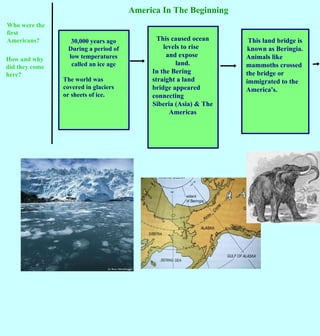
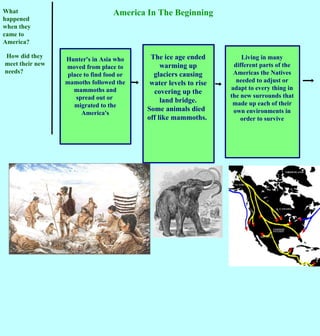
1. Around 30,000 years ago during the last ice age, the first Americans crossed into North America over a land bridge connecting Siberia to Alaska.
2. As the climate warmed, sea levels rose and the land bridge disappeared, leaving early Americans isolated in their new environments across North and South America.
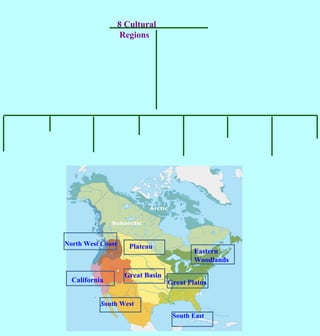
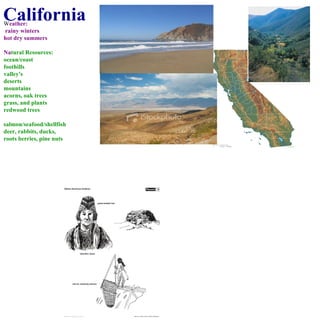
3. Native Americans adapted to their environments by utilizing local natural resources for food, clothing, shelter and tools in different ways, developing distinct cultural traditions but also sharing some beliefs and practices.