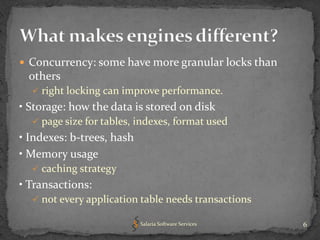
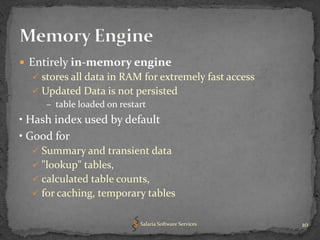
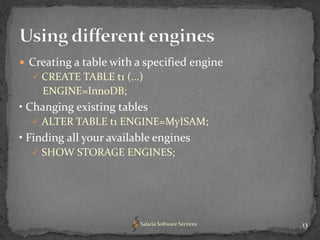
The document provides an overview of key concepts related to optimizing performance in MySQL databases, including storage engines, data types, normalization, indexing, and character sets and collations. It emphasizes choosing appropriate storage engines and data types based on application requirements, normalizing data to reduce redundancy while improving performance, and using indexes and EXPLAIN queries to optimize queries. Overall, understanding these foundational concepts can help developers design higher performing MySQL databases and applications.