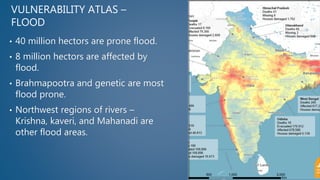
This document is a student project on natural disasters that includes an acknowledgements section, index, and sections on floods, flood prevention, roof types (flat, pitched, shell), and a conclusion. It provides information on floods such as their causes, vulnerability atlases, and the function of floodplains. It also describes the key features and advantages/disadvantages of different roof types. The conclusion restates that disasters can result in loss of life/property and defines floods, floodplains, and roofs.