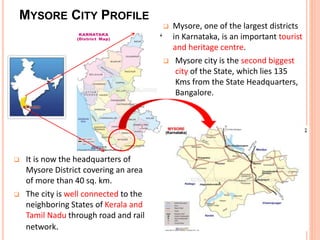
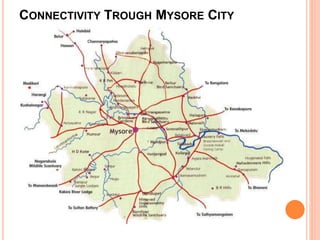
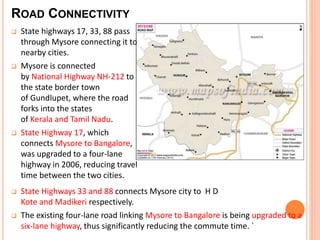
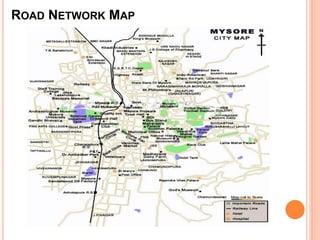
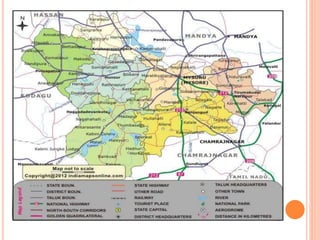
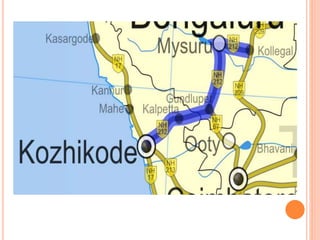
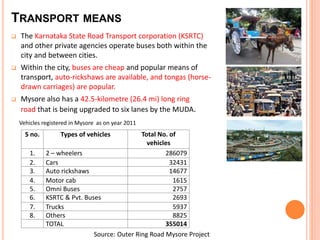
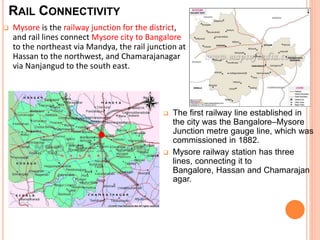
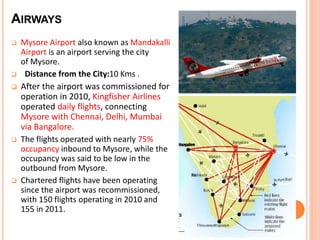
Mysore city has good transportation connectivity through roads, railways, and an airport. The document outlines Mysore's road network which includes state highways connecting it to nearby cities. Mysore railway station connects the city to Bangalore, Hassan, and Chamarajanagar by rail. Mysore Airport serves the city and was previously connected to Chennai, Delhi and Mumbai by flights until service was suspended. The document provides details on transportation systems to analyze connectivity within and from Mysore city.