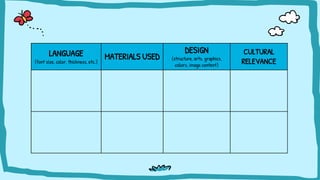
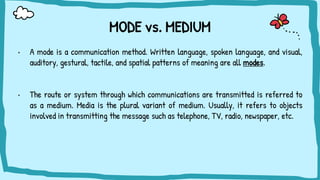
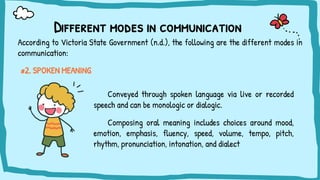
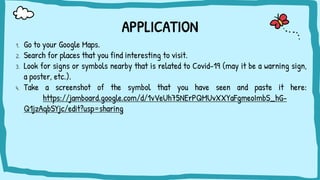
The document discusses multimodal texts, which convey meaning through integrating different modes such as written language, images, sounds, gestures, and spatial dimensions. It defines multimodal texts and different modes of communication, provides examples of multimodal texts in different formats, and describes an activity where students analyze COVID-19 signs and symbols posted on Google Maps to understand the information conveyed through visual and spatial modes.