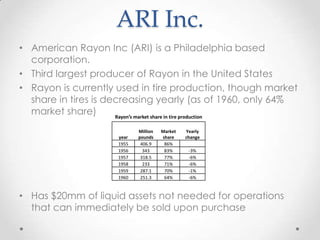
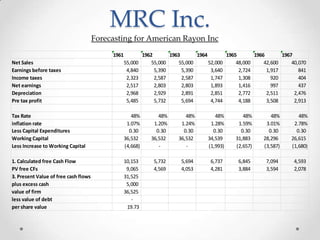
1) MRC is considering acquiring ARI for $40 million to gain $20 million in liquid assets and diversify, but ARI's rayon business is declining rapidly in the tire market.
2) While the acquisition appears financially attractive in the short-term, it does not align with MRC's long-term strategy and ARI's management style differs significantly from MRC's decentralized model.
3) Integrating the two companies would be difficult and rayon is a dying business, so the acquisition does not make strategic sense despite initial positive cash flows.