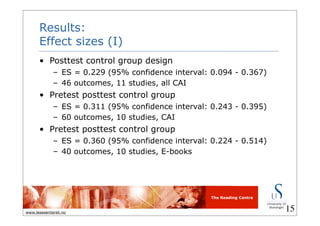
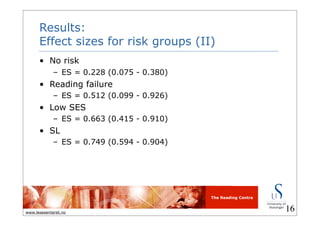
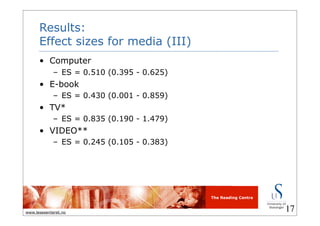
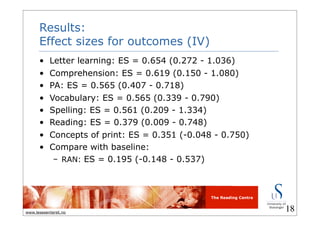
This document summarizes a meta-analysis on the effects of multimedia on early literacy development in children at risk. It found that multimedia had a small to moderate positive effect on literacy outcomes like letter learning, phonological awareness, and comprehension. Effects were larger for children from low-SES backgrounds, second language learners, and those at risk for reading failure. Computer applications and e-books had relatively large effects, while effects were greatest for letter learning, comprehension, and phonological awareness outcomes.