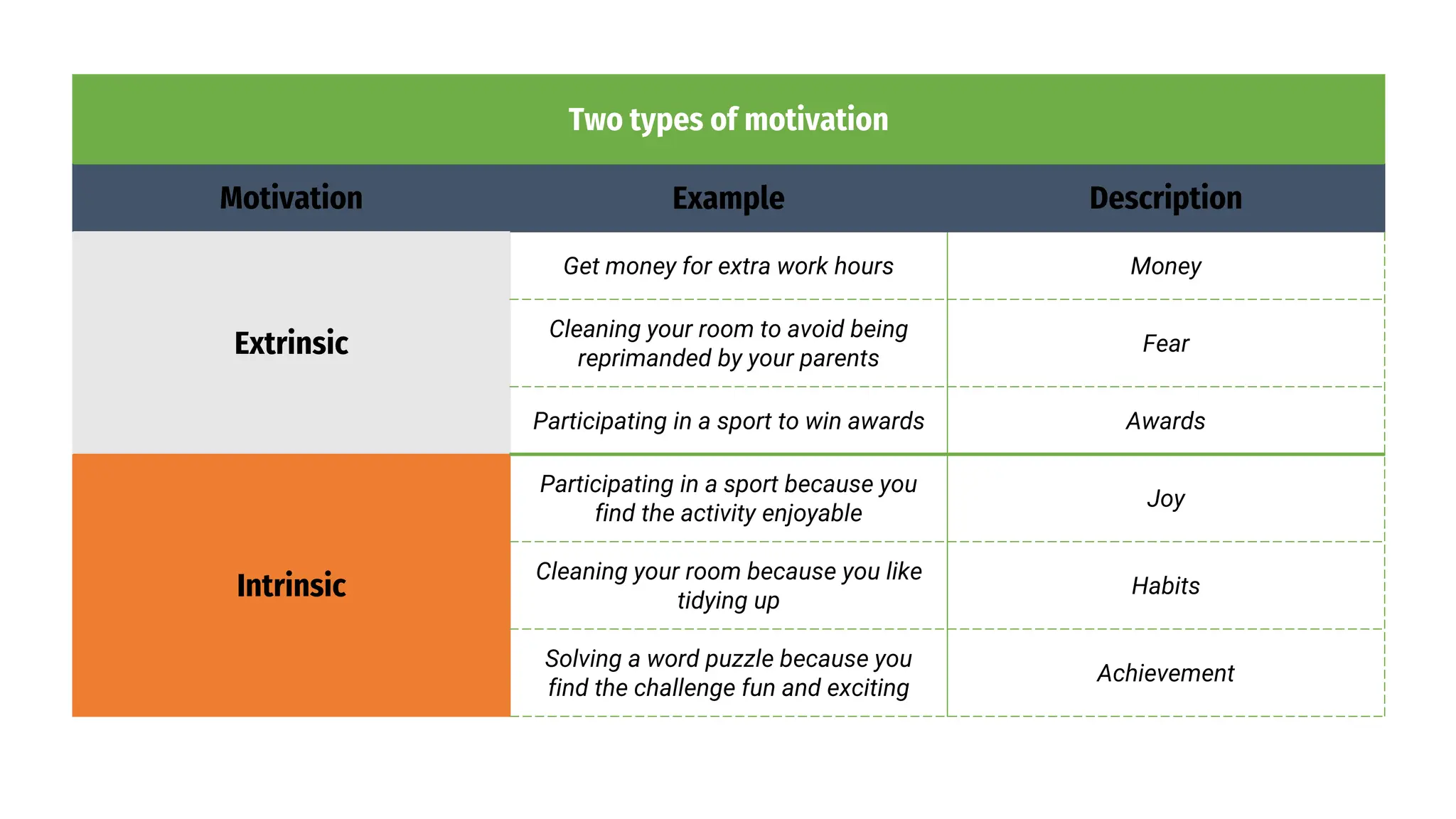
The presentation by Abanoub Amir Mahmoud Ahmed Anas Khaled Abdelrahman Mohamed Said Abdelwahed Loay Amgad discusses motivation, defining it as a psychological process that drives goal-oriented behavior and differentiating between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. It further explores Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg’s two-factor model, emphasizing the importance of hygiene factors for preventing dissatisfaction and motivational factors for enhancing job satisfaction. Additionally, the document presents McGregor’s Theory X and Y, which reflect opposing views on employee attitudes towards work, impacting management styles and organizational culture.