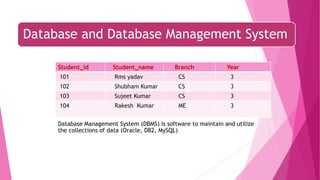
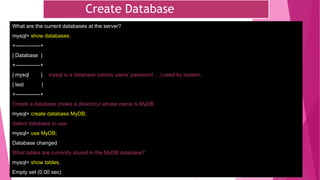
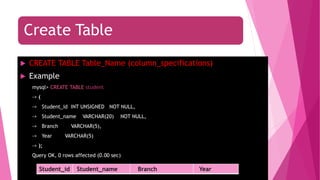
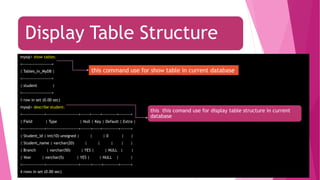
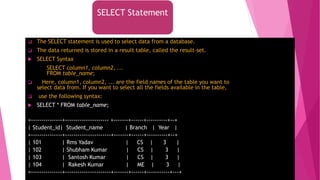
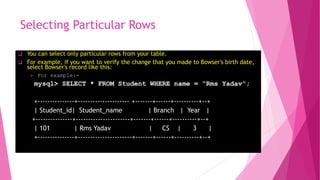
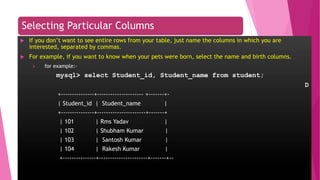
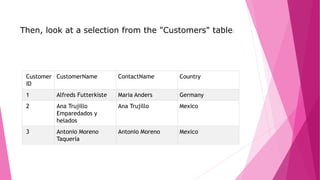
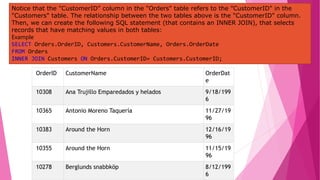
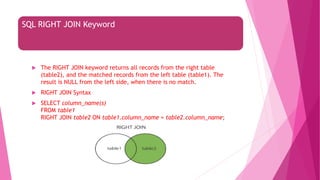
The document is an introduction to MySQL, covering the basics of database and database management systems, and detailing how to connect, create, and manipulate databases using MySQL. It includes examples of common SQL operations such as inserting, updating, and querying records, as well as explanations of keys and join operations. Additionally, it describes the structural components of data storage in MySQL and provides command syntax for executing various database tasks.