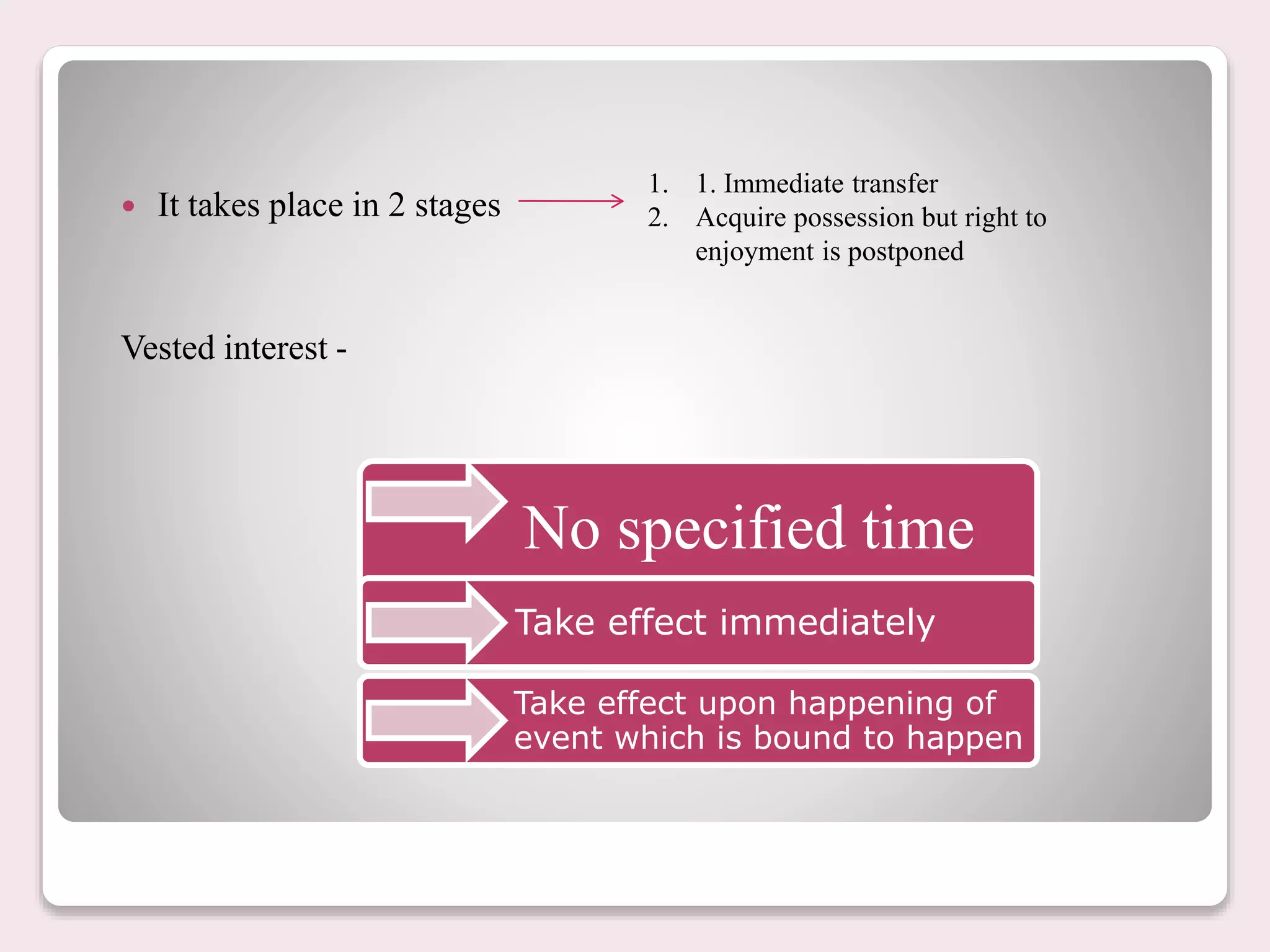
The document discusses the concepts of vested and contingent interests as defined in the Transfer of Property Act, 1882. Vested interest entails an immediate transfer and the right to possession, which can be inherited or transferred, while contingent interest depends on a specified uncertain event and is not heritable. The document includes case references to illustrate these concepts.