More Related Content
PDF
PDF
Voice Therapy: Management Of Benign Voice Disorders PPT
Vocal cord paralysis current concepts PDF
Tens en mujer con disfonia PPTX
PPTX
TRADITIONAL APPROACHES.pptx PPTX
puberphonia voice disorder management and assessment PPTX
VOICE REHABilitation after surgery final.pptx Similar to Multimodal_Voice_Therapy.pptx ahfrjjhrtk
PDF
Bilateral TVC paralysis Dr. M. Erami PDF
UNILATERAL VOCAL FOLD PARALYSIS - powerpoint presentation PPT
PPT
PPTX
Disorders of voice for undergraduates including Hoarseness PPT
Rehabilitation after treatment of cancer larynx sujay susikar PPTX
APPROACH TO A PATIENT WITH VOCAL CORD PARALYSIS PPTX
PPTX
Voice therapy to treat voice disorders PPTX
STRUCTURAL DISORDERS of the vocal cords.pptx PPTX
DOC
PPT
F081 Coclia 75 Phonosurgery PPTX
DISORDERS OF VOICE final .pptx PPT
Rehabilitation after laryngectomy PPTX
Vocal fold paralysis/ Paresis full PPTX
PPTX
Vocal cord paralysis and evaluation of hoarseness PPTX
16. vocal cord paralysis and evaluation of hoarseness kk PPTX
Neurological conditions of larynx ashly Recently uploaded
PPTX
LOW DOSE RADIATHERAPY (LDRT) IN OSTEOARTHRITIS PPTX
THE STUDY OF MIND content intro and basics.pptx PPTX
Anatomy of temporal & infratemporal fossa.pptx PPTX
1.-Dr.-Ajay-Khera- Anemia Mukt Bharat.pptx PDF
COLLOIDAL DISPERSION PPTx. S.Y B-PHARM . DOCX
Pharmacotherapeutics - II Practical Record with Clinical Examination (20 cases) PPTX
Atrial Fibrillation and difference with Atrial flutter PPTX
Infectious diseases of the head and neck 2.pptx PPTX
PERI-PROSTHETIC FRACTURE NAIL-PLATE CONSTRUCT [NPC].pptx PDF
Medicinal &Toilet Preparation Act T.Y.B-PHARM PDF
Best Sexologist Unit in Araria, Bihar @dubeyclinicpatna PDF
Police Officer Mental Health & Wellness Programs | MyOmnia PPTX
Venous cutdown for Surgery Viva, MBBS Students PPTX
sinusitis.....................................pptx PDF
Vitamin K works in conjunction with D to the Knesset .pdf PPT
Managemant of Mutilated Vital Teeth presentation PPTX
CTEV [ clubfoot] DR ARUN LAL ,DR MOHAMED ASHRAF travancore medical college k... PDF
Code of Ehics PPT, T.Y. B-PHARM ,5TH SEM PDF
A beginner-friendly introduction to gym training PDF
Seminario biología molecula - EBV-miR-BART5-3p Multimodal_Voice_Therapy.pptx ahfrjjhrtk
- 1.
- 2.
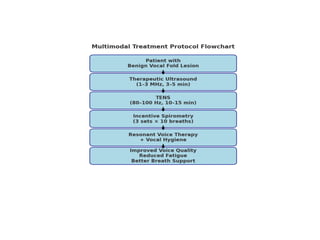
Background
• • Benignvocal fold lesions (nodules, polyps,
cysts) cause dysphonia and fatigue.
• • Standard care: voice therapy, vocal hygiene,
surgery if needed.
• • Physiotherapy-based modalities remain
underexplored in voice rehabilitation.
• • Novel approach: Ultrasound + TENS +
Incentive Spirometry.
- 3.
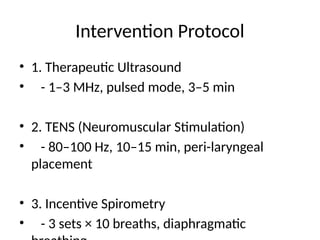
Intervention Protocol
• 1.Therapeutic Ultrasound
• - 1–3 MHz, pulsed mode, 3–5 min
• 2. TENS (Neuromuscular Stimulation)
• - 80–100 Hz, 10–15 min, peri-laryngeal
placement
• 3. Incentive Spirometry
• - 3 sets × 10 breaths, diaphragmatic
- 4.
Outcomes
• • Improvedvocal quality (GRBAS scale).
• • Reduced jitter, shimmer, increased HNR.
• • Decreased patient-reported vocal fatigue.
• • Improved respiratory control and phonation.
• • Enhanced vocal endurance.