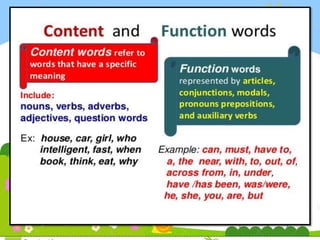
Morphology is the study of word structure and formation. It examines the smallest meaningful units called morphemes, which can be free or bound. Morphemes combine to form different types of words through processes like affixation, compounding, blending, ablaut, and abbreviations. Affixation adds prefixes or suffixes to roots to create new words. Compounding combines two or more free morphemes. Ablaut internally changes vowels to indicate grammatical functions. Morphology analyzes the classification and formation of words.