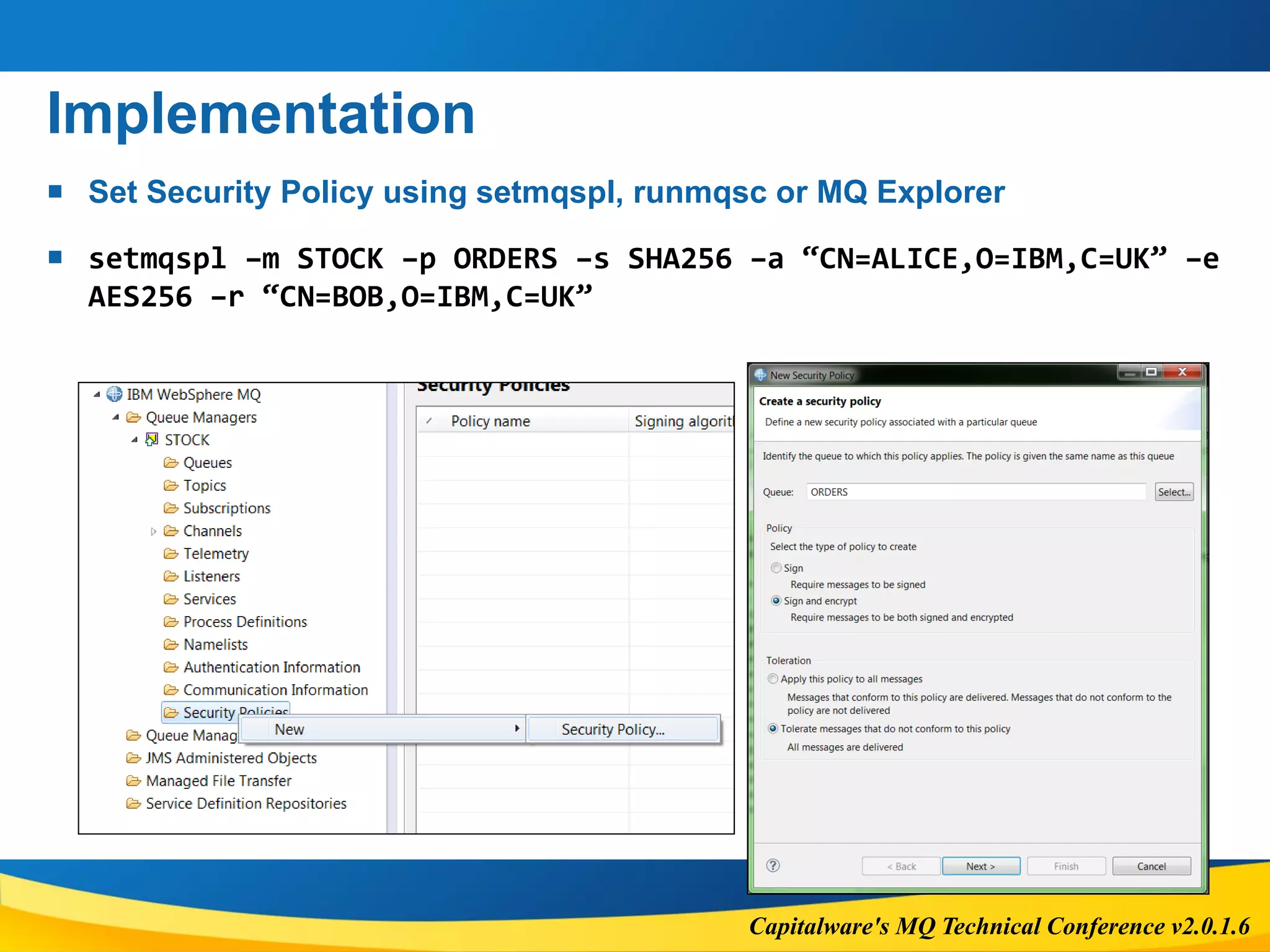
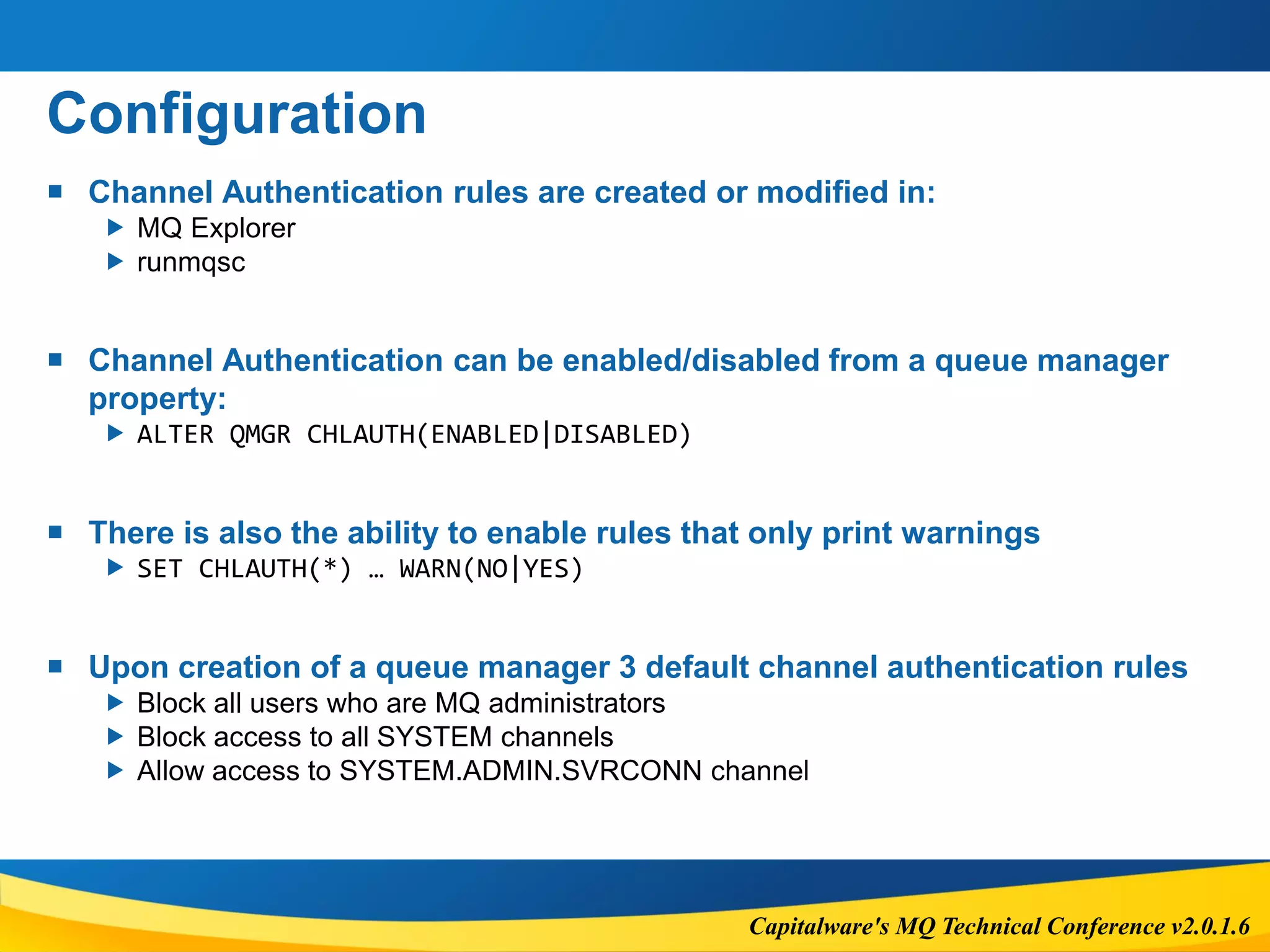
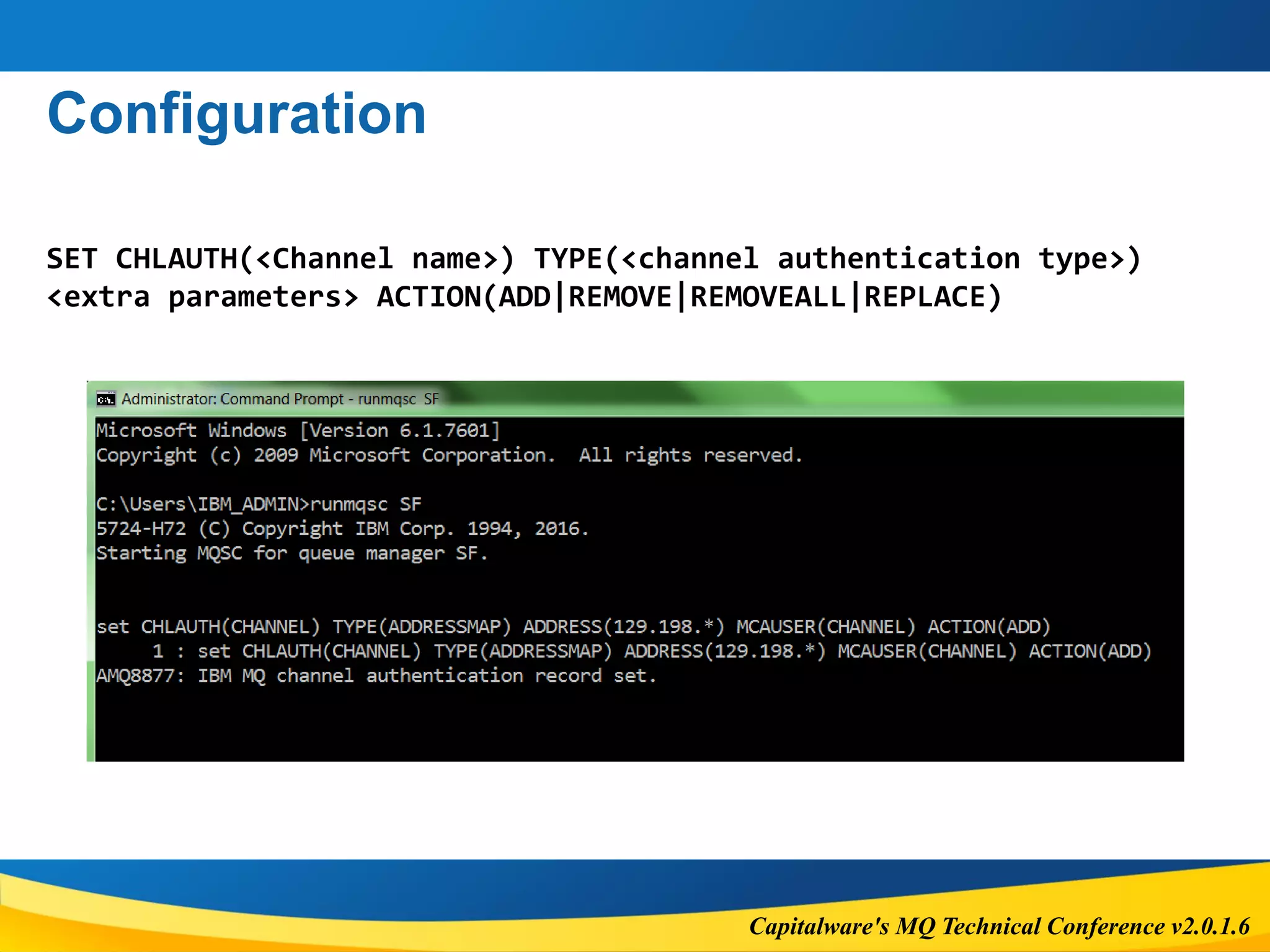
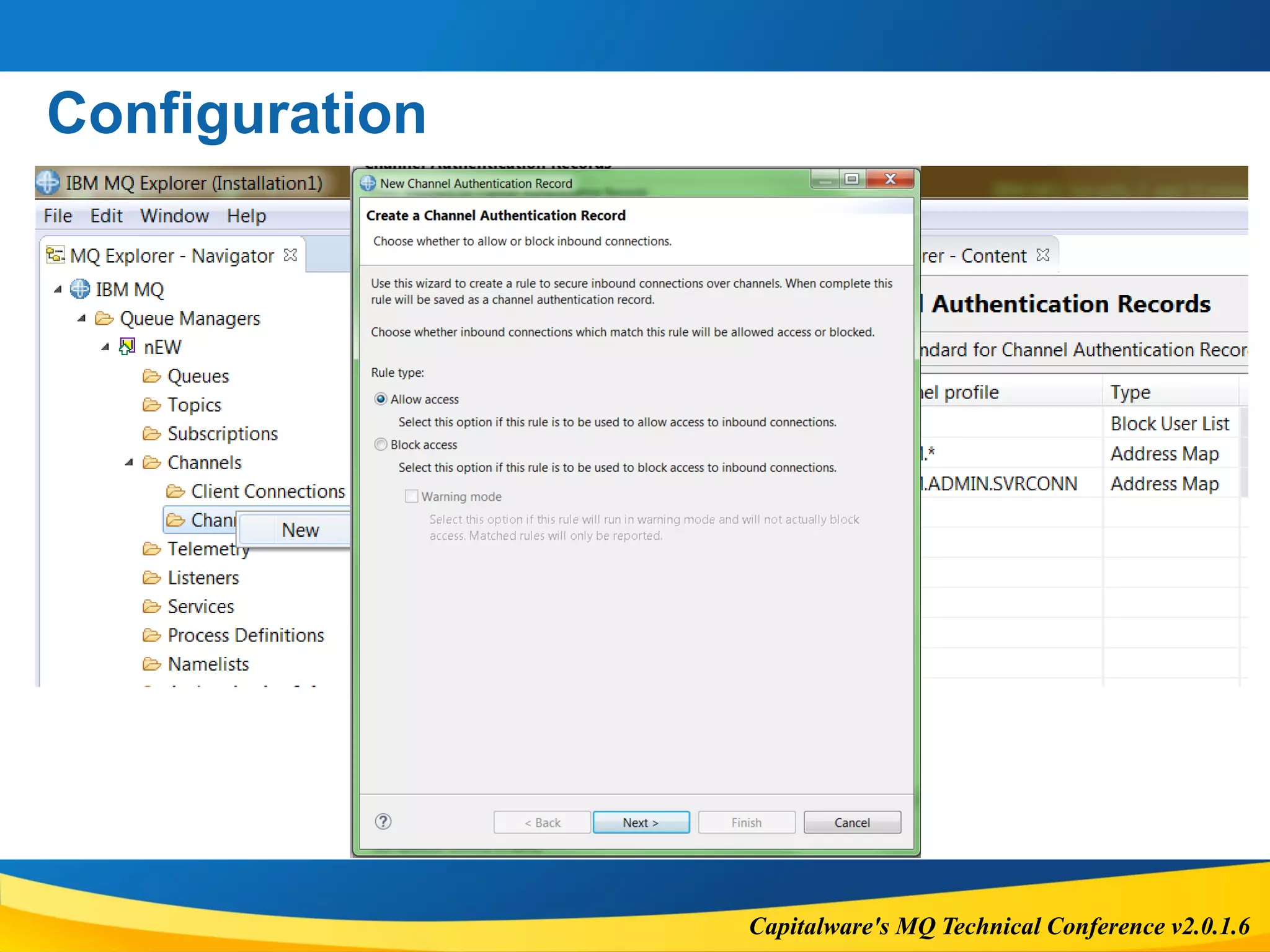
The document outlines the features and considerations of IBM MQ's Advanced Message Security (AMS) and channel authentication, providing technical details on message protection and security policies. It discusses the performance implications, supported options, potential errors, and configuration steps necessary for implementing these security measures. Additionally, it highlights the significance of authentication and authorization in managing user access and secure communications within the MQ environment.




![Capitalware's MQ Technical Conference v2.0.1.6
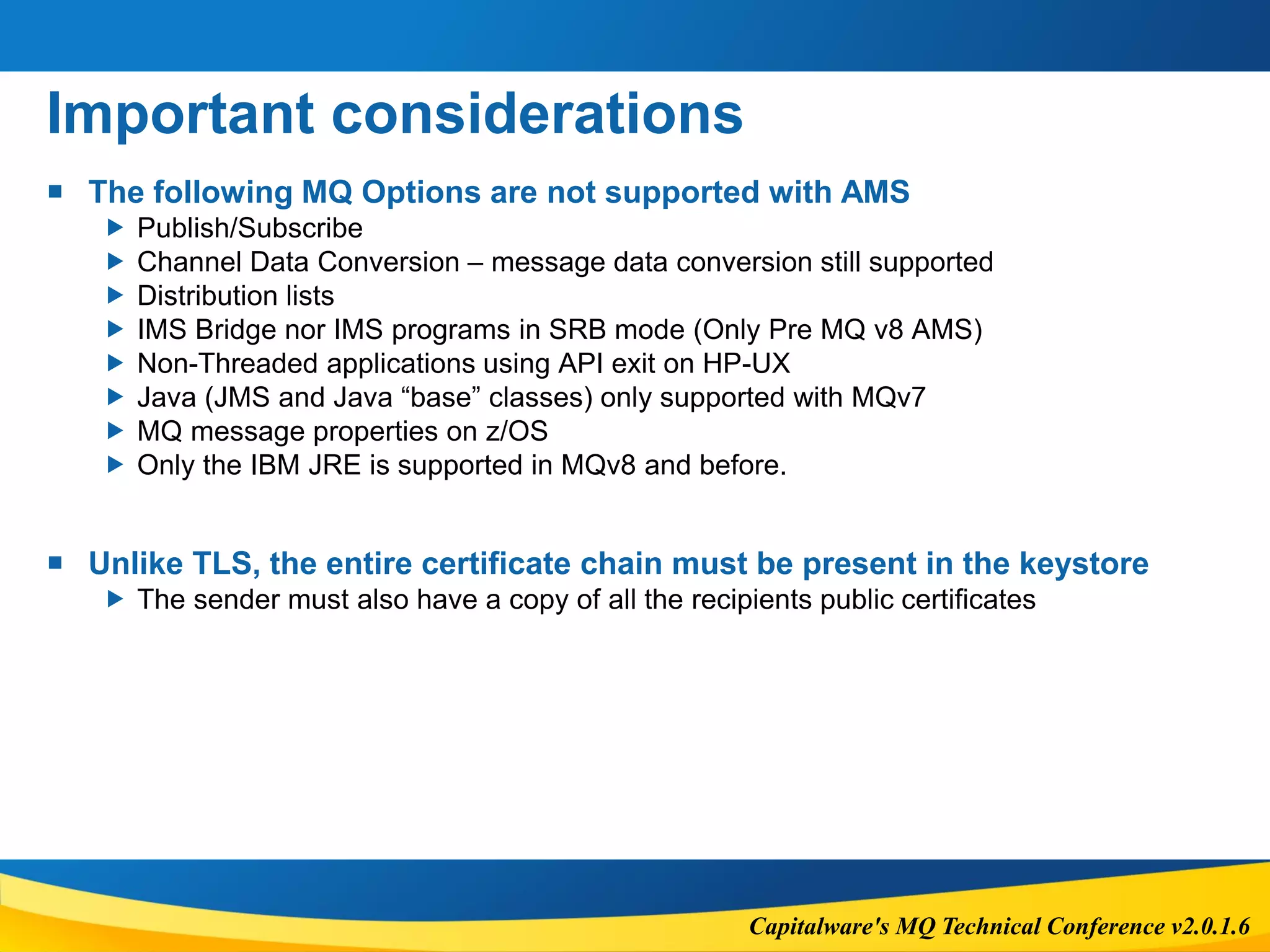
Important considerations
Performance
Increase in CPU requirements (but in relation to MQ CPU requirements)
Cryptographic operations cause a decrease of message throughput
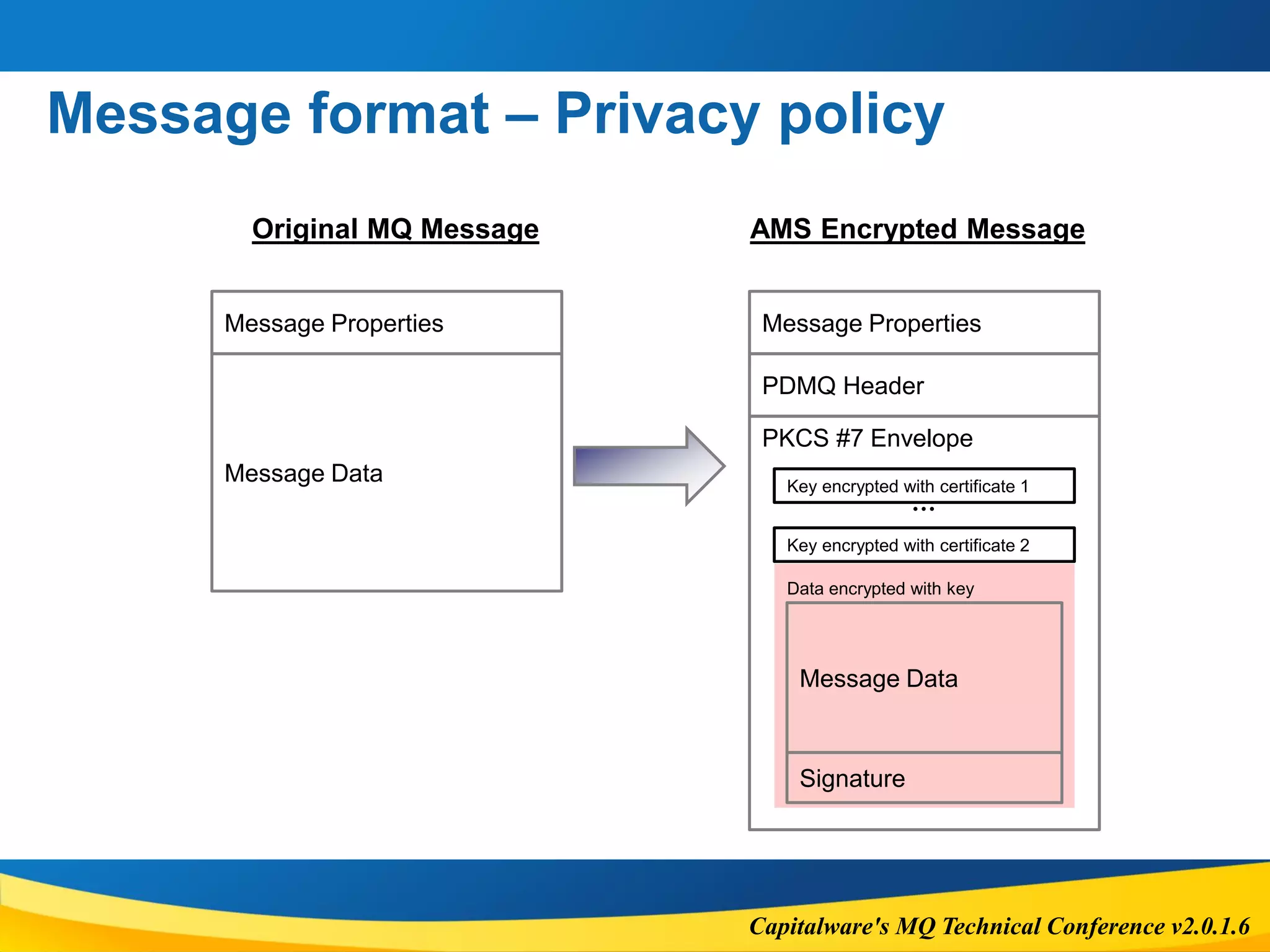
Impact depends on protection level (Integrity, Confidentiality, privacy)
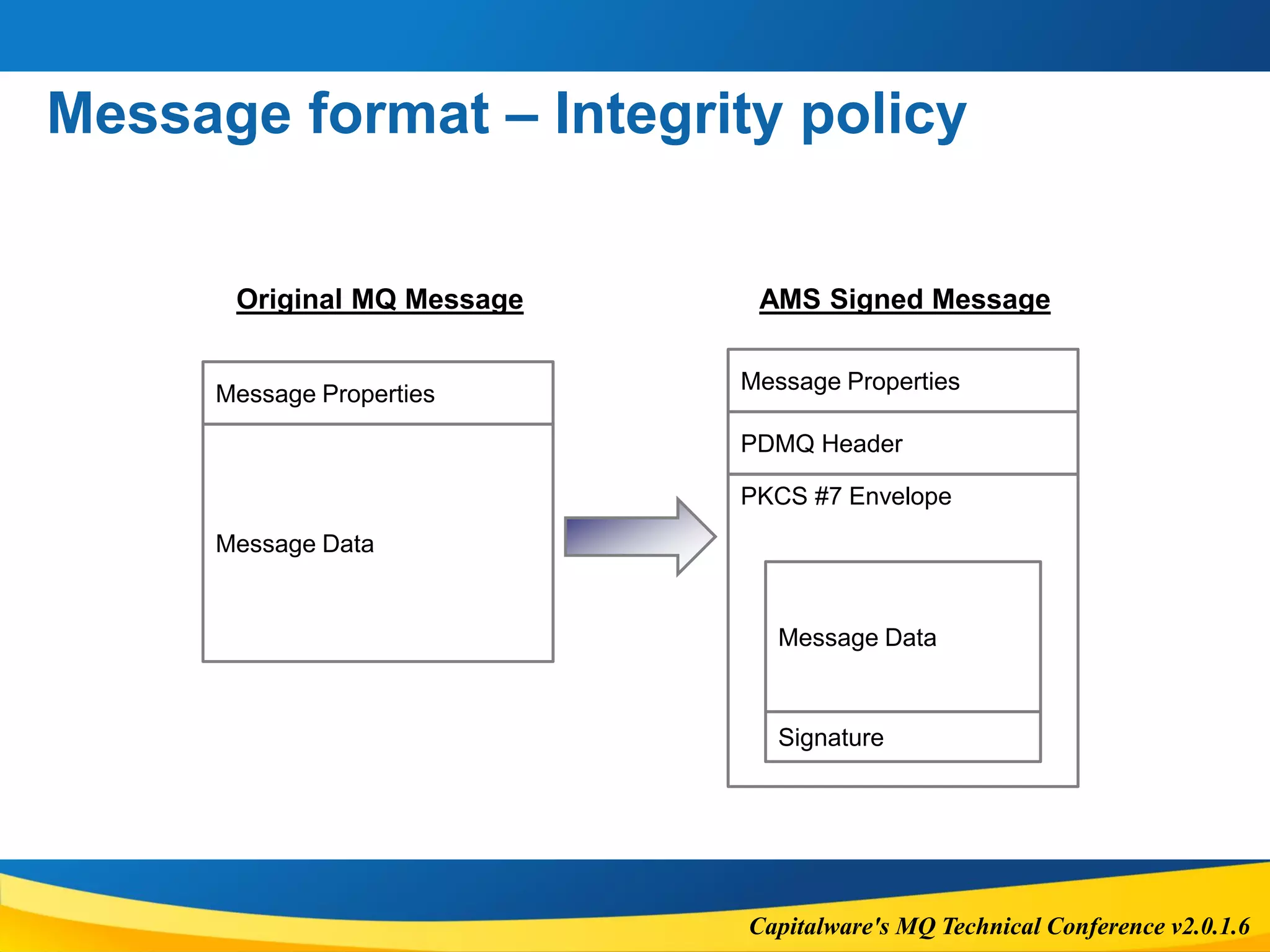
Message size
To accommodate AMS properties, overall message size will increase.
New message size = 1280 + [Old Message Length] + (200 x [# of recipients])
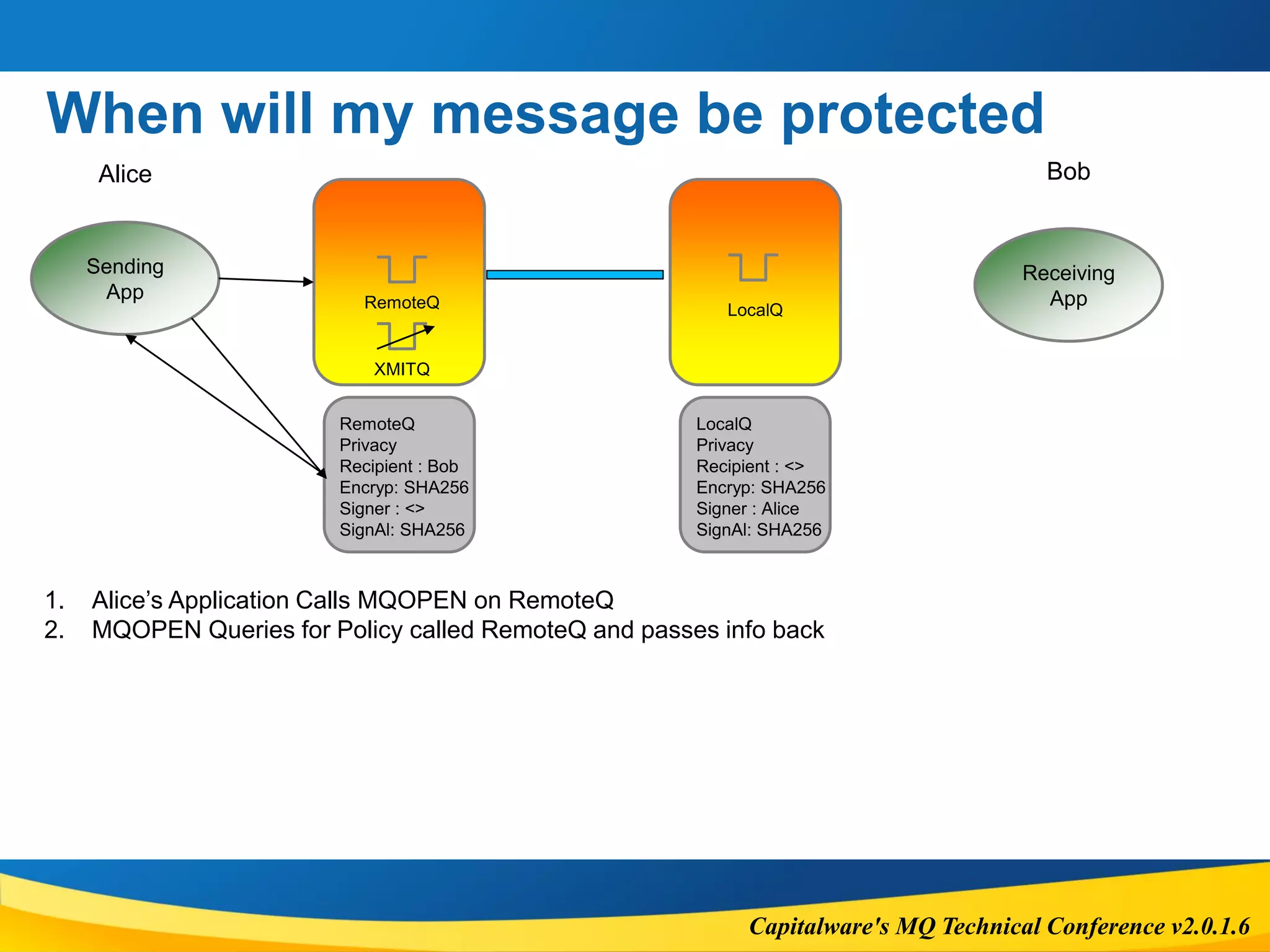
AMS does not perform access control
It just protects the message contents from change and/or reading](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ibmmqsecuritydeepdiveincludingams-161010144102/75/MQTC-2016-IBM-MQ-Security-deep-dive-including-AMS-6-2048.jpg)