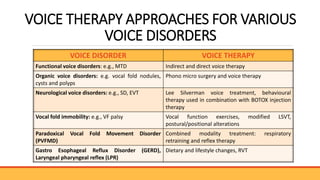
The document discusses advancements in voice therapy, including both direct and indirect techniques tailored to individual voice disorders and their severity, as well as the role of phonosurgery in treating vocal function. Key treatment methods include resonant voice therapy, vocal function exercises, and various surgical interventions, with emphasis on the importance of patient-specific approaches and outcomes. The document also references numerous studies highlighting the effectiveness of these therapies and surgical techniques in improving voice quality and function.