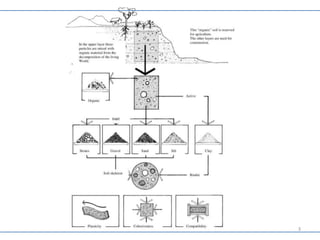
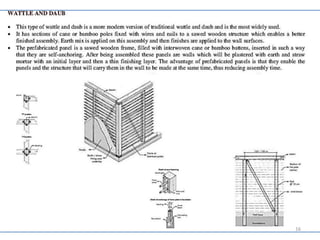
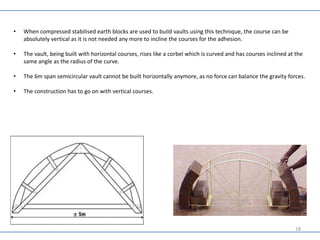
This document provides information on various mud construction techniques, including soil testing methods, stabilization techniques, and specific roofing methods like the Guna vault roof and Nubian dome. Some key points:
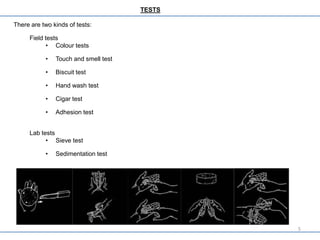
- Various field and lab tests are described to determine the composition and properties of soils for construction, including color, texture, biscuit, and sieve tests.
- Stabilization techniques can improve soil properties by adding materials like cement, straw or plant juices.
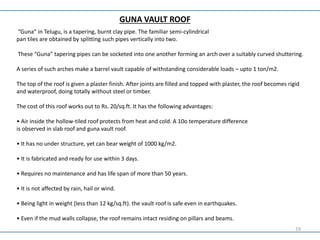
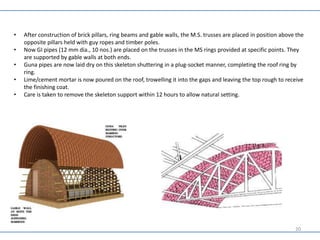
- The Guna vault roof is made from tapered burnt clay pipes socketed together in arches to form a strong, lightweight roof.
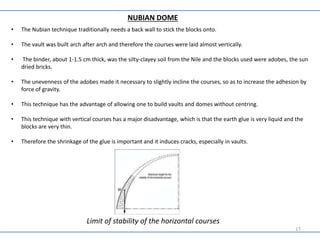
- The Nubian dome technique builds vaults and domes without centering by laying courses almost