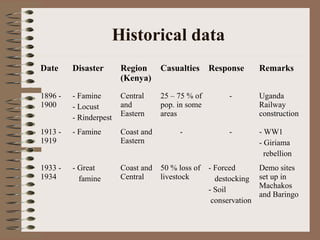
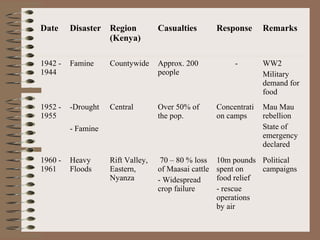
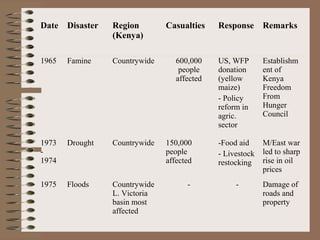
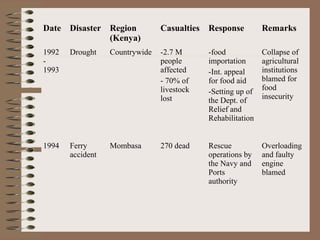
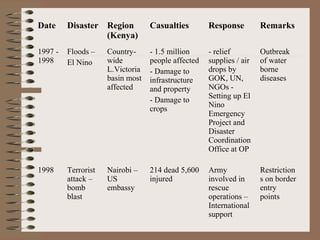
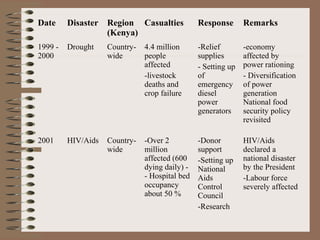
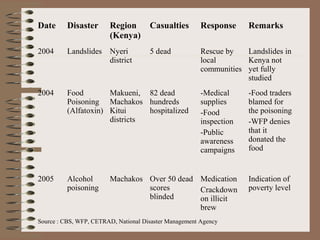
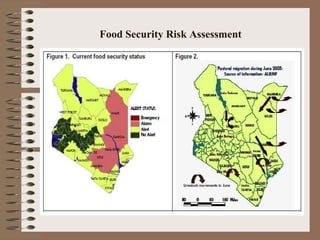
This document provides a historical perspective of disasters in Kenya from 1900 to 2005 based on data from various sources. It outlines the major disasters including famines, floods, disease epidemics, and traffic accidents. Emerging disasters mentioned are fires, landslides, invasive species, terrorism, food poisoning, and potential tsunamis. The document discusses contributing factors like climatic variability and population increase, as well as compounding factors such as political instability. It notes trends of increasing frequency, magnitude and severity of disasters. While disaster management capacity is developing, the response has typically been reactive with low budgetary support and reliance on external aid. The document concludes by outlining challenges and opportunities to strengthen capacity going forward.