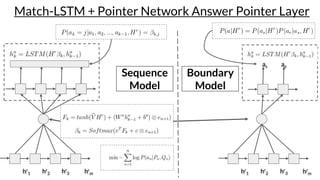
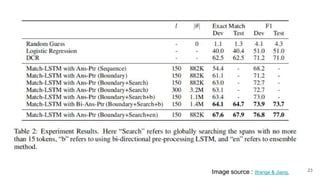
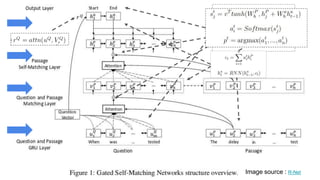
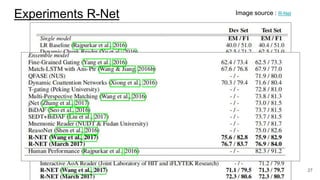
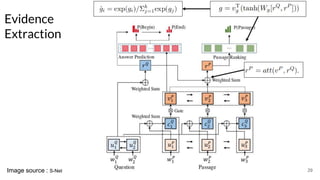
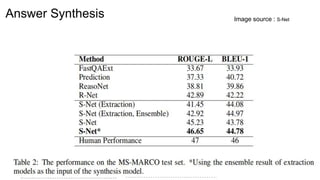
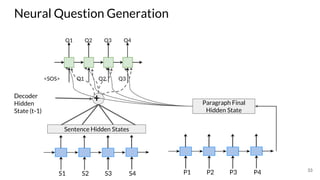
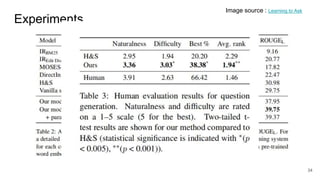
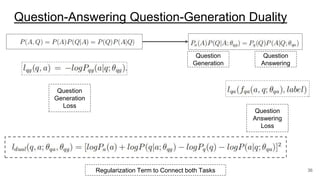
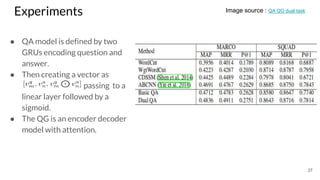
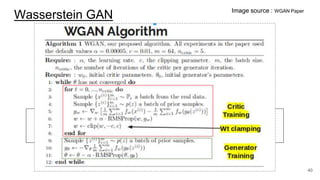
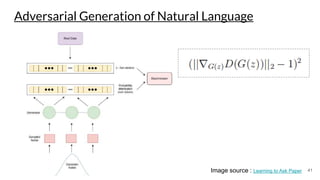
The document discusses various techniques in neural question generation and answering, highlighting models such as memory networks and seq2seq architectures with attention mechanisms. Key topics include challenges like vanishing gradients in recurrent networks, and datasets like the Stanford Question Answering Dataset used for training. The presentation also outlines future directions for improving generation frameworks and exploring new GAN methodologies.