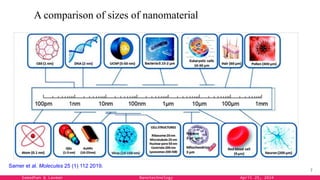
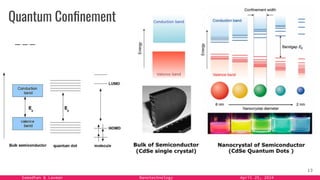
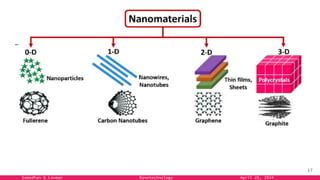
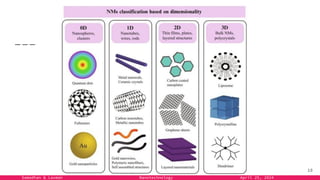
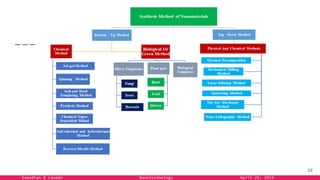
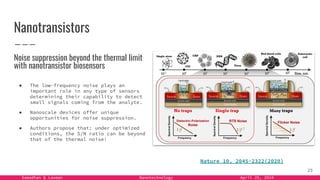
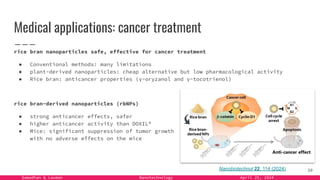
The document provides an overview of nanotechnology, detailing its definition, history, and applications across various fields such as medicine, energy, and electronics. It highlights the unique properties of materials at the nanoscale, the challenges of production, and the potential of nanotechnology to create innovative solutions for environmental and health issues. The authors emphasize the need for interdisciplinary collaboration to fully harness the capabilities of nanotechnology for societal benefits.