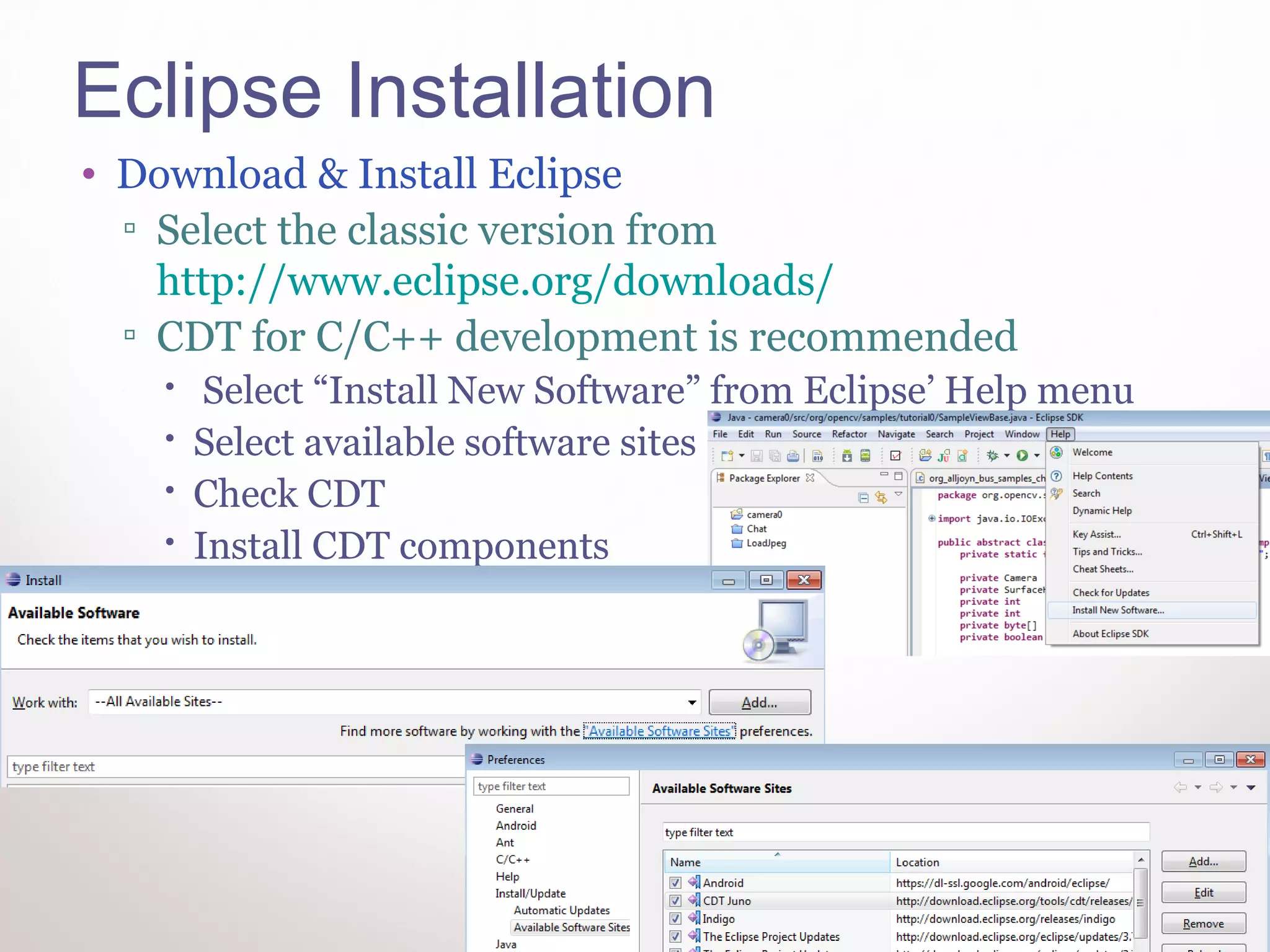
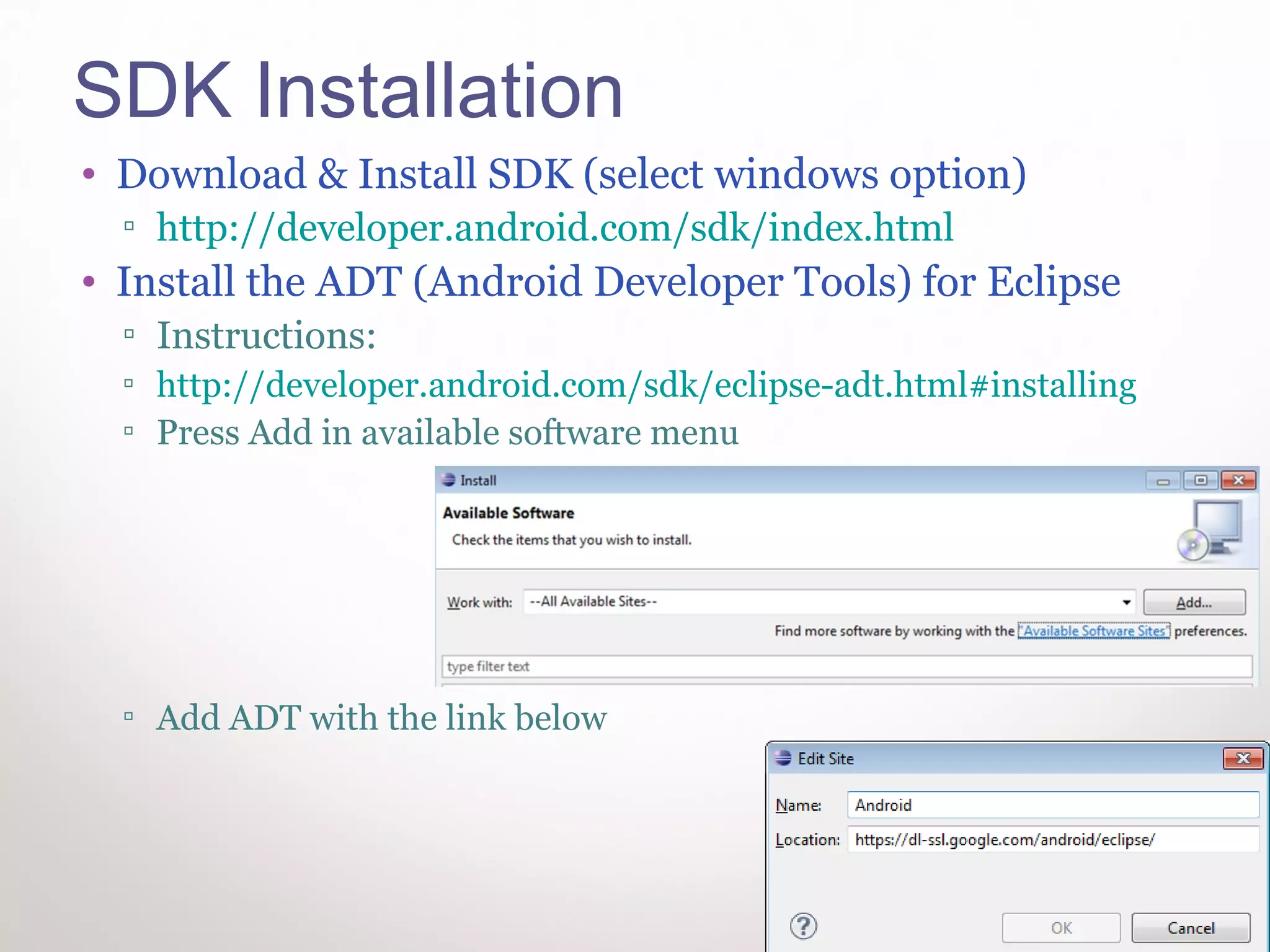
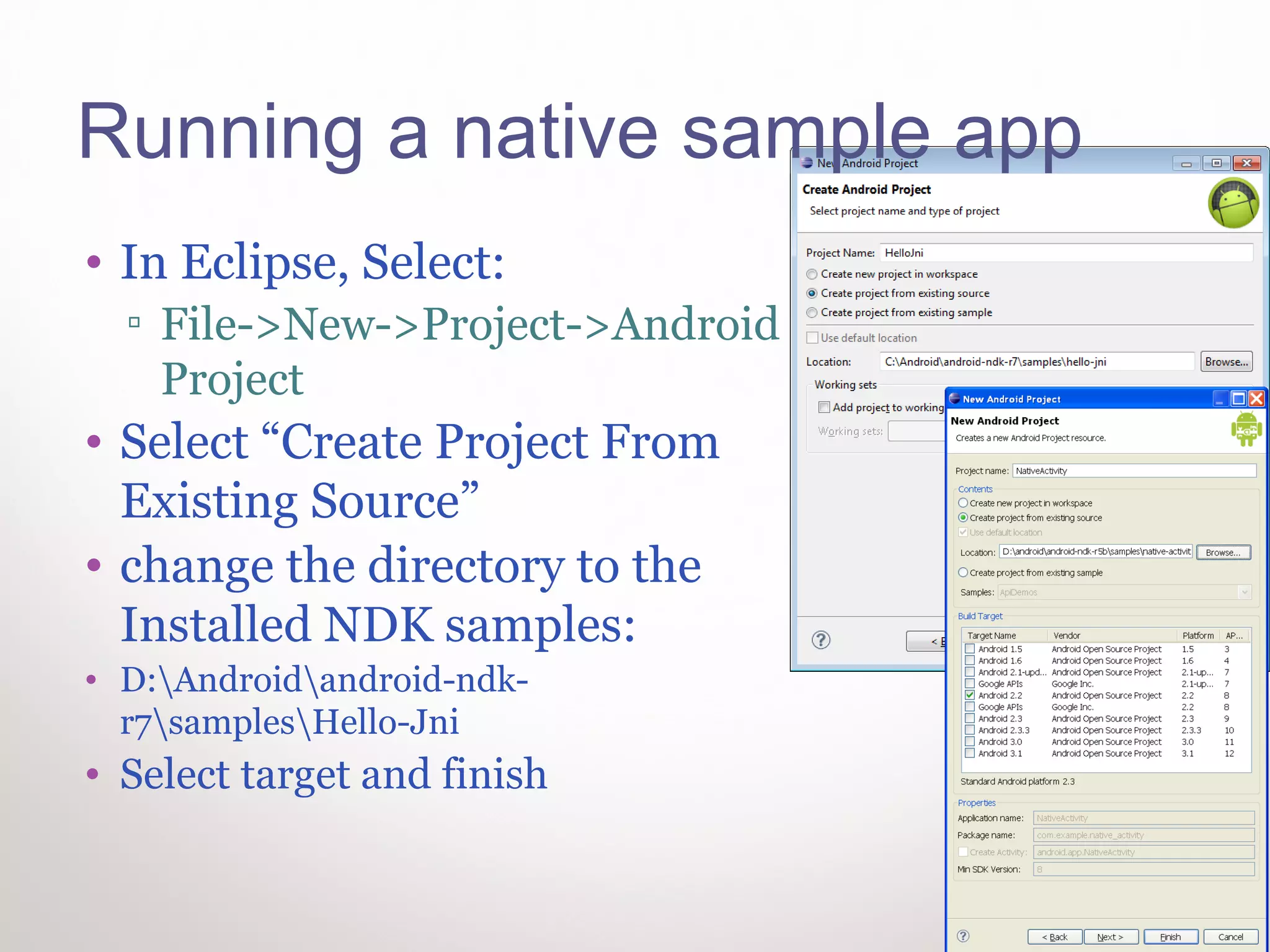
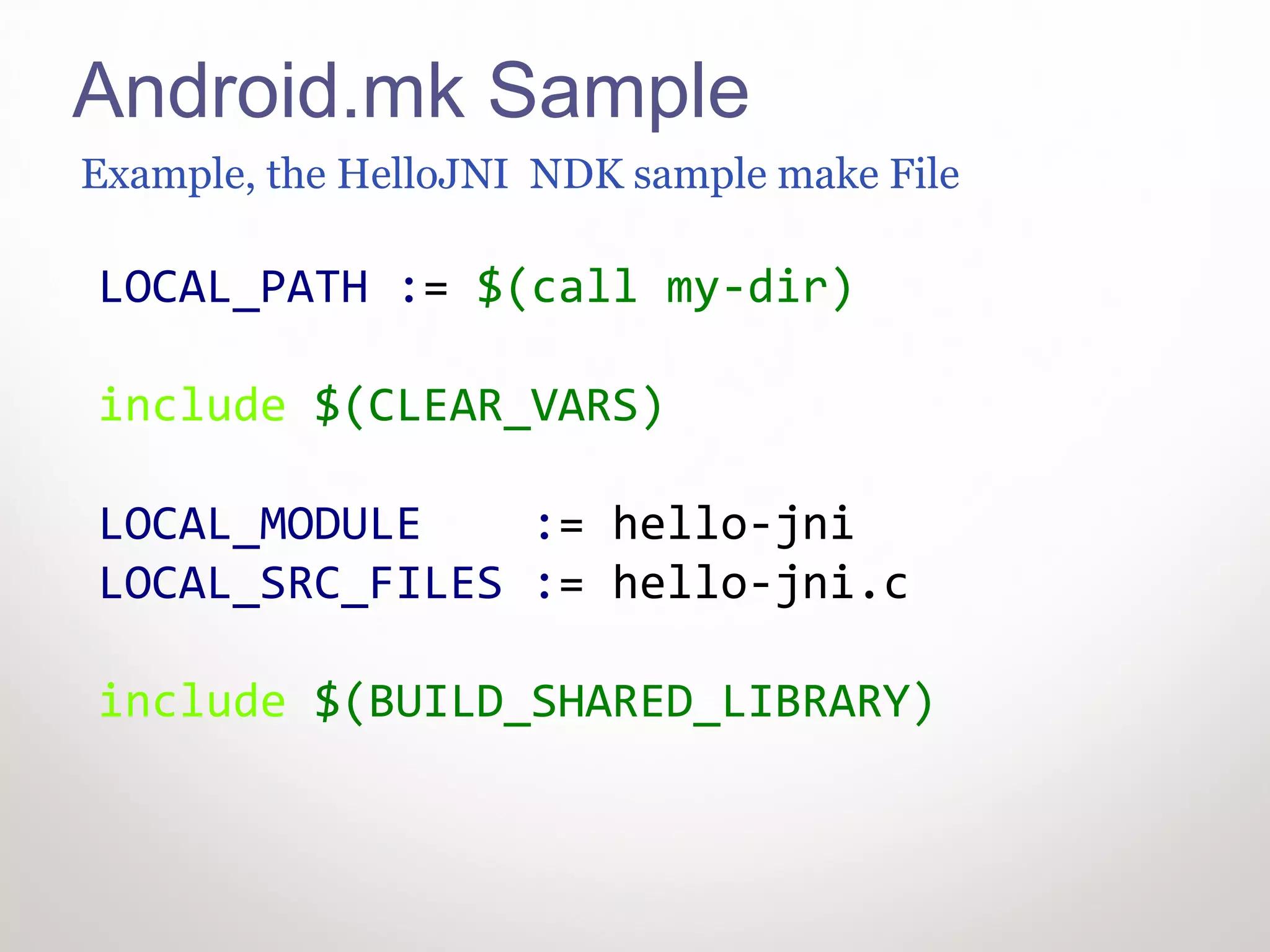
This document provides instructions for Windows developers to get started with native Android development. It outlines how to install Eclipse, the Android SDK, USB drivers, the NDK, and Cygwin. It then walks through running a sample native application in Eclipse. The code is reviewed, explaining the Java code calls the native C code, and the Android.mk and Application.mk files configure the native application build. Contact information is provided for additional Android programming help.