Recommended
PDF
PPT
4.3 derivative of exponential functions
PPT
4.3 derivatives of inv erse trig. functions
PPTX
Indeterminate forms and L'Hospital's Rule
PPT
PPTX
PPT
PPT
Indeterminate Forms and l’Hospital’s Rule
PPT
L'Hôpital's Rule for Indeterminate Limit
PDF
PDF
Differential Calculus Lecture on L'Hôpital's Rule
PPT
Chapter 4 Applications of Differentiation James Stewart
PPTX
Lesson 5 indeterminate forms
PDF
MAT221: CALCULUS II - Indeterminate Forms.pdf
PPTX
PDF
slides-2WBB0-class-10.pdf wowowowwowowow
PDF
Lesson 17: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hopital's Rule (Section 041 slides)
PDF
Lesson 17: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hôpital's Rule
PDF
Lesson 17: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hôpital's Rule
PPT
PPTX
PPTX
Differential_Calculus_Indeterminate_Forms_Presentation.pptx
PDF
Lesson 17: Indeterminate forms and l'Hôpital's Rule (handout)
PDF
Lesson 17: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hopital's Rule (Section 021 slides)
PPTX
PPT
PDF
Lesson 18: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hôpital's Rule
PDF
Lesson 18: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hôpital's Rule
PDF
22PEOIT4C Artificial Intelligence Unit 2 QB Final.pdf
PPTX
Module 2 of MU ML of Semester 5 with notes
More Related Content
PDF
PPT
4.3 derivative of exponential functions
PPT
4.3 derivatives of inv erse trig. functions
PPTX
Indeterminate forms and L'Hospital's Rule
PPT
PPTX
PPT
PPT
Indeterminate Forms and l’Hospital’s Rule
Similar to Multi variable calculus important steps to solveMA-123-8.pdf
PPT
L'Hôpital's Rule for Indeterminate Limit
PDF
PDF
Differential Calculus Lecture on L'Hôpital's Rule
PPT
Chapter 4 Applications of Differentiation James Stewart
PPTX
Lesson 5 indeterminate forms
PDF
MAT221: CALCULUS II - Indeterminate Forms.pdf
PPTX
PDF
slides-2WBB0-class-10.pdf wowowowwowowow
PDF
Lesson 17: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hopital's Rule (Section 041 slides)
PDF
Lesson 17: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hôpital's Rule
PDF
Lesson 17: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hôpital's Rule
PPT
PPTX
PPTX
Differential_Calculus_Indeterminate_Forms_Presentation.pptx
PDF
Lesson 17: Indeterminate forms and l'Hôpital's Rule (handout)
PDF
Lesson 17: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hopital's Rule (Section 021 slides)
PPTX
PPT
PDF
Lesson 18: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hôpital's Rule
PDF
Lesson 18: Indeterminate Forms and L'Hôpital's Rule
Recently uploaded
PDF
22PEOIT4C Artificial Intelligence Unit 2 QB Final.pdf
PPTX
Module 2 of MU ML of Semester 5 with notes
PPTX
Diagram of Control Valves used in Industrial Fluid Power.pptx
PDF
TU/e - 2025-2026 - Lecture Geotechnics 3 - Arkesteijn
PDF
1.39 inch Flexible Round AMOLED Display for Smartwatch
PPTX
TechSprint Intro Session GDGOC PUSSGRC
PPTX
Starter Generator Testing – Why It Is Critical for Aerospace & Defence Platforms
PPTX
RTOS_Automatic_Room_Light_Controller_ Exp.no.1.pptx
PPTX
Design and Development of Friction Stir Welding joints of Aluminium and Coppe...
PDF
TU/e - Lecture Geotechnics - Case Singelgrachtgarage-Marnix - Arkesteijn
PPTX
1.2-Structure of Ceramics_ Materials Science.pptx
PDF
Java Programming core java and basics concepts
PPTX
1.1 Structure of Materials_Material science.pptx
PPTX
Ion exchange or demineralization to soften water.pptx
PPTX
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) Numericals-2026.pptx
PPTX
Treatment strategies for vertical maxillary excess.pptx
PDF
22PEOIT4C Artificial Intelligence Unit II notes Final.pdf
PDF
Foundations of AI and ML - Mechanical Engineering Perspectives.pdf
PDF
Branches of AI – perception, reasoning, learning, and action.pdf
PPTX
uCOS_II_LED_Multitasking_Exp.no.2.pptx uCOS_II_LED_Multitasking_Exp.no.2.pptx
Multi variable calculus important steps to solveMA-123-8.pdf 1. Page 1 of 12
MA-123: Calculus
1st
Semester
Lecture -8
Dr. Muhammad Shabbir
Assistant Professor
University of Engineering and Technology
Lahore Pakistan
2. Page 2 of 12
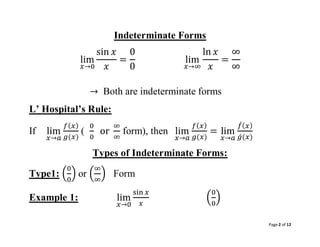
Indeterminate Forms
lim
𝑥→0
sin 𝑥
𝑥
=
0
0
lim
𝑥→∞
ln 𝑥
𝑥
=
∞
∞
→ Both are indeterminate forms
L’ Hospital’s Rule:
If lim
𝑥→𝑎
𝑓(𝑥)
𝑔(𝑥)
(
0
0
or
∞
∞
form), then lim
𝑥→𝑎
𝑓(𝑥)
𝑔(𝑥)
= lim
𝑥→𝑎
𝑓
́(𝑥)
𝑔́(𝑥)
Types of Indeterminate Forms:
Type1: (
0
0
) or (
∞
∞
) Form
Example 1: lim
𝑥→0
sin 𝑥
𝑥
(
0
0
)
3. Page 3 of 12
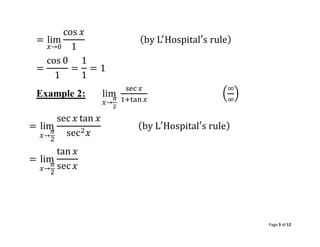
= lim
𝑥→0
cos 𝑥
1
(by L′
Hospital′s rule)
=
cos 0
1
=
1
1
= 1
Example 2: lim
𝑥→
𝜋
2
sec 𝑥
1+tan 𝑥
(
∞
∞
)
= lim
𝑥→
𝜋
2
sec 𝑥 tan 𝑥
sec2𝑥
(by L′Hospital′s rule)
= lim
𝑥→
𝜋
2
tan 𝑥
sec 𝑥
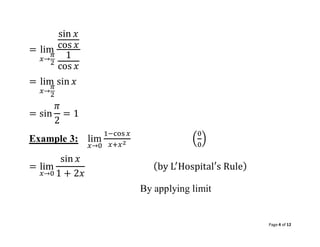
4. Page 4 of 12
= lim
𝑥→
𝜋
2
sin 𝑥
cos 𝑥
1
cos 𝑥
= lim
𝑥→
𝜋
2
sin 𝑥
= sin
𝜋
2
= 1
Example 3: lim
𝑥→0
1−cos 𝑥
𝑥+𝑥2
(
0
0
)
= lim
𝑥→0
sin 𝑥
1 + 2𝑥
(by L′
Hospital′s Rule)
By applying limit
5. Page 5 of 12
=
sin 0
1 + 2(0)
=
0
1
= 0
Note: L’ Hospital’s rule is only applicable in (
0
0
) or (
∞
∞
) forms.
Type 2: (∞ × 0) or (0 × ∞) Form
We convert Type 2 into Type 1 and then apply the L’ Hospital’s
rule
Example 4: lim
𝑥→∞
𝑥(𝑎
1
𝑥 − 1) (∞ × 0)
6. Page 6 of 12
= lim
𝑥→∞
((𝑎
1
𝑥
⁄ )−1)
1
𝑥
(
0
0
)
=
𝑎
1
𝑥
⁄
ln 𝑎 (−
1
𝑥2)
−
1
𝑥2
= 𝑎0
ln 𝑎=ln 𝑎
Type 3: (∞ − ∞) or (∞ + ∞) Form.
We convert Type 3 into Type 1 and then apply the L’ Hospital’s
rule.
Example 5: lim
𝑥→0
[
1
𝑥
− cot 𝑥] (∞ − ∞)
7. Page 7 of 12
= lim
𝑥→0
[
1
𝑥
−
cos 𝑥
sin 𝑥
]
= lim
𝑥→0
[
sin 𝑥 − 𝑥 cos 𝑥
𝑥 sin 𝑥
] (
0
0
)
= lim
𝑥→0
[
cos 𝑥 − (−𝑥 sin 𝑥 + cos 𝑥)
𝑥 cos 𝑥 + sin 𝑥
] (by L′
Hospital′s rule)
= lim
𝑥→0
[
𝑥 sin 𝑥
𝑥 cos 𝑥 + sin 𝑥
] (
0
0
)
= lim
𝑥→0
[
𝑥 cos 𝑥 + sin 𝑥
2 cos 𝑥 − 𝑥sin 𝑥
] (by L′Hospital rule)
By applying limit
=
0 × cos 0 + sin 0
2 cos 0 − sin 0
8. Page 8 of 12
=
0
2
= 0
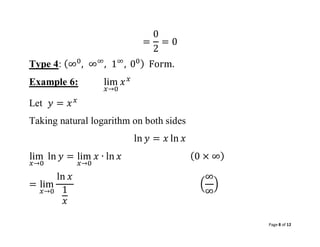
Type 4: (∞0
, ∞∞
, 1∞
, 00) Form.
Example 6: lim
𝑥→0
𝑥𝑥
Let 𝑦 = 𝑥𝑥
Taking natural logarithm on both sides
ln 𝑦 = 𝑥 ln 𝑥
lim
𝑥→0
ln 𝑦 = lim
𝑥→0
𝑥 ∙ ln 𝑥 (0 × ∞)
= lim
𝑥→0
ln 𝑥
1
𝑥
(
∞
∞
)
9. Page 9 of 12
= lim
𝑥→0
1
𝑥
−
1
𝑥2
(by L′Hospital rule)
= lim
𝑥→0
−𝑥
lim
𝑥→0
ln 𝑦 = 0
ln [lim
𝑥→0
𝑦] = 0
lim
𝑥→0
𝑦 = 𝑒0
lim
𝑥→0
𝑥𝑥
= 1
Example 7: lim
𝑥→0
(1 + 𝑥)
1
𝑥
⁄
(1∞)
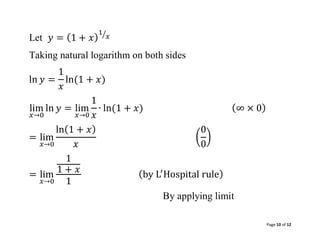
10. Page 10 of 12
Let 𝑦 = (1 + 𝑥)
1
𝑥
⁄
Taking natural logarithm on both sides
ln 𝑦 =
1
𝑥
ln(1 + 𝑥)
lim
𝑥→0
ln 𝑦 = lim
𝑥→0
1
𝑥
∙ ln(1 + 𝑥) (∞ × 0)
= lim
𝑥→0
ln(1 + 𝑥)
𝑥
(
0
0
)
= lim
𝑥→0
1
1 + 𝑥
1
(by L′
Hospital rule)
By applying limit
11. Page 11 of 12
=
1
1 + 0
1
= 1
lim
𝑥→0
ln 𝑦 = 1 => ln [lim
𝑥→0
𝑦] = 1 => (lim
𝑥→0
𝑦 = 𝑒1
)
lim
𝑥→0
(1 + 𝑥)1/𝑥
= 𝑒
Example 8: lim
𝑥→0
𝑒𝑥−𝑒sin𝑥
𝑥−sin 𝑥
(
0
0
)
= lim
𝑥→0
(1 + 𝑥 +
𝑥2
2!
+
𝑥3
3!
+ ⋯ ) − (1 + 𝑥 +
𝑥2
2!
−
𝑥4
8!
+ ⋯ )
𝑥 − (𝑥 −
𝑥3
3! +
𝑥5
5!
+ ⋯ )
12. Page 12 of 12
= lim
𝑥→0
(1 +
𝑥2
2!
+
𝑥3
3!
− 1 − 𝑥 −
𝑥2
2!
+
𝑥4
8!
+ ⋯ )
𝑥 − 𝑥 +
𝑥3
3!
−
𝑥5
5!
+ ⋯
‘x’ is very small so neglect 4th
and higher power of ‘x’.
= lim
𝑥→0
𝑥3
3!
⁄
𝑥3
3!
⁄
= 1
Exercise 7.5
Q (7-66) (Odd)


![Page 6 of 12
= lim
𝑥→∞
((𝑎
1
𝑥
⁄ )−1)
1
𝑥
(
0
0
)
=
𝑎
1
𝑥
⁄
ln 𝑎 (−
1
𝑥2)
−
1
𝑥2
= 𝑎0
ln 𝑎=ln 𝑎
Type 3: (∞ − ∞) or (∞ + ∞) Form.
We convert Type 3 into Type 1 and then apply the L’ Hospital’s
rule.
Example 5: lim
𝑥→0
[
1
𝑥
− cot 𝑥] (∞ − ∞)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ma-123-lec-8-250319140617-4c99c3ca/85/Multi-variable-calculus-important-steps-to-solveMA-123-8-pdf-6-320.jpg)
![Page 7 of 12
= lim
𝑥→0
[
1
𝑥
−
cos 𝑥
sin 𝑥
]
= lim
𝑥→0
[
sin 𝑥 − 𝑥 cos 𝑥
𝑥 sin 𝑥
] (
0
0
)
= lim
𝑥→0
[
cos 𝑥 − (−𝑥 sin 𝑥 + cos 𝑥)
𝑥 cos 𝑥 + sin 𝑥
] (by L′
Hospital′s rule)
= lim
𝑥→0
[
𝑥 sin 𝑥
𝑥 cos 𝑥 + sin 𝑥
] (
0
0
)
= lim
𝑥→0
[
𝑥 cos 𝑥 + sin 𝑥
2 cos 𝑥 − 𝑥sin 𝑥
] (by L′Hospital rule)
By applying limit
=
0 × cos 0 + sin 0
2 cos 0 − sin 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ma-123-lec-8-250319140617-4c99c3ca/85/Multi-variable-calculus-important-steps-to-solveMA-123-8-pdf-7-320.jpg)
![Page 9 of 12
= lim
𝑥→0
1
𝑥
−
1
𝑥2
(by L′Hospital rule)
= lim
𝑥→0
−𝑥
lim
𝑥→0
ln 𝑦 = 0
ln [lim
𝑥→0
𝑦] = 0
lim
𝑥→0
𝑦 = 𝑒0
lim
𝑥→0
𝑥𝑥
= 1
Example 7: lim
𝑥→0
(1 + 𝑥)
1
𝑥
⁄
(1∞)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ma-123-lec-8-250319140617-4c99c3ca/85/Multi-variable-calculus-important-steps-to-solveMA-123-8-pdf-9-320.jpg)
![Page 11 of 12
=
1
1 + 0
1
= 1
lim
𝑥→0
ln 𝑦 = 1 => ln [lim
𝑥→0
𝑦] = 1 => (lim
𝑥→0
𝑦 = 𝑒1
)
lim
𝑥→0
(1 + 𝑥)1/𝑥
= 𝑒
Example 8: lim
𝑥→0
𝑒𝑥−𝑒sin𝑥
𝑥−sin 𝑥
(
0
0
)
= lim
𝑥→0
(1 + 𝑥 +
𝑥2
2!
+
𝑥3
3!
+ ⋯ ) − (1 + 𝑥 +
𝑥2
2!
−
𝑥4
8!
+ ⋯ )
𝑥 − (𝑥 −
𝑥3
3! +
𝑥5
5!
+ ⋯ )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ma-123-lec-8-250319140617-4c99c3ca/85/Multi-variable-calculus-important-steps-to-solveMA-123-8-pdf-11-320.jpg)
