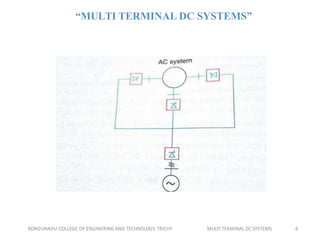
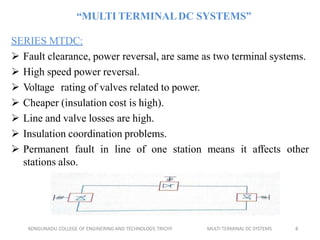
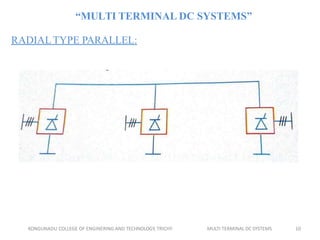
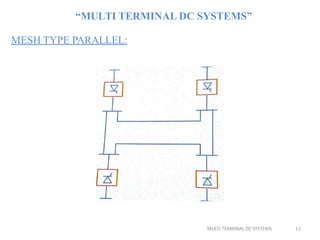
This document discusses multi-terminal DC (MTDC) systems. MTDC systems have multiple converter terminals and can be configured as series, parallel, radial, or mesh systems. Series MTDC involves connecting terminals in series, which allows power transfer between stations but has high insulation and losses costs. Parallel MTDC keeps the voltage constant between terminals while allowing individual control of current, enabling power sharing with lower losses. Radial and mesh topologies further expand options for power flow control in MTDC networks. The document provides examples of MTDC applications for integrating remote generation, asynchronous interconnections, and managing overloads.