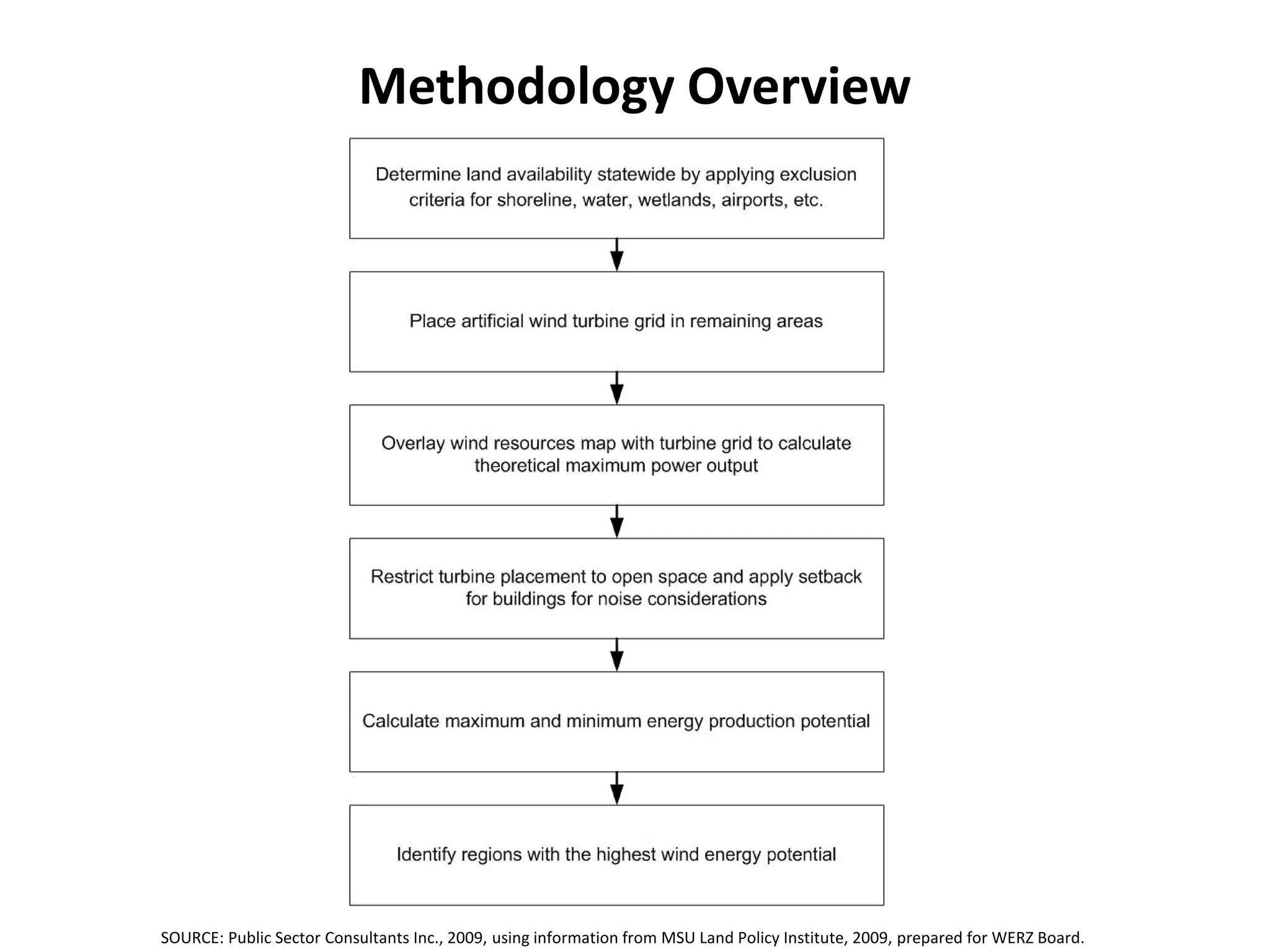
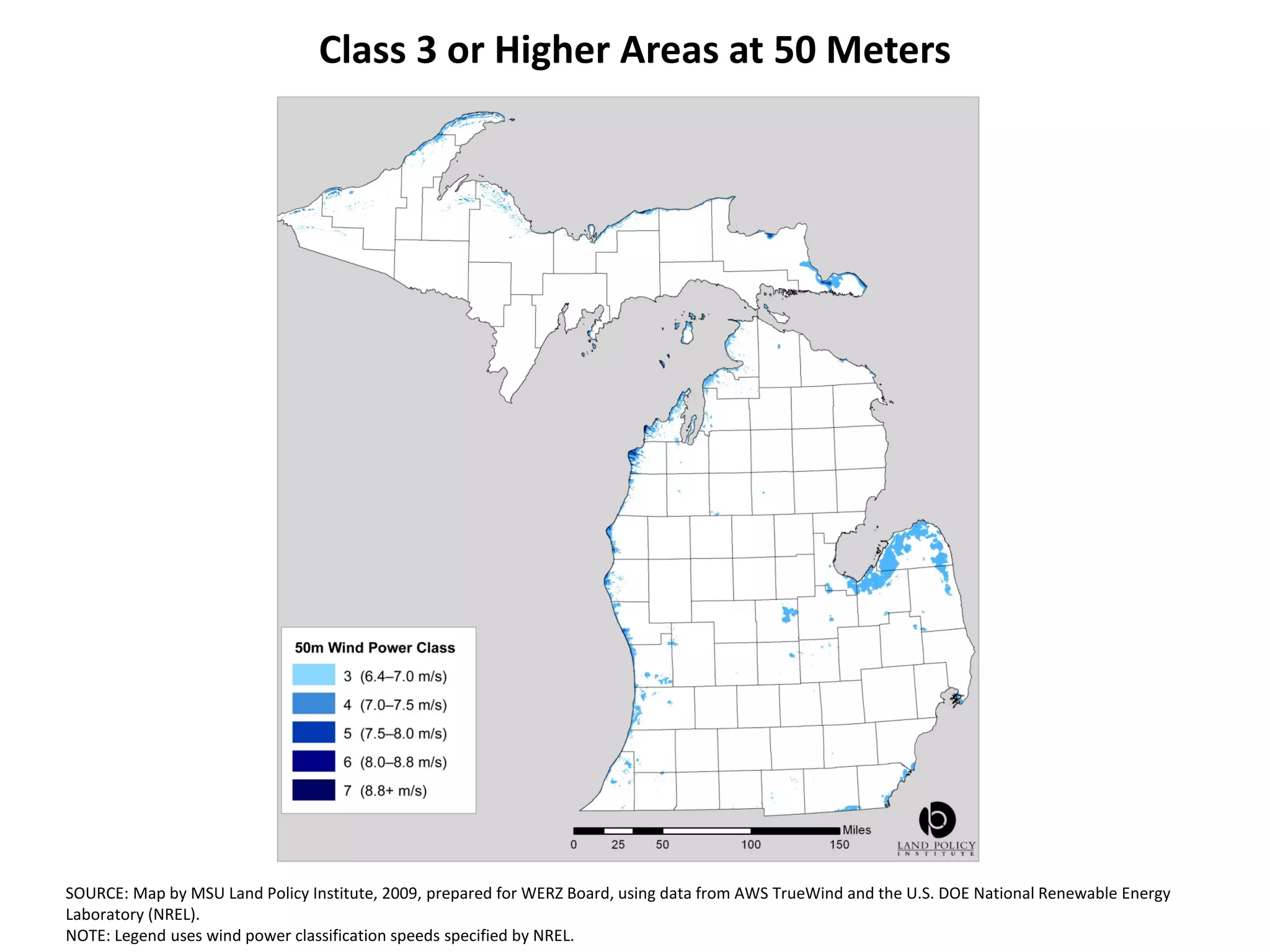
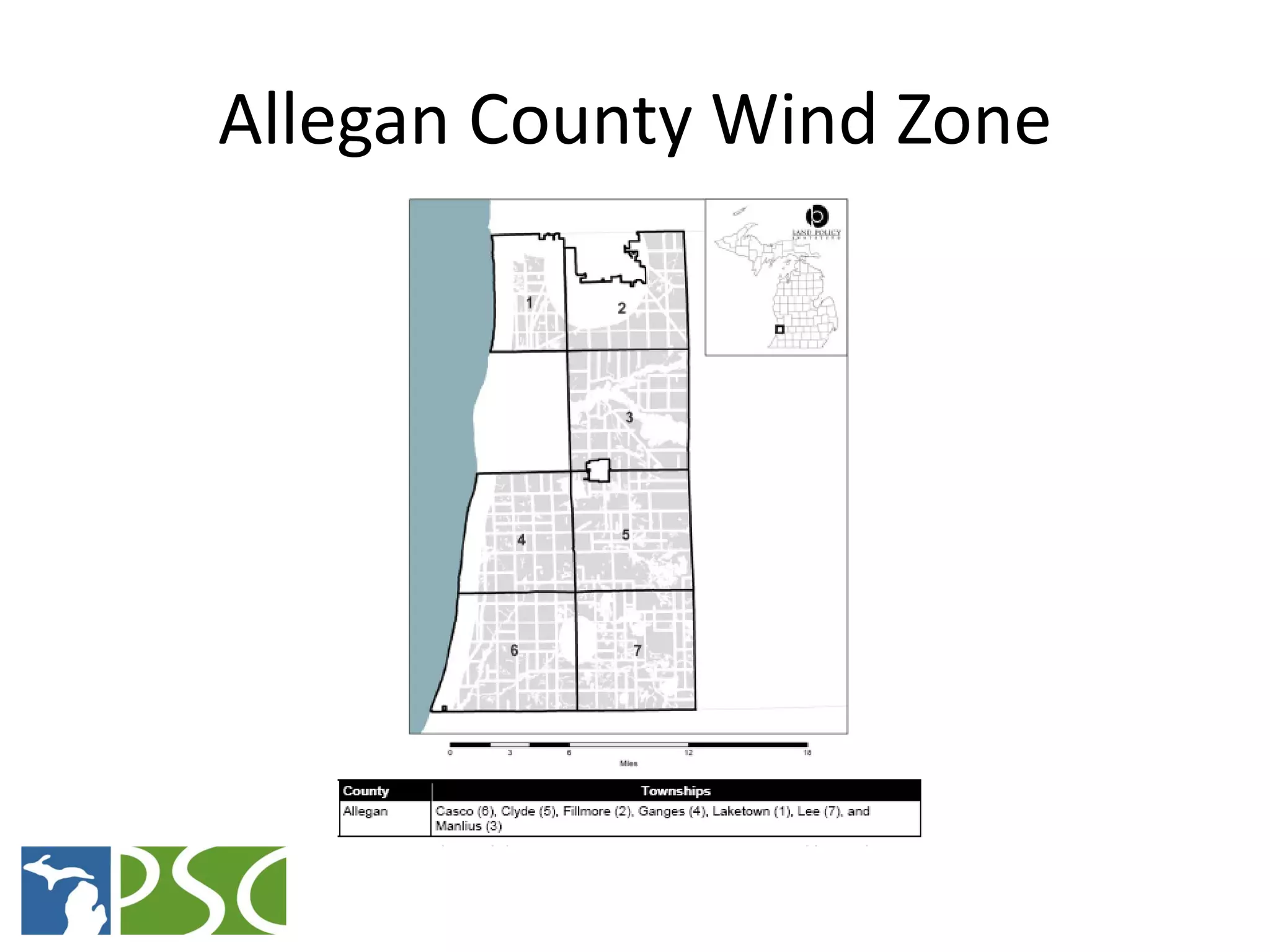
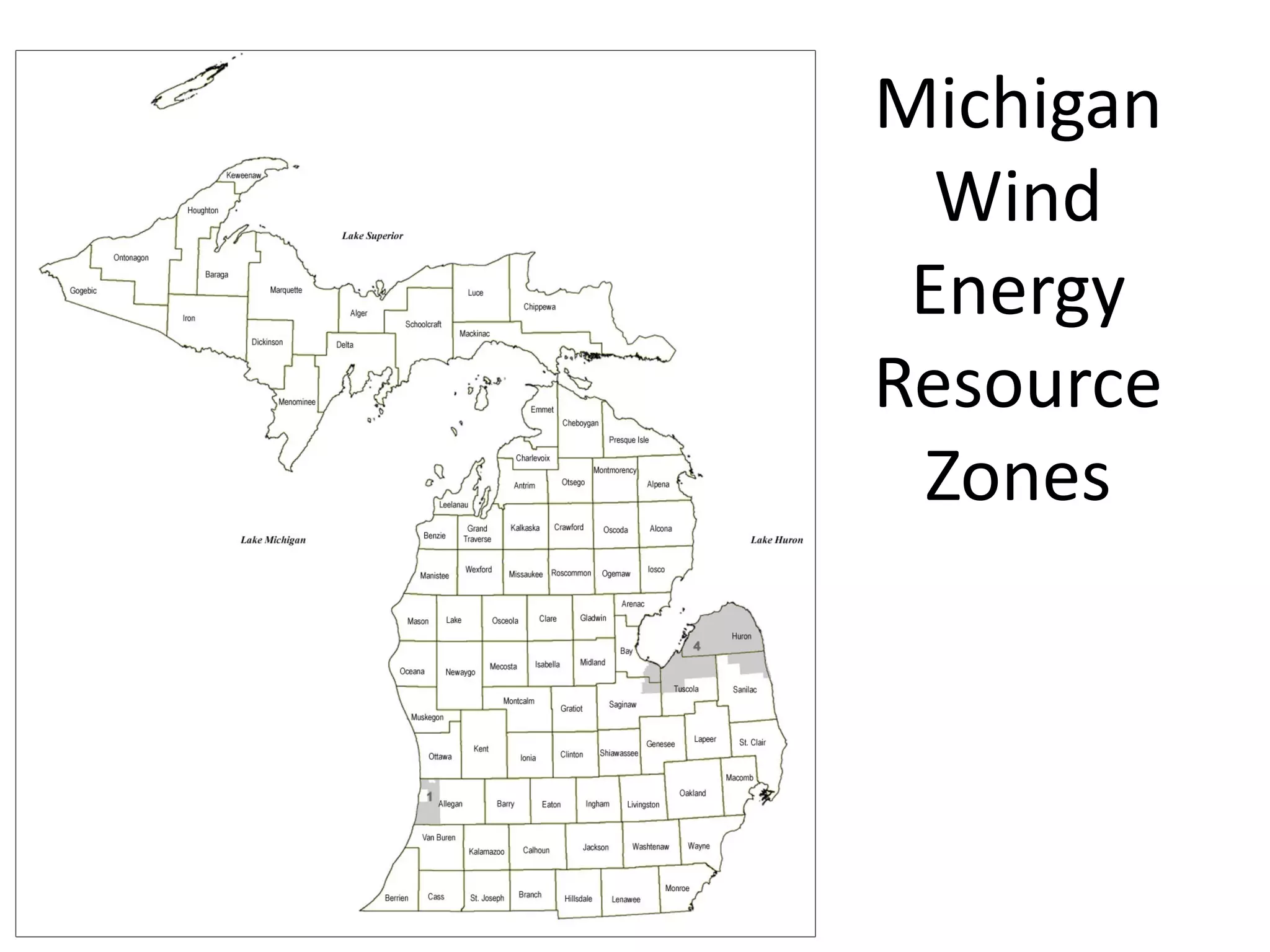
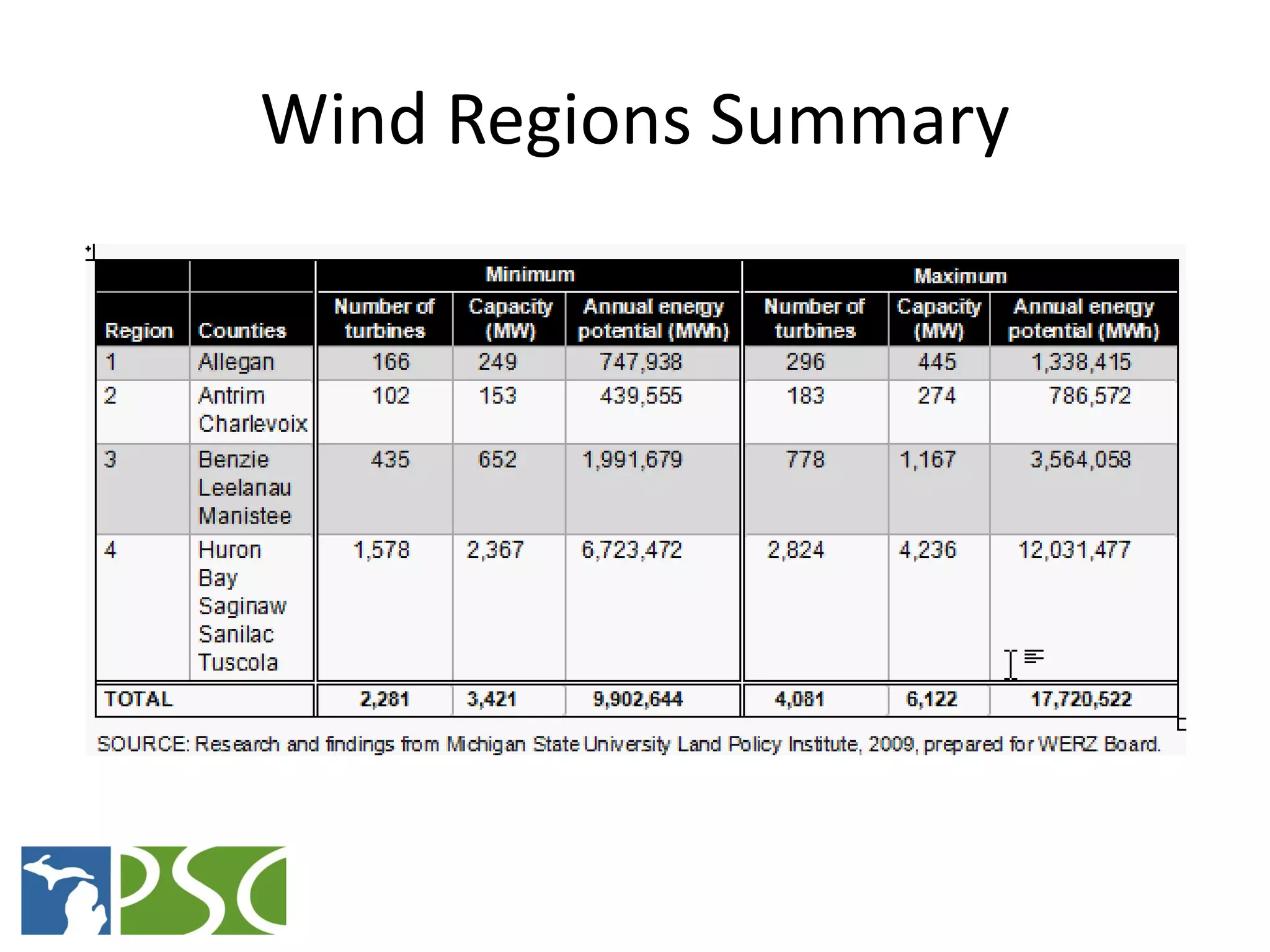
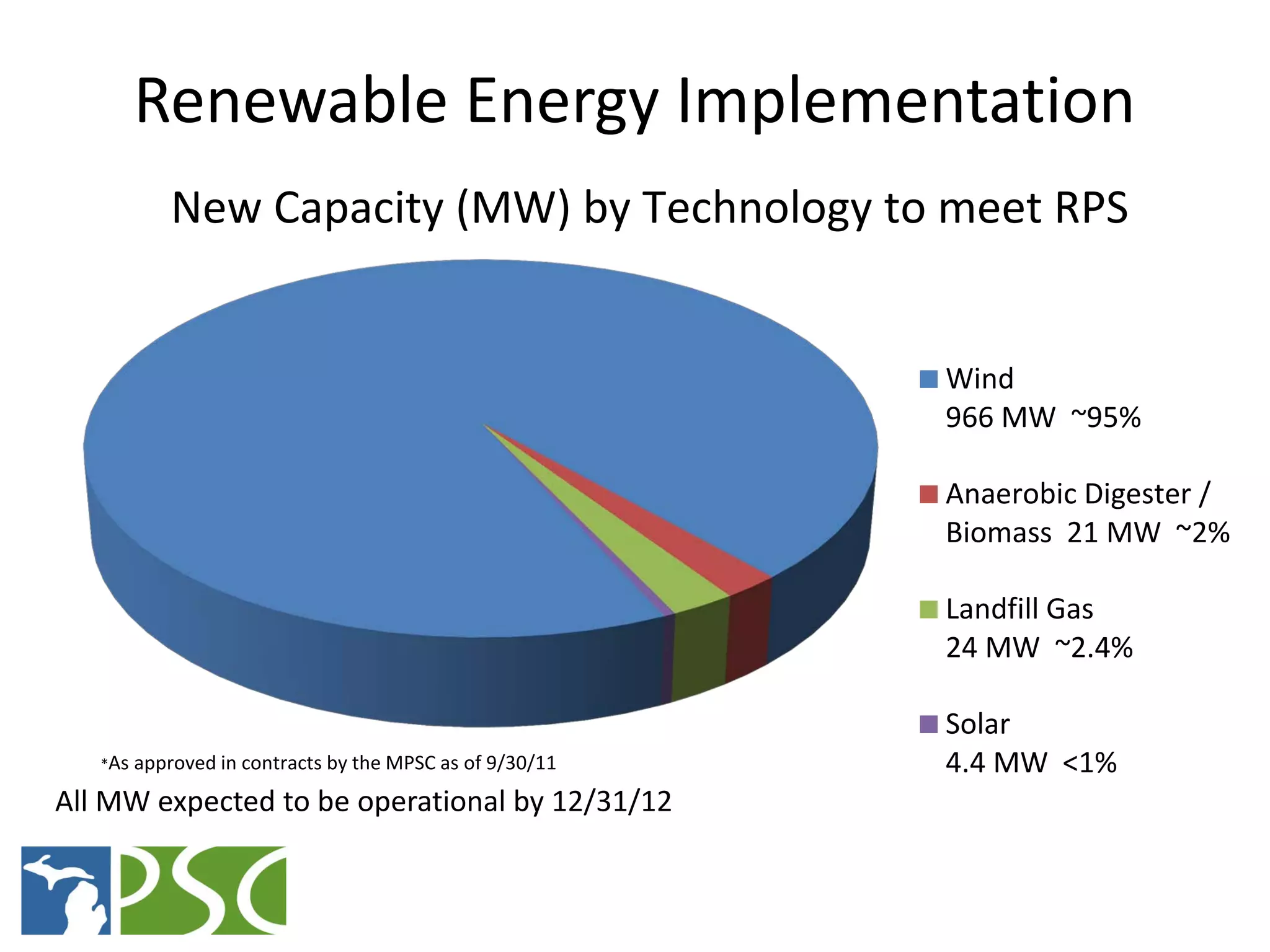
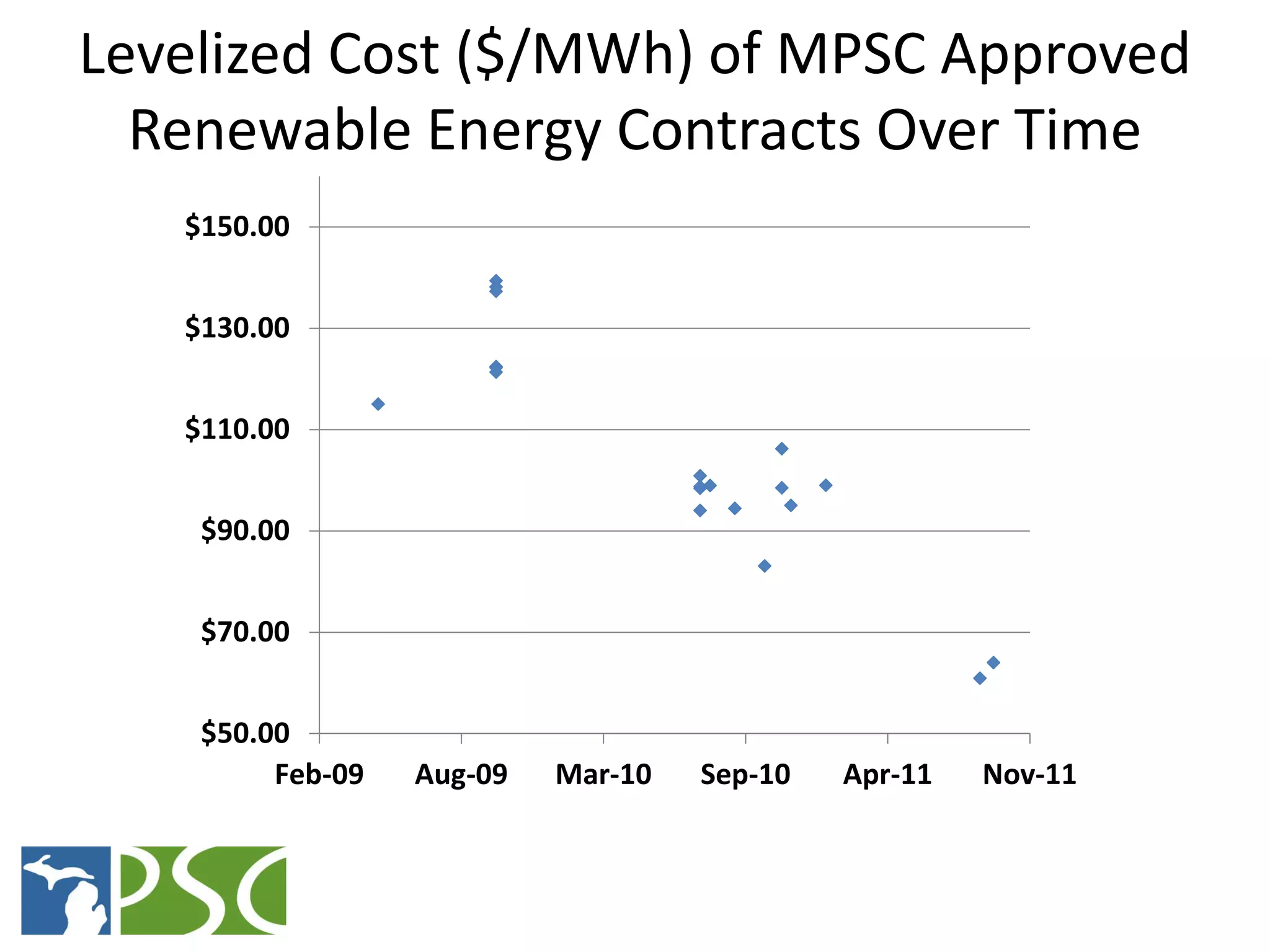
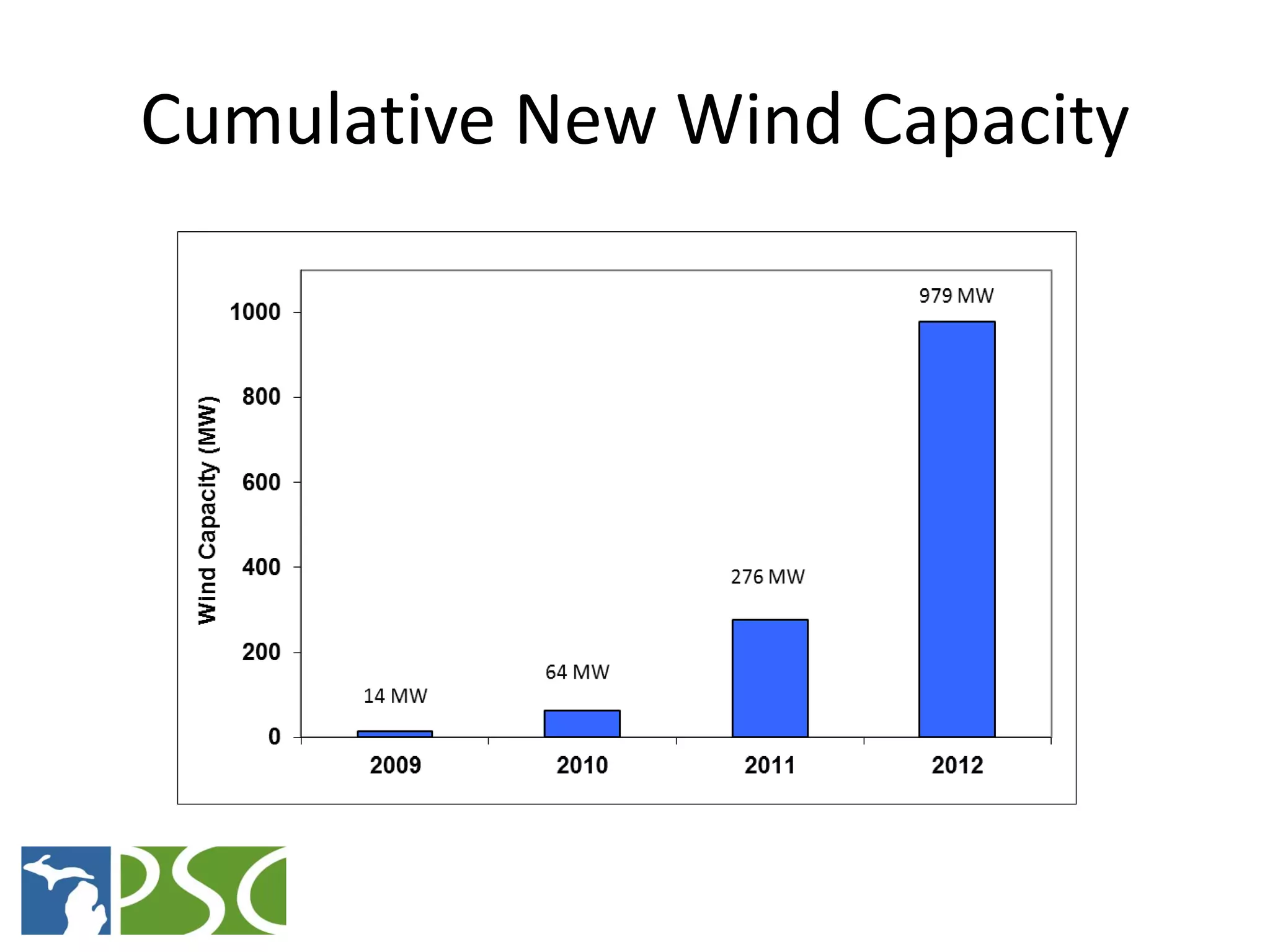
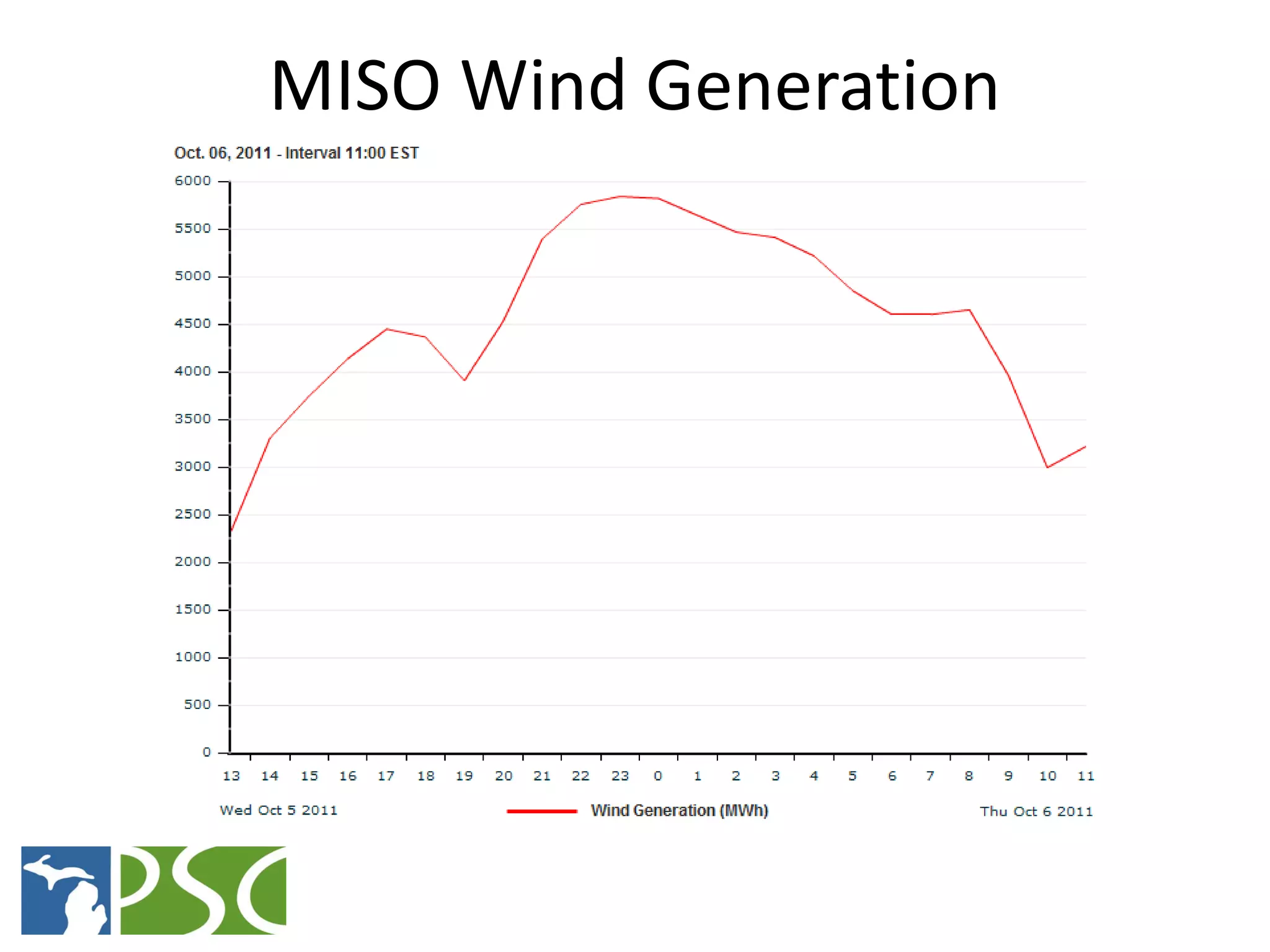
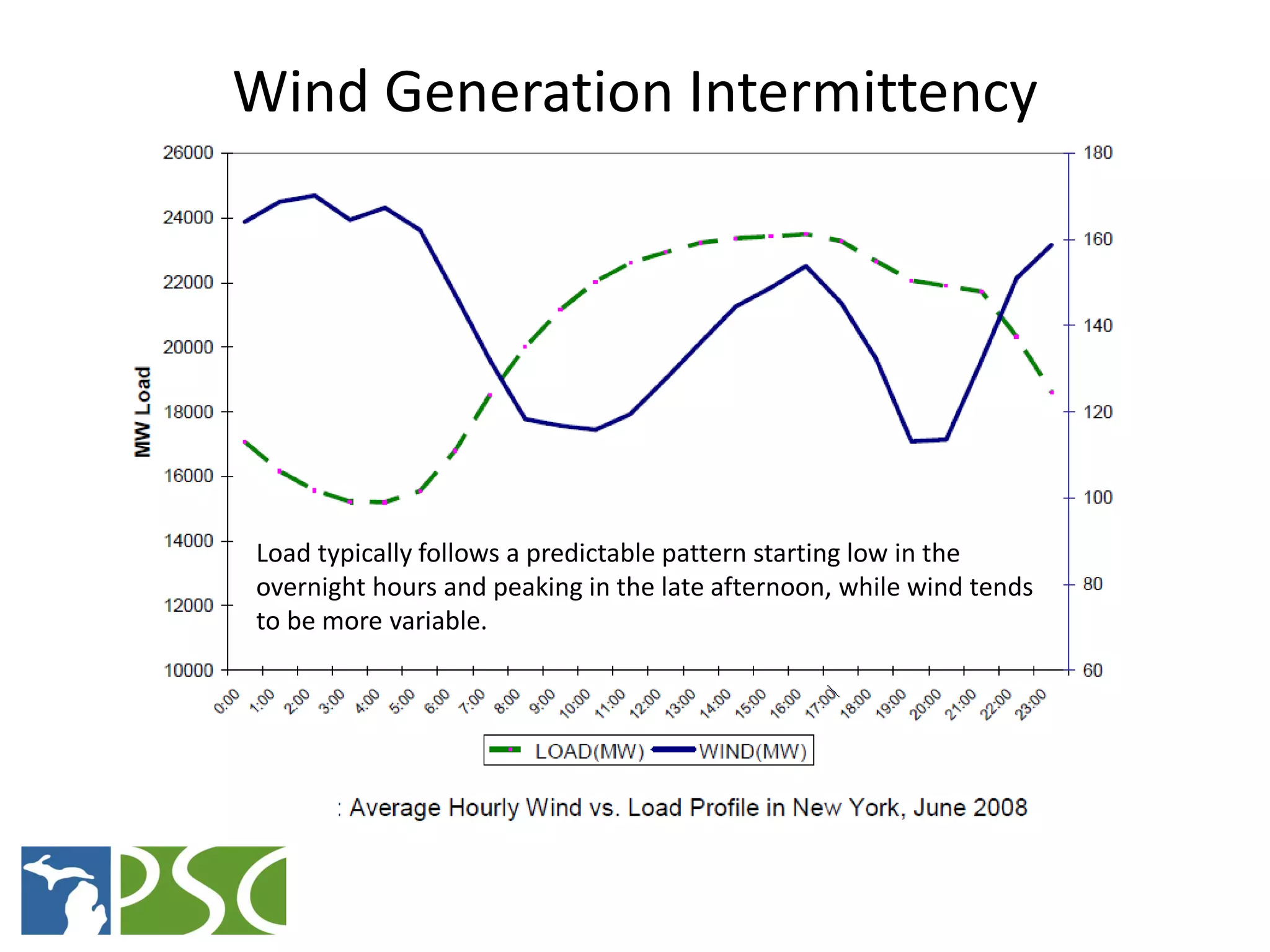
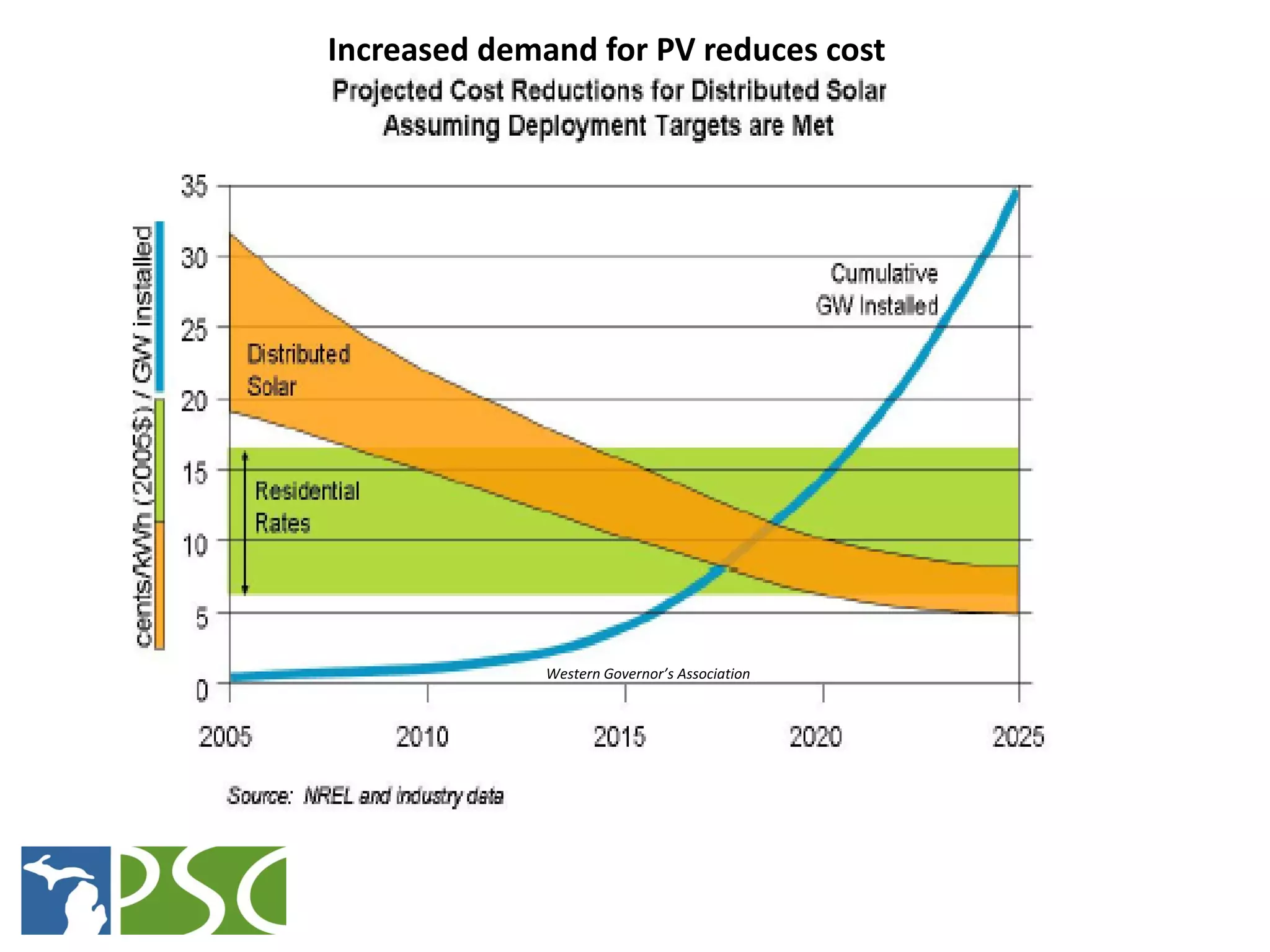
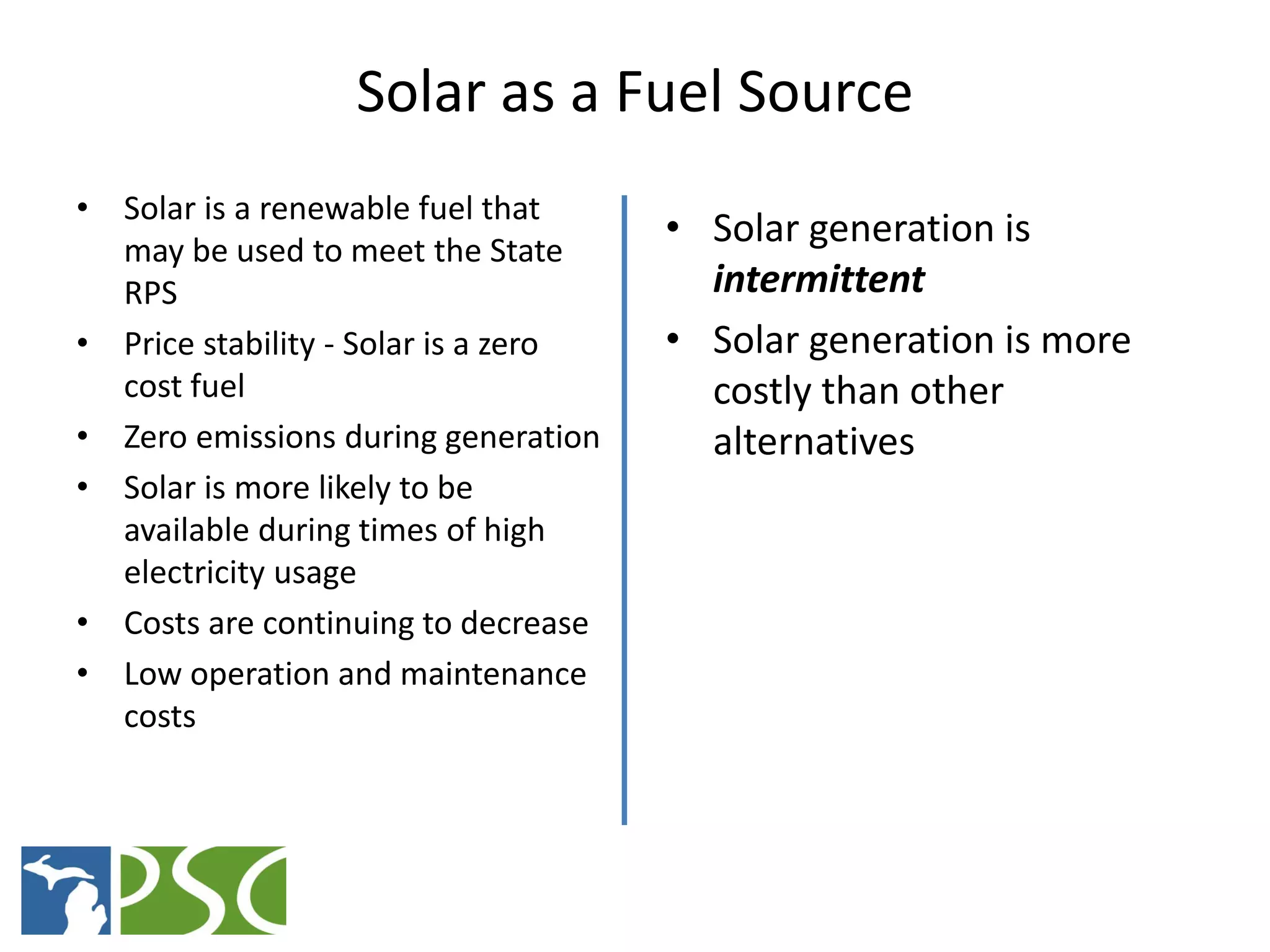
The document discusses wind and solar energy options for meeting Michigan's renewable portfolio standard. It summarizes the state's identification of wind energy zones and approval of various renewable energy contracts. Wind energy currently makes up the majority of approved capacity but costs have decreased over time. Integrating intermittent wind generation presents challenges but can be addressed through diversification, storage and regional coordination. Solar adoption is growing in Michigan although it remains more expensive than other alternatives currently.