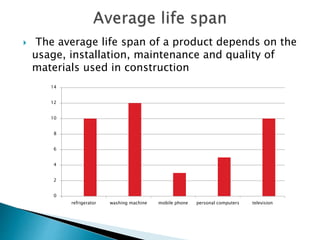
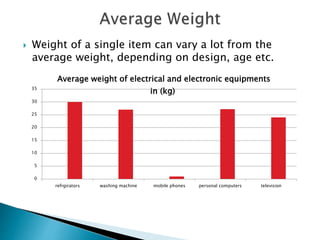
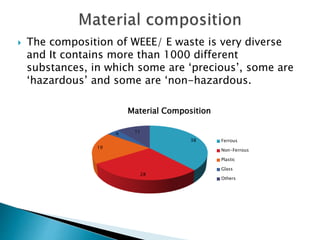
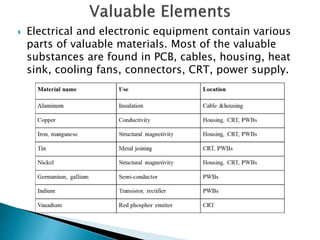
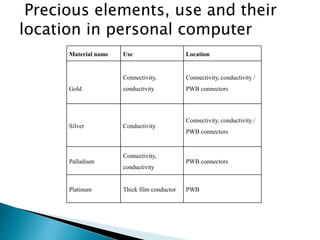
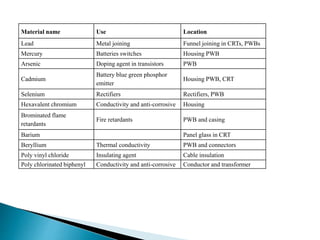
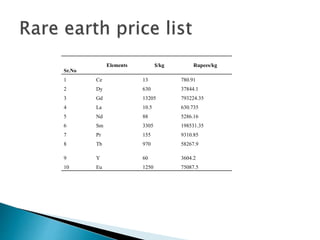
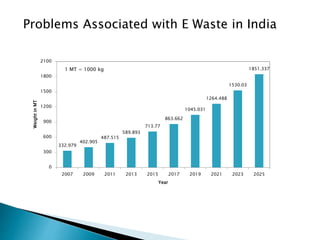
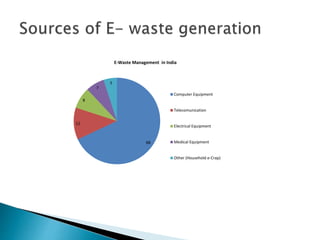
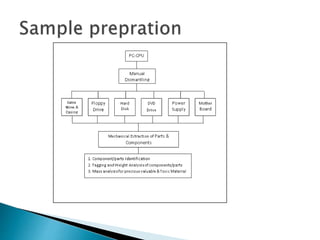
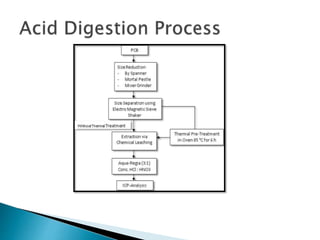
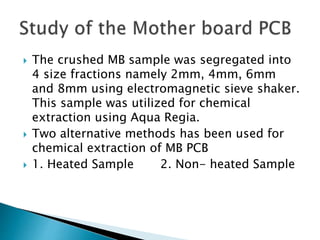
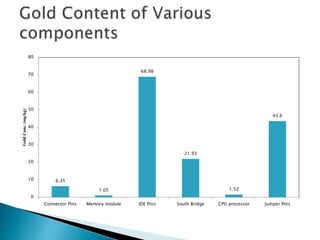
The document discusses a study to analyze the composition of e-waste and extract valuable materials. It found that e-waste contains valuable, precious and toxic materials. The study analyzed different e-waste components to determine their material composition and gold content. It investigated the effect of particle size reduction and heating on copper extraction from printed circuit boards. Finer particle sizes and heating improved extraction efficiency. Certain components like IDE pins and jumper pins had higher concentrations of gold. The study aims to optimize recovery of materials from e-waste.