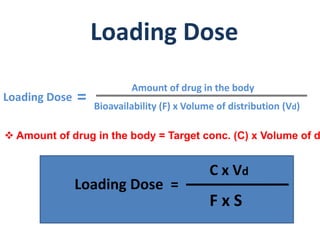
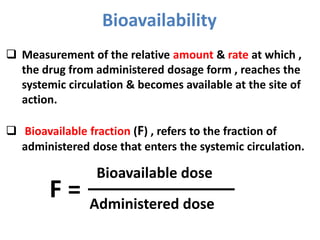
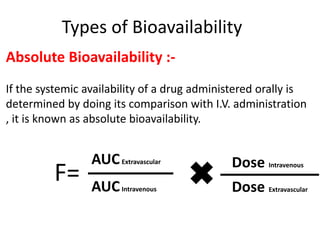
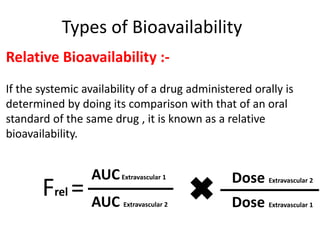
This document discusses multiple dosage regimens including loading doses, bioavailability, and repetitive intravenous injections. It defines loading dose as the initial dose needed to achieve the target concentration based on volume of distribution and bioavailability. It describes bioavailability as the fraction of the administered dose that reaches systemic circulation, and distinguishes between absolute and relative bioavailability. It also defines bioequivalence as formulations having absorption rates and extents that are not statistically different. Finally, it examines repetitive intravenous injections and how the drug amount remaining in the body decreases exponentially with each dose based on the elimination constant and dosing interval.