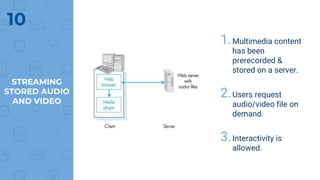
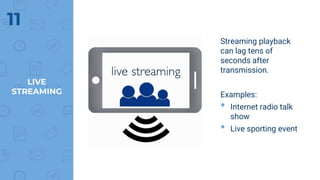
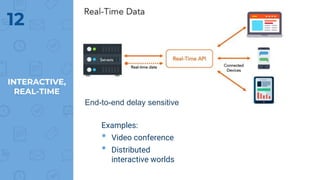
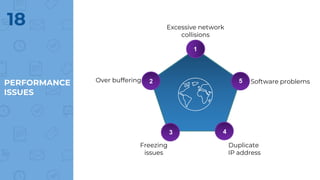
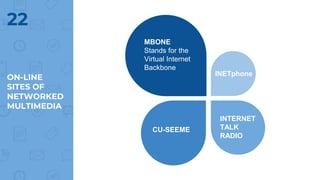
The document provides an outline of multimedia networking, explaining its definition, significance, applications, and the technical challenges involved. It details the tools required for multimedia applications, emphasizes the importance of real-time data transmission, and identifies performance issues related to multimedia systems. Finally, it lists desirable features for effective multimedia networking and online resources for further information.